Normally, the pathological reflexes are not evident because they are suppressed by cerebrum at brainstem or spinal cord level by 6 months of age.
Importance:
- If present bilaterally: indicates upper motor neuron lesion
- If present unilaterally: indicates lower motor neuron lesion
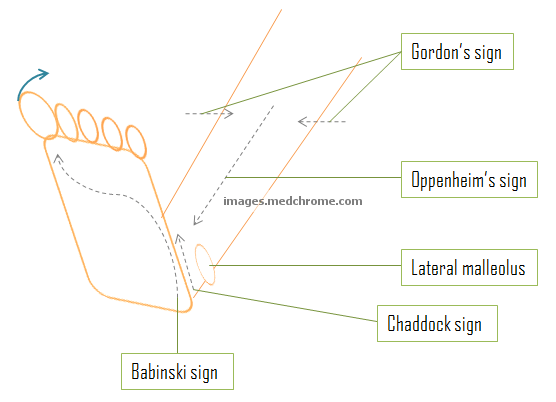
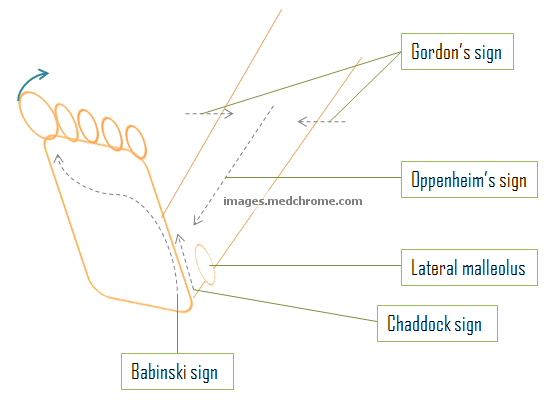
Up-going (dorsiflexion) toe can be elicited at various sites and all indicated Upper Motor Neuron (UMN) lesion. Use a blunt-pointed object like fingernail or tip of a key or a reflex hammer to stroke the skin. The complete response is extension of big toe and fanning of 4 small toes. These are normal in newborn upto 6 months of age after which they are suppresed by the cerebrum. Babinski sign is the commonest method used to elicit this.
1. Babinski sign (phénomène des orteils): Stroking the lateral aspect of the sole of the foot in the direction as shown in the picture
2. Chaddock sign: Stroking the skin beneath the lateral (external) malleolus
3. Oppenheim’s sign (Oppenheimer sign): Stroking the antero-medial tibial surface
4. Gordon’s sign: Squeezing of the lower calf muscles firmly
Clinical Pearl:
How do you elicit pathological reflex in a patient with both feet amputated?
Answer: The Hoffman reflex
Flicking of terminal phalanx of index, middle or ring finger leads to reflex flexion of distal phalanx of thumb and of distal phalanx of index or middle finger (whichever was flicked). It indicates tetany or upper motor neuron lesion.