Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) is the commonest cause of episodic vertigo and is characterized by acute attacks of transient vertigo initiated by certain head positions, lasting seconds to minutes, accompanied by nystagmus that fatigues on repeated testing.
Important terminologies linked with pathogenesis of BPPV:
- Otoconia: Calcium carbonate crystals released from degenerating macula
- Canalithiasis: Otoconia moving within semi-circular canal
- Cupluolithiasis: Otoconia adherent to cupula of semicircular canal
Note:
Canalithiasis is more common
Commonly Posterior semicircular canal is involved
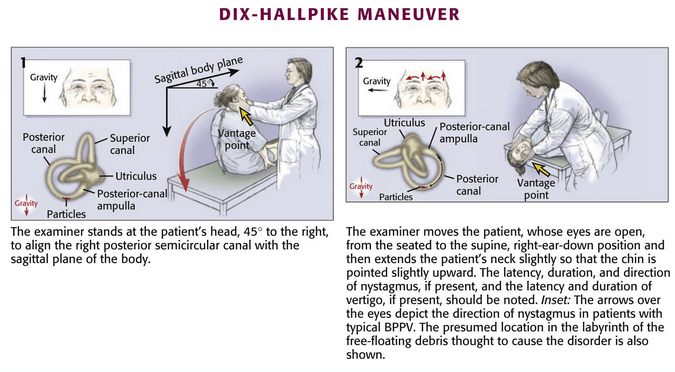
Clinical test for Diagnosis of BPPV: Dix-Hallpike Maneuver
Synonyms: Nylen-Barany maneuver
Contraindications:
- Severe cervical spine disease
- Unstable spinal injury
- High-grade carotid stenosis
- Unstable heart disease.
Procedure:
- Make the patient sit on examination table, such that the shoulders would level on the edge of table when lying down
- Always start the examination with the ear that is least suspected
- Turn the patient’s head to 45° towards the test ear, by holding the both sides of the patient’s head with your hands
- Instruct the patient to fix his/her eyes on a point directly in front of him/her and keep the eyes open throughout the test
- Supports the patient’s head as the patient lies back quickly from a sitting to supine position, ending with the head hanging 30 degrees off the end of the examination table
- Observe* the patient in this position for 30 seconds
- Then the patient returns to the upright position and is observed* for 30 seconds.
- Repeat the entire maneuver with the head turned 45 degrees toward the opposite side.
Observe*
- Nystagmus
- Vertiginous symptoms
Interpretation:
When the head is turned to the affected right ear, the nystagmus occurs as follows:
1. When the head is lowered 30 degree below the bed, the fast phase of the nystagmus is upward , rotating toward the affected ear
2. When the patient is brought back to the sitting position, the fast phase of the nystagmus is downward , rotating toward the affected ear