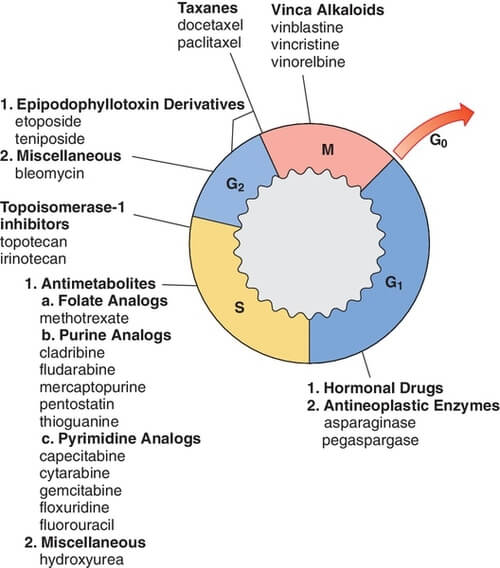
Stages of Cell Cycle Interphase Mnemonic: Go Sally Go! Make Children 1. G1 phase 2. S phase 3. G2 phase 4. Mitosis 5. Cytokinesis 1. G1 (Gap 1) phase: Early and late phase divided by Restriction (R) point Functions: Preparation for DNA replication (synthesis of replication proteins cyclin D) Thymidine…
Author: Epomedicine

Apoptosis Made Easy
Definition of Apoptosis Apoptosis is: Origin of the word “apoptosis”: Caspases – Central Regulators of Apoptosis Caspases = Cysteine Aspartate Specific Proteases 2 types of caspases: Initiator caspases: Executioner caspases: 3 Pathways of Caspase Activation 1. Activation of Initiator of Extrinsic Pathway Receptor-ligand interaction mediated: Can mediate intrinsic (mitochondrial) pathway…
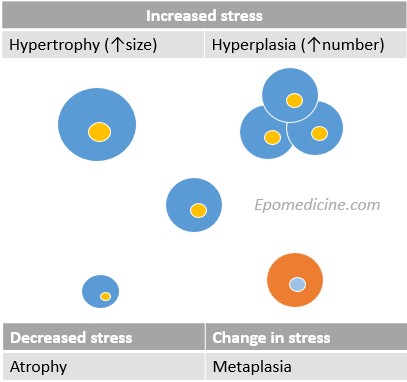
Cellular Adaptations
Hypertrophy, Hyperplasia, Atrophy and Metaplasia are the main four types of cellular adaptations. Adaptations are: Reversible changes In the number, size, phenotype, metabolic activity or functions of cells In response to the changes in the environment (stress). Hypertrophy Definition: Increase in cell size Occurs in: non-dividing (permanent) cells: cardiac and…
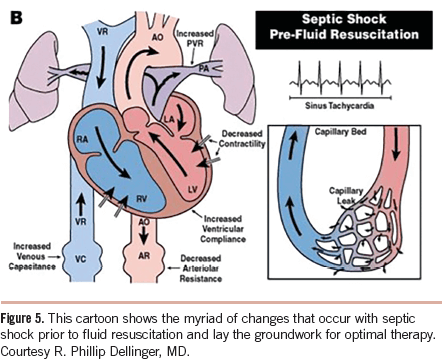
Septic Shock Fluid Resuscitation
Endpoints of resuscitation MAP: > or = 65 mmHg Urine output: > 0.5 ml/kg/hr; despite ↓RBF (Renal Blood Flow) it can be normal due to – Atrial natriuretic factor are elevated in sepsis Hypoproteinemia in sepsis – low plasma colloid osmotic pressure is less able to facilitate oncotic reabsorption. CVP:…
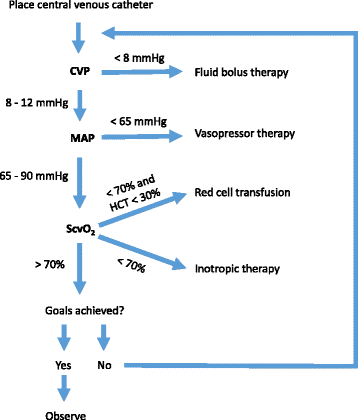
Is there no role of Early Goal Directed Therapy (EGDT) in Sepsis and Septic shock?
