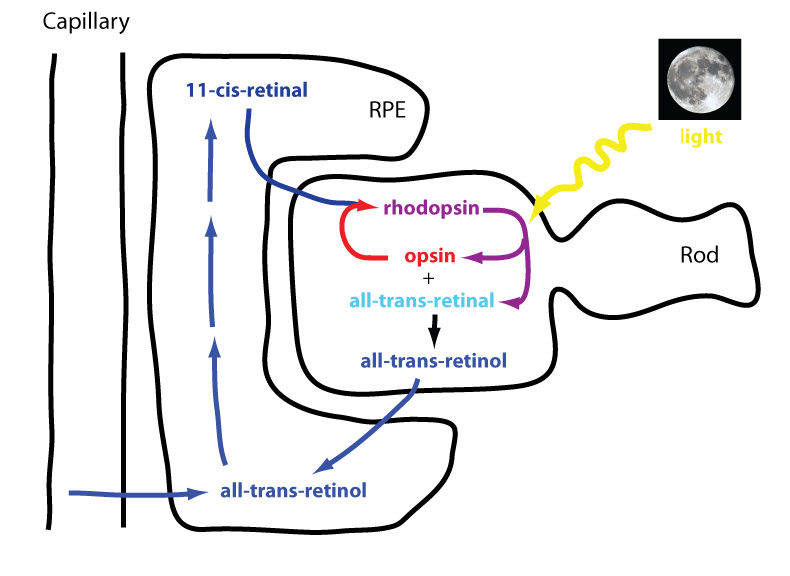
11-cis-retinal combines with opsin protein to form rhodopsin. Light stimulates conversion of rhodopsin bound 11-cis-retinal to all-trans-retinol (all-trans-retinol is transported from photoreceptor cells to retinal pigment epithelium), which subsequently dissociates from opsin (bleaching), leading to membrane depolarization and initiation of action potential in photoreceptors in the neural retina. Once in…
Tag: Ophthalmology
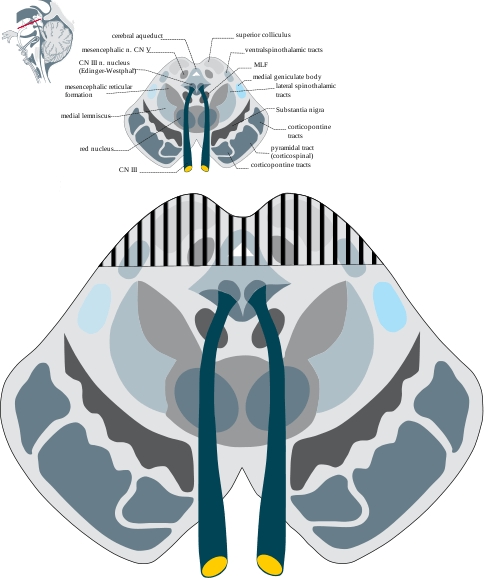
Parinaud Syndrome – Anatomical Basis
Synonyms: Dorsal midbrain sydnrome, Pretectal syndrome Main components of Parinaud syndrome: Vertical gaze palsy Convergence-retraction nystagmus Pupillary light-near dissociation Lid retraction (Collier’s sign) Anatomical basis of Parinaud syndrome: Site of lesion: Dorsal midbrain Close to cerebral aqueduct and pineal gland – hydrocephalus and pinealoma Arterial supply – posterior cerebral artery…
Embryology of Eye : Mnemonic
Surface ectoderm derivatives Mnemonic: LEVeL Lens Epithelium All ocular adnexa including mebomian gland and glands of Zeis and Moll Skin Cornea Conjunctiva Vitreous (portion) Lacrimal glands and drainage system Neuro-ectoderm (Optic vesicle and cup) derivatives Mnemonic: MORE Muscles of pupil (constrictor and dilator pupillae) Optic nerve Retinal pigment epithelium Epithelium…
Ethambutol Induced Optic Neuropathy
Mechanism of Ethambutol induced optic neuropathy Ethambutol is metabolized to a chelating agent. The chelating agent formed then may impair the function of metal-containing mitochondiral enzymes, such as the copper containing cytochrome-c oxidase of complex IV and the iron containing NADH:Q oxidoreductase of complex I. These mitochondrial respiratory chain play…
