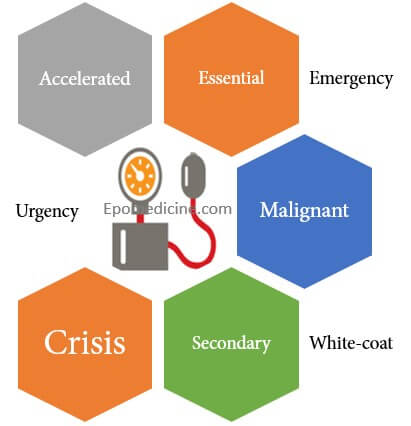
There are various terminologies used to describe hypertension which may overlap and are a source of confusion to the medical students and health professionals. Essential or Primary or Idiopathic hypertension Hypertension in which secondary causes have been excluded. Identifiable etiologic factors of essential hypertension: Obesity Insulin resistance High alcohol intake…
Author: Epomedicine
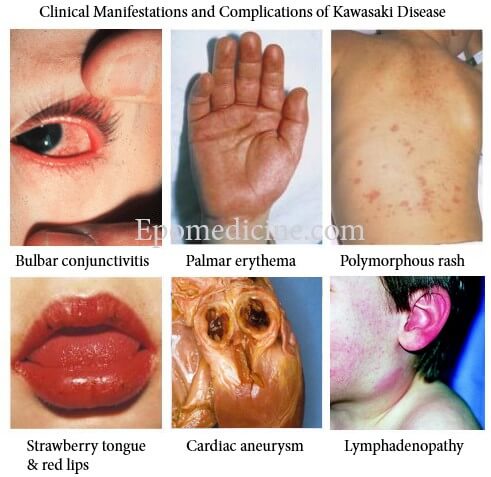
Kawasaki Disease – Diagnostic Criteria Mnemonic
The diagnostic criteria of Kawasaki Disease can be remembered using a mnemonic – “FEBRILE“. Fever: >5 days plus ≥4 of the following Enathem: Lips: Erythema, fissuring or crusting Oropharynx: Diffuse injection Tongue: Strawberry tongue Bulbar conjunctivitis: Bilateral, painless and non-exudative Rash: Polymorphous rash Internal organ involvement (not the part of criteria)…
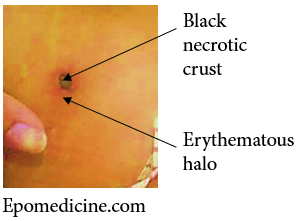
Eschar
Synonyms Tache noire Definition of Eschar An eschar is a local skin lesions coated by a thick coagulated crust or slough that usually results from burn or infection. Causes of Eschar Tick bite fever Scrub typhus Anthrax Tularaemia Spider bites Disseminated fungal infection Post-burn Diagnostic Clues Cigarette-burn Sign In scrub…
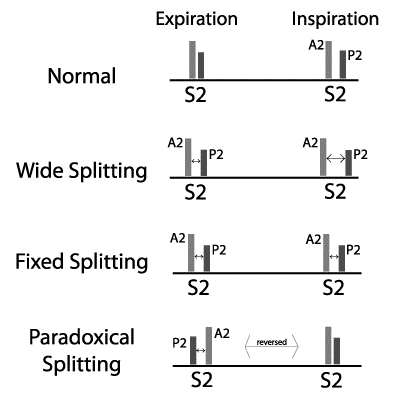
Abnormalities of First and Second Heart Sound
In the chapter of cardiac cycle, we have discussed the mechanism of production of heart sounds and their physiologic splitting. First Heart Sound (S1) Mechanism Closure of atrioventricular valves. It is best appreciated in mitral and tricuspid area of chest for respective components. Loud S1 Slamming a door from a…
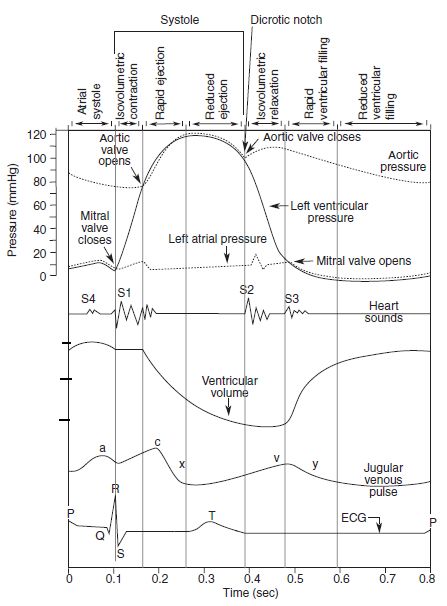
Cardiac Cycle – Summary and Wigger’s Diagram
