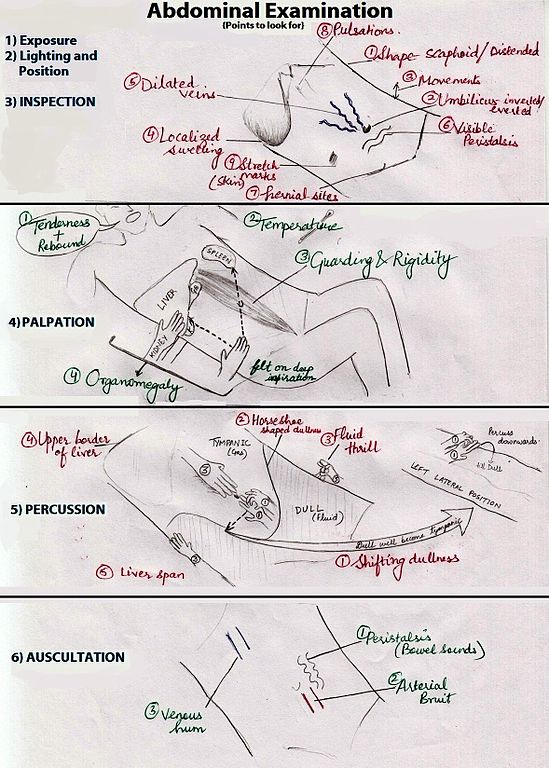
1. Forgetting to Expose abdomen adequately:
Before examination, patient should ideally be exposed from the nipples to mid thigh. Failure to do so may lead to missed findings during examination e.g. Hernia
2. Abdominal symmetry and movement:
Abdominal symmetry and movement should be examined tangentially and from leg end. Comment should be made on movement of all quadrants with respiration.
3. Forgetting to relax abdomen before palpation:
Flex the legs at knees and arms should be by side of body. Head should be rested on a pillow. Only after abdomen is in the relaxed position, palpation should be proceeded.
4. Missing points on palpation:
a. Remember to ask for pain in any site before palpating. The part with pain should be skipped and palpated at the end.
b. Look for rigidity and guarding besides tenderness.
c. Tenderness should be assessed by looking at facial expression +/- guarding
d. Remember to palpate urinary bladder.
e. Hernial orifices should be palpated and is commonly missed point.
f. Make the patient sit and check for renal angle fullness and tenderness.
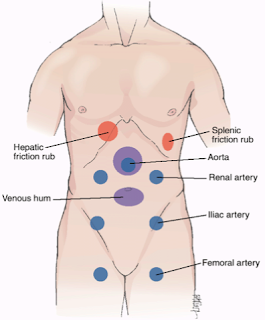
5. Remember: Shifting dullness is done in percussion and fluid thrill is done in palpation, in a patient with abdominal distension.
6. Auscultation:
Look for Renal bruit, Hepatic bruit. etc. in indicated cases. Bowel sound should be listened to. When bowel sounds are not present, one should listen for a full 3 minutes before determining that bowel sounds are, in fact, absent.
Recommended reading
https://meded.ucsd.edu/clinicalmed/abdomen.htm
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK420/

MD Pediatrics and Fellowship Neonatology, he chooses to stay anonymous. He often writes his views online as well as share few important topics for medical students, doctors and specially parents. He does research in pediatrics.

But steps are in wrong order