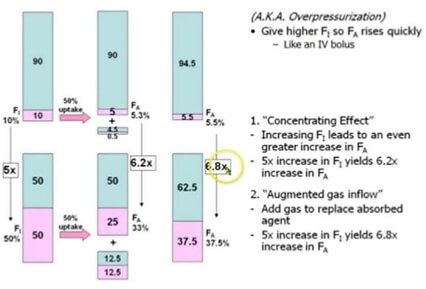
Concentration effect The higher the concentration of an inhaled anesthetic, the faster the alveolar concentration approaches the inhaled concentration. This is referred to as concentration effect and is clinically significant only in cases where gases are administered in high concentration: Nitrous oxide Xenon Ostwald’s blood gas solubility coefficient: ratio of…
Tag: Respiratory system
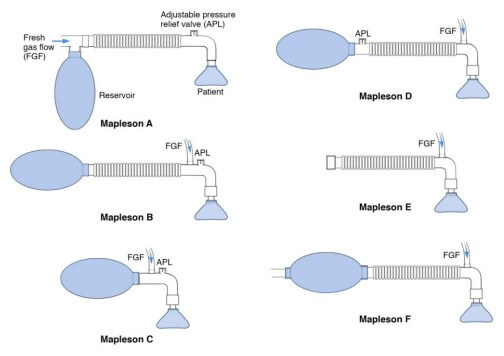
Mapleson Breathing Circuit Made Easy
Anatomy of Mapleson Breathing Circuit Basically, a mapleson breathing circuit consists of following parts: 1. Face mask (towards patient end) 2. Reservoir bag (towards operator end) Accommodates fresh gas flow during expiration acting as a reservoir available for the following inspiration. Acts as a monitor of patient’s ventilatory pattern during…
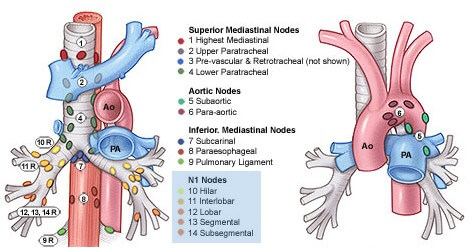
TNM and Staging of Lung Cancer Simplified
The current staging system is recommended for the classification of both non–small cell and small cell lung carcinomas and for carcinoid tumors of the lung . TNM Staging of Lung Cancer Primary Tumor (T) The “T” staging of bronchogenic carcinoma is a bit complex compared to others. Five things must…
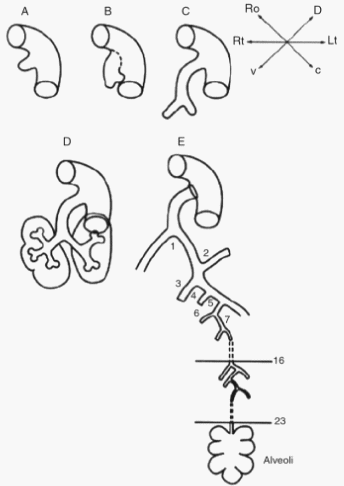
Lung Development – Embryology Made Easy
Remember the mnemonic – “Every Premature Child Takes Air“. The development of lungs comprises of 5 distinct stages: Embryonic (3-8 weeks, i.e. embryonic period) Pseudoglandular (5-16 weeks) Canalicular (16-26 weeks) Terminal saccular (26-36 weeks) Alveolar (36 weeks to 40 weeks and continues to childhood) The first and last stages, i.e….
