Start with WIPERS
Then ABG
1. Allen’s test (modified):
- Exsanguination: Ask the patient to make tight fist for about 30 seconds
- Occlusion: Occlude the radial and ulnar artery simultaneously with fingers
- Release:
- Fist: Hand must stay blanched, else occlusion pressure is not enough (restart the test)
- Ulnar artery:
- Reperfusion within 5-15 seconds: Negative Allen’s test (Good blood flow)
- No reperfusion within 5-15 seconds: Positive Allen’s test (Circulation of ulna artery is not sufficient)
In case of Positive Allen’s test: DO NOT puncture radial artery
2. Bad things:
- Allergy to LA
- Absolute contraindications: Cellulitis, Peripheral vascular disease, Arteriovenous fistula, For local anesthesia (Allergy to LA)
- Relative contraindications: Coagulopathy (including Anticoagulant use)
3. Gather equipment needed
Then Procedure
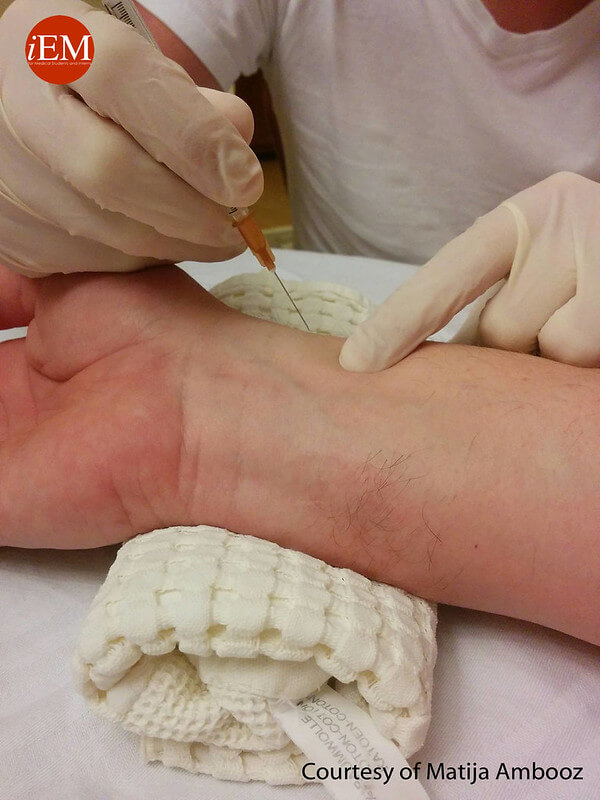
1. Position:
- Position the patient so that they are sitting or lying down comfortably, ideally with their wrist supported by a pillow.
- Extend the wrist fully
2. Site preparation:
- Don the non-sterile gloves
- Identify site: Palpate the radial artery just proximal to the point of maximum pulsation with non-dominant hand
- Sterilize the skin with an alcohol wipe and allow it to dry and do not re-palpate
3. Local anesthesia (skin): Offer the patient local anesthesia –
- 25 G needle (orange) and 2 ml syringe
- 1% lignocaine
4. ABG sampling:
- Use 23 G needle (blue) and 2 ml syringe (heparinized with 0.1 ml 1:1000 heparin)
- Hold the syringe like a pen with a dominant hand
- Insert the needle at 45-60 degrees with the bevel facing upwards while palpating the artery with other hand
- Advance the needle slowly until a flash of blood is seen in the needle hub
- Collect 1-2 ml of arterial blood (bright red and fills quickly in pulsatile fashion)
5. Post sampling:
- Discard the needle safely
- Elevate the arm and apply firm pressure to puncture site for 5 minutes
- Expel any air bubbles from syringe and seal it with a cap
- Label the syringe (Patient details, FiO2, Body temperature)
- Roll the syringe in the palms of your hands for 10 seconds (to ensure heparin mixing)
- Send the sample within 15 minutes of collection for analysis