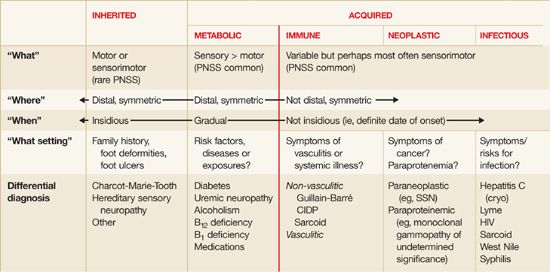
Step 1: What system is involved – motor, sensory, autonomic or mixed? a. Sensory involvement Positive neuropathic sensory symptoms (PNSS) – suggest Acquired polyneuropathy prickling, tingling, asleep like numbness Pain – suggest Small fiber neuropathy due to toxic, metabolic, ischemic or idiopathic cause electric shock, burning, freezing, tightness, throbbing, allodynia…
Tag: Nervous system
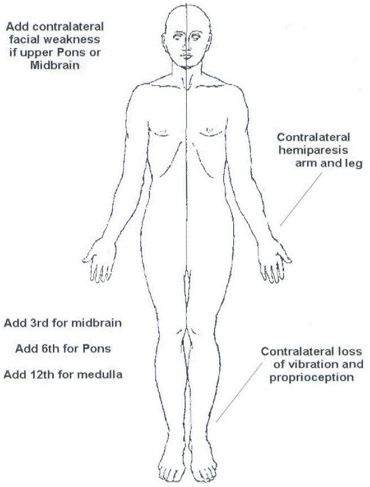
Medial Medullary (Dejerine’s) Syndrome : Anatomical basis mnemonic
As already discussed in the previous section about Lateral Medullary (Wallenberg) Syndrome: 6 “S” pass/lie on the Side (latetral) of Medulla Except the anteromedian part supplied by vertebral artery, rest of the medulla is supplied by PICA Let us now review the relevant anatomy and physiology of the medial portion…
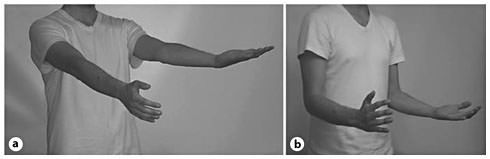
Pronator Drift (Barre’s sign) : Neurological Examination
Components of pronator drift Progress from distal to proximal: Downward arm drift Forearm pronation Flexion of the wrist and elbow Method of assessment for pronator drift When the patient extends both arms upright in the supinated position and hold them at shoulder height for atleast 10 seconds (Patients should be…
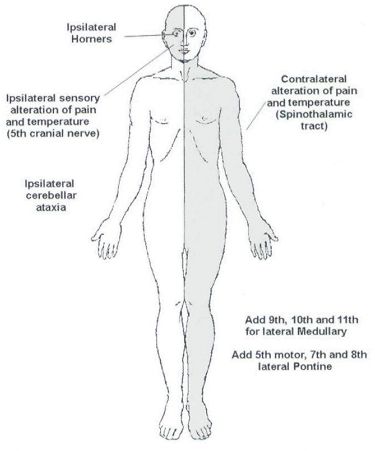
Anatomical basis of Wallenberg (Lateral Medullary) Syndrome : Mnemonic
Before proceeding into the disease itself, let’s review – relevant anatomy of the medulla with a simple mnemonic. The Side (lateral) part of Medulla contains 6 “S“ 1. Spinocerebellar tract Posterior spinocerebellar tract: Ascends and enters to ipsilateral cerebellum via ipsilateral inferior cerebellar peduncle Anterior spinocerebellar tract: Ascends and enters…
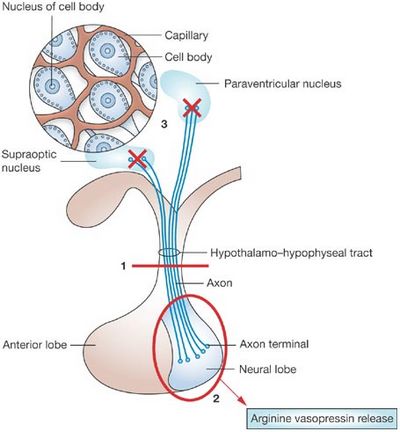
Craniopharyngioma – Case Discussion
Case Summary A 38 year old female came with: Headache for 6 months Diminution of peripheral vision bilatetrally Irregular menstrual cycle for the last 1 year Now, polydypsia and excessive urination Her prolactin level was 115.6 ng/ml (increased), FSH was 1.3 mIU/ml (decreased) and LH was 0.242 mIU/ml (decreased). CT…
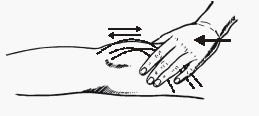
Clonus : Clinical Examination and Mechanism
Definition of clonus Clonus is a rhythmic sustained involuntary muscular contraction (generally 5-8 Hz) evoked by sudden passive stretch of the muscle and tendon. Eliciting Clonus Clonus is commonly elicited in gastrocnemius (ankle clonus). Other sites where clonus can be elicited are quadriceps (patellar clonus), finger flexors and jaw. 1….
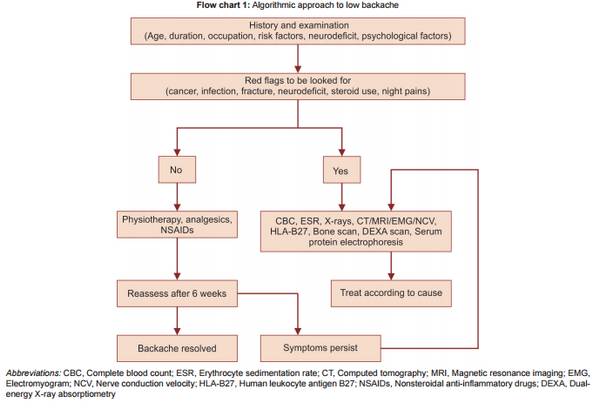
Approach to Low Back Pain
Definition of Low Back Pain Low back pain (LBP) is defined as pain, muscle tension or stiffness localized below the costal margin and above the inferior gluteal folds, with or without leg pain (sciatica). “Diagnostic triage” after excluding non-spinal causes of low back pain classifies LBP into 3 broad categories:…
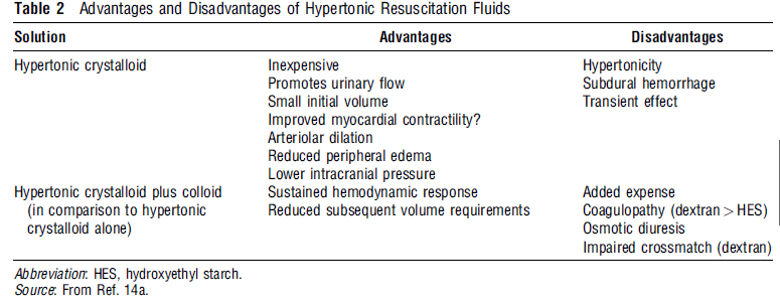
Head trauma fluid resuscitation
Peculiarities of cerebral circulation: 1. Brain and spinal cord is isolated from endothelium by BBB composed of continuous capillaries that limits movement of proteins and electrolytes 2. Fluid movement is primarily determined by osmolar gradient (in contrast to peripheral tissues – transcapillary gradient of large macromolecules) 3. Hence, administration of…