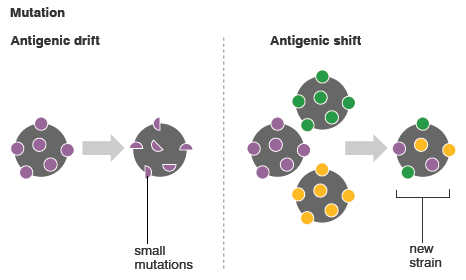
Antigenic Drift
Nature of antigenic variation: Minor
Mechanism:
- Gradual accumulation of amino acid substitutions due to point mutation in the hemagglutinin (H) and neuraminidase (N) genes.
- As mutations accumulate, antibodies generated by exposure to previous strains do not neutralize current strains to the same extent, resulting in only limited or partial immunity to the new strains.
Gives rise to: Epidemics
Shown by: Influenza A and B viruses
Antigenic Shift
Nature of antigenic variation: Major
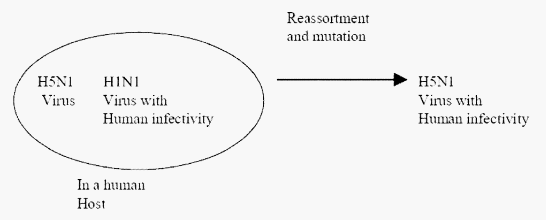
Mechanism: Expression of a new allele of hemagglutin or neuraminidase through the following mechanism –
- Genetic reassortment: Non-human influenza is selective in its tropism, and cannot easily replicate in humans. However, avian influenza viruses may replicate in non-avian, non-human reservoirs (like swine). A pig that was co-infected with both avian and human strains of influenza might result in a genetic reassortment that produces a novel virus capable of replication in and transmission between humans.
- Mutation: Mutations may occur directly in a non-human virus, such as an avian virus, that allow the virus to readily spread from person to person.
Gives rise to: Pandemics and Epidemics
Shown by: Influenza A virus