International Surviving Sepsis Campaign has recommended Early Goal Directed Therapy for the management of severe sepsis and septic shock. Recently, three large multicenter studies – the ProCESS (Protocolized Care for Early Septic Shock), ARISE (Australasian Resuscitation In Sepsis Evaluation), and ProMISe (Protocolized Management In Sepsis) demonstrated no difference in the…
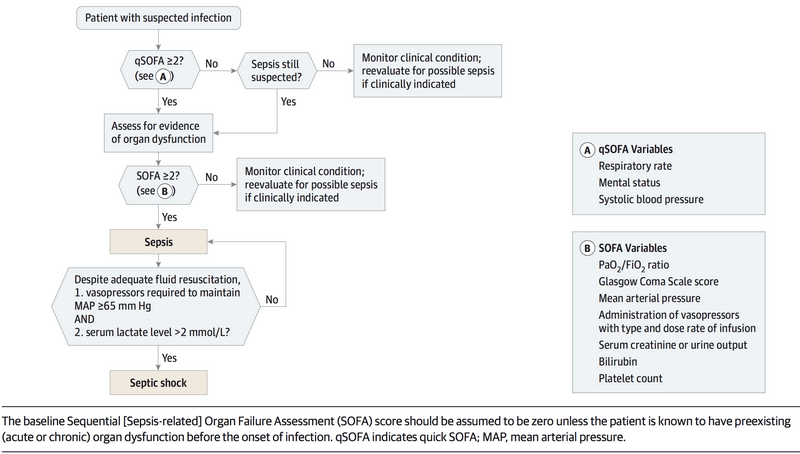
Understanding New Definition of Sepsis (Sepsis-3)
The Sepsis-2 definition used SIRS criteria and the term “Severe sepsis” which has been recently eliminated by the Sepsis-3. The new sepsis definitions recommend using a change in baseline of the total SOFA score of two or more points to represent organ dysfunction. New Definition of Sepsis and Septic Shock…
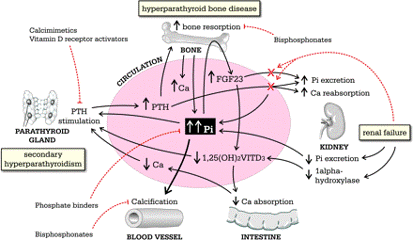
Complications of Long Term Dialysis
A) Cardiovascular complications 1. Exacerbation or Precipitation of CHF – Voluminous AV Fistula AV shunting → Decreased TPR → BP fall → Sympathetic stimulation & RAAS activation → Ventricular remodeling → Heart failure Several studies have investigated the cut-off fistula access flow that is associated with a higher risk of high-output cardiac failure, with results ranging…
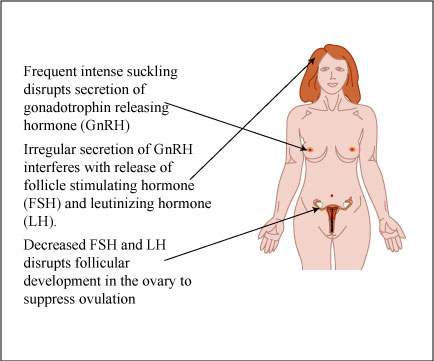
Management of Puerperium
Normal puerperium has been already discussed earlier here. A) Immediately after labor within 1 hour Blood pressure and heart rate atleast every 15 minutes Monitor amount of vaginal bleeding Palpate fundus to ensure amount adequate contractions (if relaxed – massage uterus to enhance oxytocin release) B) 1st several hours 1….