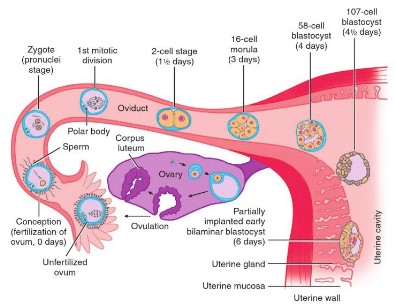
Following events occur in the zygote formed in the week zero of development: Cleavage Approximately 24 hours after fertilization the zygote begins with the first cleavage division. Series of mitotic divisions of the zygote (occurs in fallopian tube) to form small daughter cells called blastomeres. Characteristics of cleavage in humans:…
Author: Epomedicine
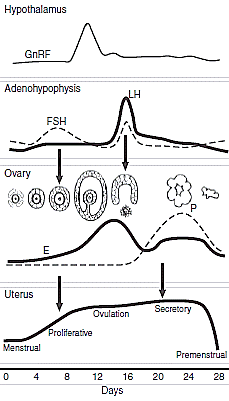
Embryology Week 0: Gametogenesis, Ovulation and Fertilization
Gametogenesis – formation of gametes from primitive germ cells Spermatogenesis, begins at puberty and occurs in seminiferous tubules (spermiogenesis occurs in sertoli cells). One spermatogenesis takes an average of 74 days to complete. Oogenesis Stages Spermatogenesis Migrate at 6th week of development 1. Primordial Germ Cells / PGCs (46, 2n) – epiblast…
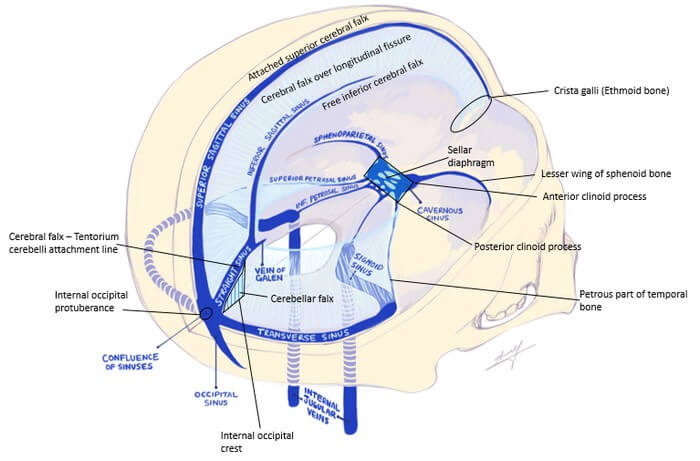
Dural Reflections and Venous Sinuses
Dura mater (pachymenix) is the outer meningeal layer consisting of: Dural Reflections These are the infoldings formed by the inner meningeal layer reflecting away from the fixed periosteral dural layer. Two vertical reflections – Separate the right and left hemisphere Two horizontal reflections Dural Venous Sinuses 1. Superior sagittal sinus:…
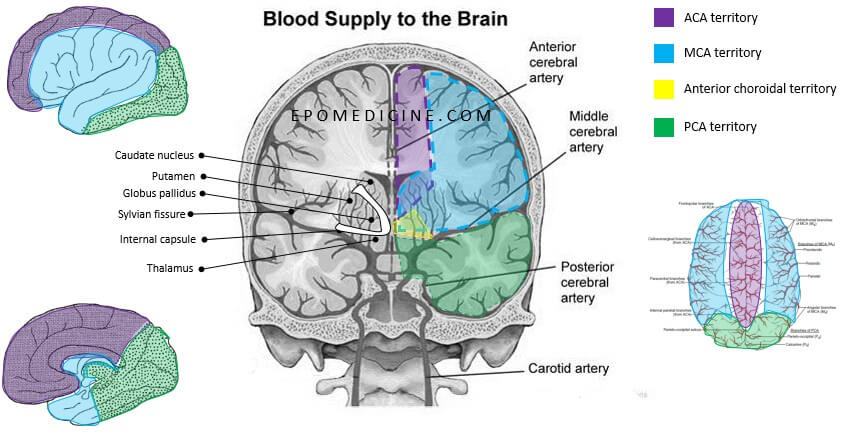
Circle of Willis and Forebrain Blood Supply
We have already discussed earlier on the intracranial course of Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) and Circle of Willis formation with the help of a simple mnemonic. General Concepts of Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal Cord 1. Spinal cord, Hind-brain and Mid-brain: Veterbro-basilar system 2. Forebrain: Circle of willis which…
