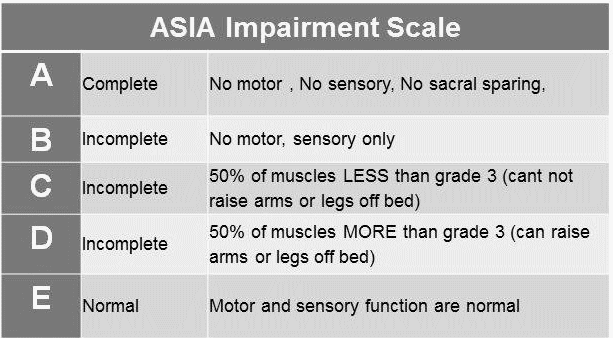
Check S4-5 S4-5: Perianal area <1 cm lateral to the mucocutaneous junction (taken as one level) 1. Sensory (-) and Motor (-): AIS A (Complete)i.e. N-0-0-0-0-N sign (No sacral sparing) 2. Sensory (+) and Motor (-): AIS Bi.e. Sensory (+) means any sensation present in S4/S5 or anal sensation Motor…
Author: Epomedicine
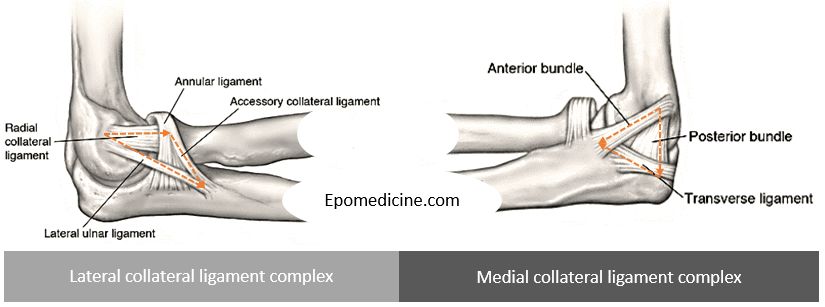
Elbow ligaments : Simplified Anatomy
Lateral collateral ligament complex Restraint to varus and posterolateral rotatory instability. Anatomy is more variable. LCL arises from lateral humeral condyle at a point through which the axis of rotation passes – it maintains a uniform tension throughout the arc of motion. Annular ligament is a “U” shaped ligament that…
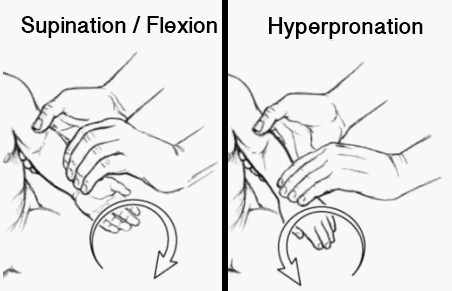
Pulled elbow reduction
Synonyms: Nursemaid’s elbow, Radial head subuluxation, Elbow subluxation Age: Commonly 1-4 years After 5 years of age, the attachment of the annular ligament to the neck of the radius strengthens Enlargement of the proximal radial epiphysis with growth may also improve stability Presentation: History of pull may be absent in…
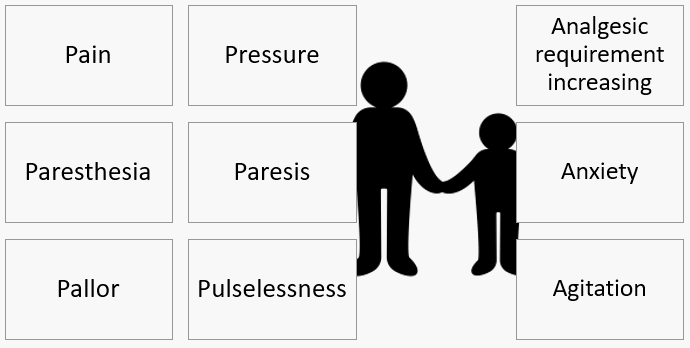
6 Ps and 3 As of Compartment Syndrome
Clinical features A. Adolescents and Adults Mnemonic: 6 Ps (by Hargens and Mubarak) Pain (may be absent in cases of nerve damage): Pain out of proportion to other physical findings (requiring increasing analgesic requirement) *: Earliest symptom Pain on passive stretch of the muscles in concerned compartment * Low sensitivity…
General Principles – Pediatric Fracture Management
Children are not just mini-adults • Higher head to torso ratio: Head injury & Upper C-spine fractures • Light weight – projectile when struck • BSA to Wt. ratio – higher (rapid hypothermia) • Large cardiopulmonary reserves – normal SBP in significant hypovolemia Growth contribution by Proximal & Distal Physes…
DIY N95 Mask
With the ongoing pandemic of COVID-19, world is facing an acute shortage of surgical and respirator masks. And along with this “face mask movement“, globally “face mask making movement” has also started. Fabric materials may provide only minimal levels of respiratory protection against virus-size submicron aerosol particles (e.g. droplet nuclei)…

LRINEC score for Necrotizing fascitis – Mnemonic
The LRINEC (Laboratory Risk Indicator for Necrotizing Fasciitis) score is a tool to distinguish ordinary skin infections from necrotizing fasciitis. Mnemonic: NeC WASH Na level: <135 mmol/L: 2 points Creatinine: >1.6 mg/dl: 2 points WBC: <15,000/cu.mm: 0 points 15,000-25000/cu.mm: 1 point >25,000/cu.mm: 2 points Acute phase reactant (CRP): >/= 150:…
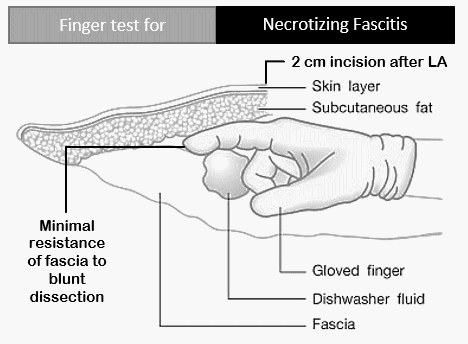
Finger test for Necrotizing Fascitis
Synonyms: Finger sweep test Finger test can be performed under Local anesthesia or General anesthesia in: Emergency department Bedside in wards Operation theaters Procedure: Area is infiltrated with local anesthetic A 2 cm test incision down to fascia is made in the suspected area The tissues are visually examined for:…