Cardiac Cycle Opening and closing of valves When the valve opens, different compartments act as a single chamber (atrio-ventricle or aorto-ventricle). For a blood to flow, pressure in “giver” must be higher then that in “receiver”. Pressure difference opens or closes the valve: Role of atrial contraction in Ventricular filling…
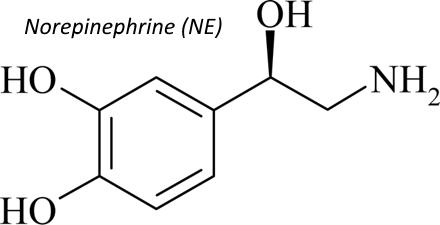
Early vs Delayed Norepinephrine Use in Septic Shock
Norepinephrine has numerous effects in sepsis including veno-constriction (increasing preload), arterial constriction (increasing systemic vascular resistance), positive inotropy, improved cardiac output, and improved renal perfusion. This addresses all the major derangements observed in cases of septic shock. It is important to realize that MAP doesn’t necessarily equate perfusion. Increasing the…
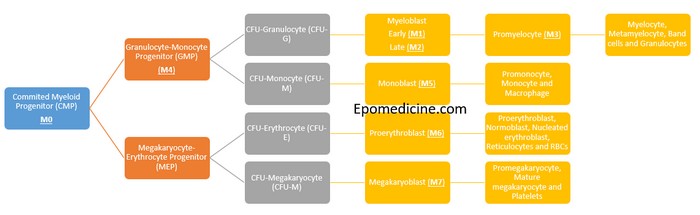
Concept of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) FAB Classification
There is no need of mnemonics to remember the FAB classification of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML); just remember the process myeloid differentiation. A simple schematic diagram with few intermediate processes and stimulating factors eliminated will meet our purpose here. The cells belonging to the myeloid lineage are: Granulocytes: Neutrophils, Eosinophils…
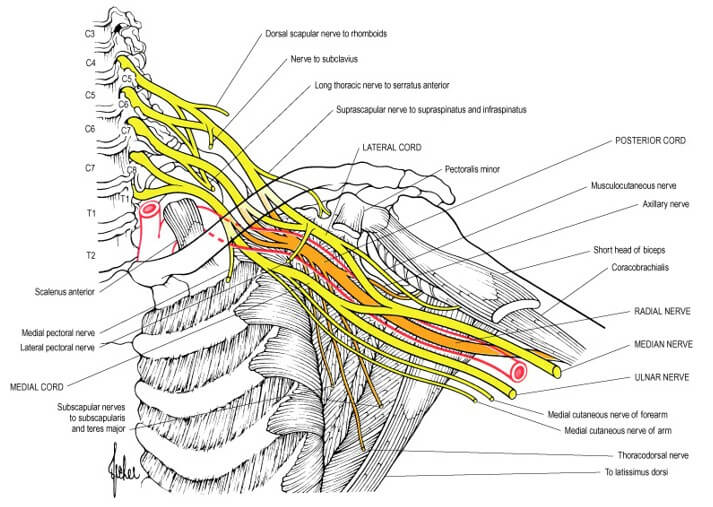
Brachial Plexus Simplified with Mnemonics
Components of Brachial Plexus Mnemonic: Randy Travis Drinks Cold Beer From proximal to distal, brachial plexus consists of: How are the roots formed? From the Ventral Rami of C5 to T1 spinal nerves. Extent and course: Intervertebral foramina to Transverse process to Interscalene triangle (bounded by anterior scalene and middle…