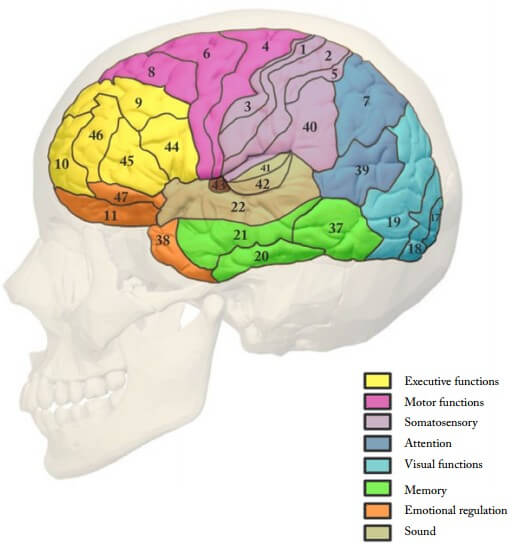
Brodmann Areas and Lesions
Frontal Lobe Area 4 (Precentral gyrus): Primary motor cortex (gigantopyramidal – only area that contains giant pyramidal cells of Betz) Lesion: Contralateral spastic paralysis (UMNL) Area 6 (Superior frontal gyrus; agranular frontal): Premotor cortex and Supplementary motor cortex (Motor planning) Lesion: Apraxia (Unable to perform movements in correct sequence) Area…
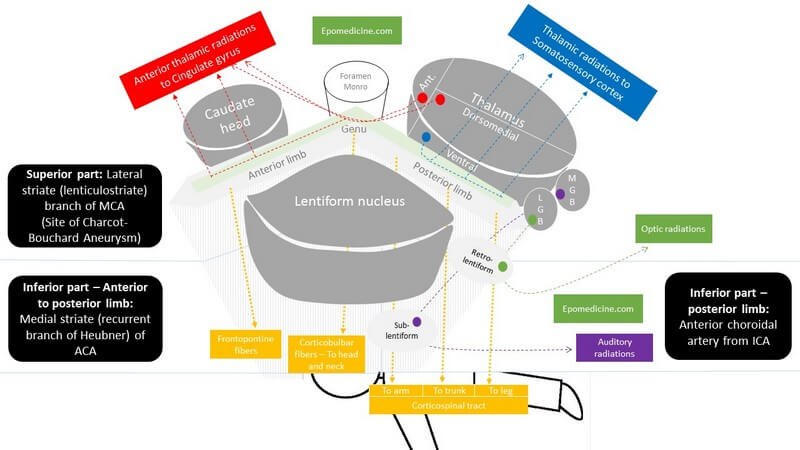
Internal Capsule Simplified
Internal Capsule is a “boomerang” shaped (on horizontal section) and “funnel” shaped, i.e. tapering from superior to inferior (on sagittal section) white matter structure sandwiched between: Medially: Head of Caudate nucleus and Thalamus Laterally: Lenticular nucleus (Globus pallidus and Putamen) Parts of Internal Capsule 1. Anterior limb: Carries fibers to…
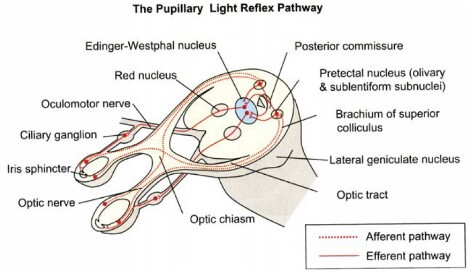
Visual Pathway : Supplement Knowledge
Everyone must be aware of the normal visual pathway and their defects. Here, I’ve tried to enlist the topics related to the visual pathway that are “nice to know” but you may have missed it or failed to understand properly. Below is the basic visual pathway: Wilbrand’s knee Anterior…
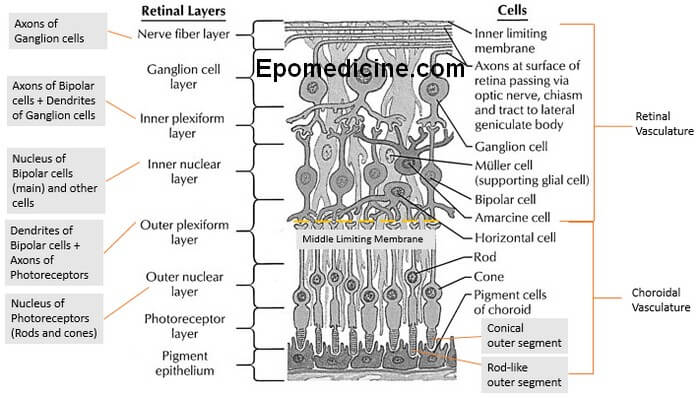
Retinal Layers Simplified
The ten layers of retina – this microscopic anatomy is frequently asked in examinations and also important from the physiological viewpoint. There are plenty of mnemonics around the web, but we will proceed in a different approach to remember the 10 retinal layers easily. A. Retina is 3 neuron system…