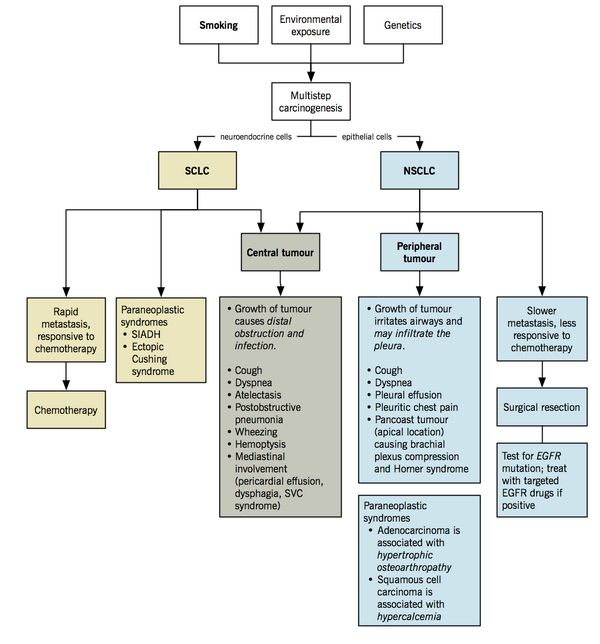
Bronchogenic Carcinoma Etiopathogenesis
INCIDENCE Male > Female Age group: 50-75 years Second highest cancer in both sexes after prostate (male) and breast (female) Smokers > Non-smokers ETIOLOGY OF LUNG CANCER A. Cigarette smoking: Smoking is the single most important risk factor for lung cancer, which can cause all types of lung cancer but…
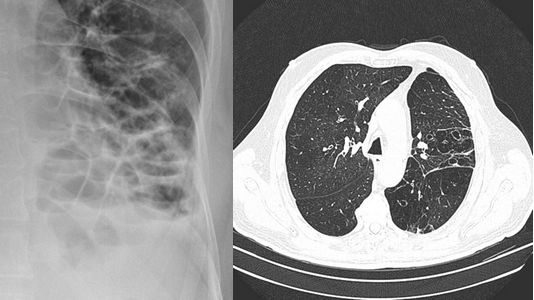
Bronchiectasis Revision Notes
DEFINITION OF BRONCHIECTASIS Bronchiectais refers to the end-stage of variety of pathologic processes characterized by abnormal, irreversibly dilated thick-walled bronchi due to destruction of elastic and muscular components of bronchial wall. MORPHOLOGICAL CLASSIFICATION OF BRONCHIECTASIS Mnemonic: CVS 1. Cylindircal (Fusiform):
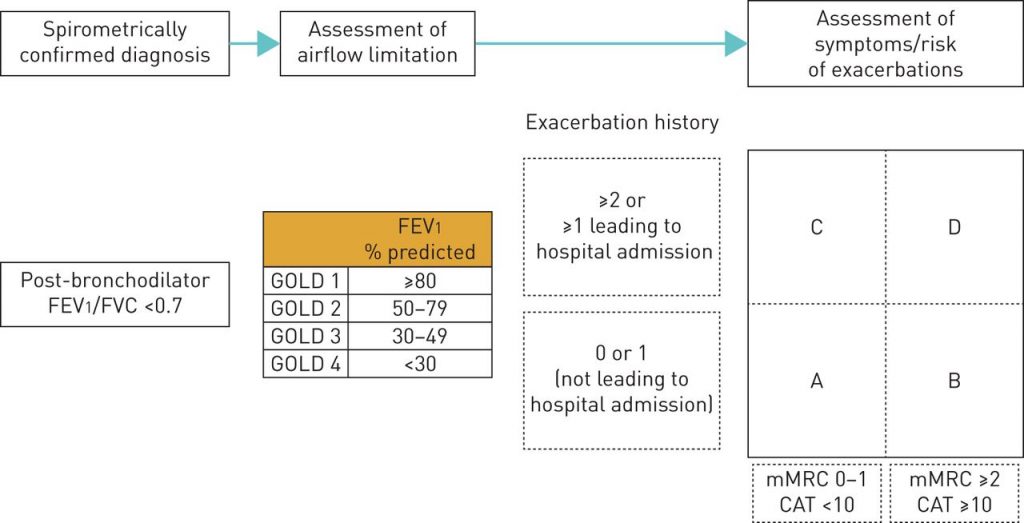
COPD Revision Notes
DEFINITION OF CHRONIC OBSTRUCTIVE PULMONARY DISEASE (COPD) According to GOLD, COPD is a common preventable and treatable (not curable) disease characterized by: Persistent airflow limitation (Post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC < 0.7), usually progressive (excludes Asthma) Due to airway and/or alveolar abnormalities usually caused by significant exposure to noxious particles or gases. Chronic…
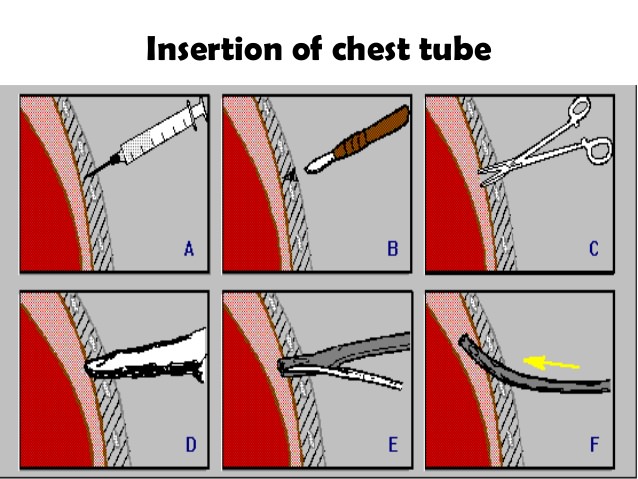
Chest Tube Insertion or Tube Thoracostomy
Indications of chest tube insertion Pneumothorax: In any ventilated patient (positive airway pressure will force air into the pleural cavity and produce tension pneumothorax) Tension pneumothorax after initial needle thoracocentesis Persistent or Recurrent pneumothorax after simple aspiration Large secondary spontaneous pneumothorax in patients >50 years Pleural effusion: Malignant pleural effusion…