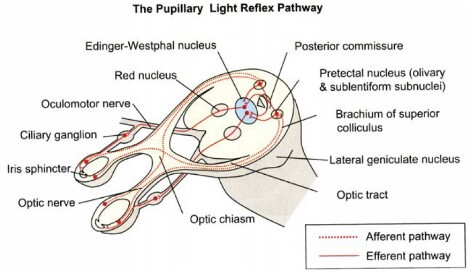
Visual Pathway : Supplement Knowledge
Everyone must be aware of the normal visual pathway and their defects. Here, I’ve tried to enlist the topics related to the visual pathway that are “nice to know” but you may have missed it or failed to understand properly. Below is the basic visual pathway: Wilbrand’s knee Anterior…
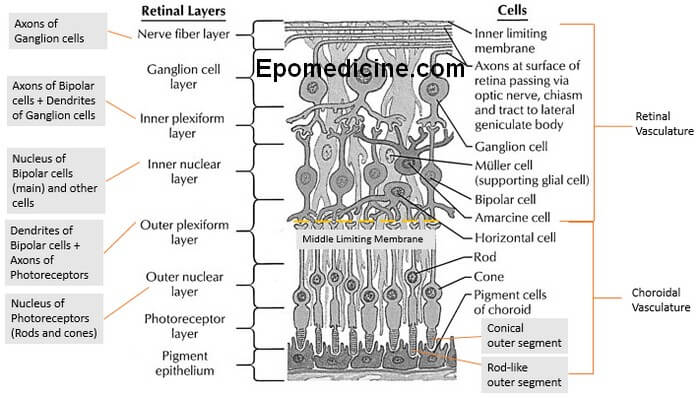
Retinal Layers Simplified
The ten layers of retina – this microscopic anatomy is frequently asked in examinations and also important from the physiological viewpoint. There are plenty of mnemonics around the web, but we will proceed in a different approach to remember the 10 retinal layers easily. A. Retina is 3 neuron system…
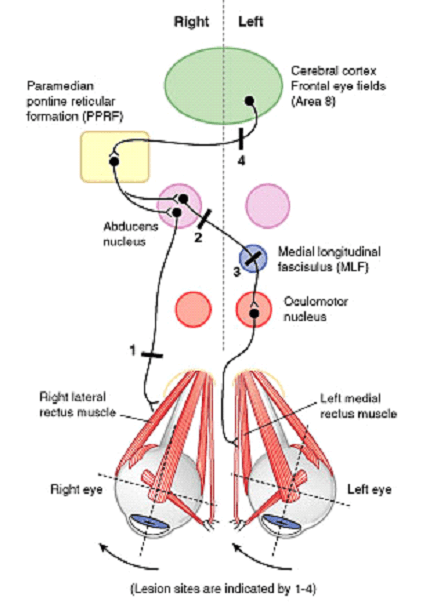
Horizontal Conjugate Gaze Pathway
Components of Pathway For both eyes to look at a side: Contralateral Frontal Eye Field (Brodmann area 8) Ipsilateral PPRF (Paramedial Pontine Reticular Formation) Ipsilateral CN VI Nucleus Contralateral Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF) Contralateral CN III Nucleus Horizontal Conjugate Gaze Pathway Lesions of Conjugate Gaze Pathway Abducens (CN VI) nerve:…
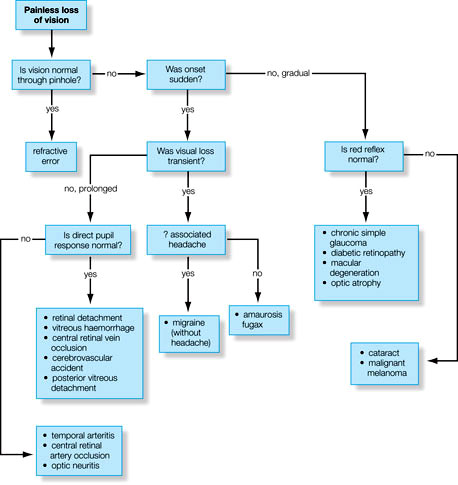
Vision loss – General Appoach
Diagnosis of the etiology of vision loss requires a step-wise systematic approach. The vision loss may be sudden or gradual, painful or painless, unilateral or bilateral, etc. One needs to take a detailed ocular history and examination. Step 1: Sudden or gradual vision loss? a. Sudden: vascular occlusion (e.g., AION, CRAO, CRVO)…