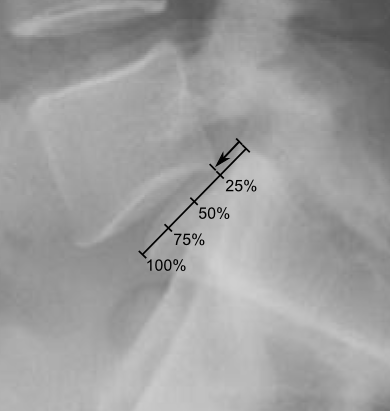
Indications for surgery Age group Spondylolisthesis Indications Pediatric Low grade Failure to respond to conservative treatment (9-12 months)Progressive slippageIntractable low back or radicular painNeurological deficit and deterioration High grade Neurological symptomsSevere sagittal plane spinal deformity Adult Low grade Failure of non-operative treatmentProgressive slippageSymptomatic and radiographically unstable isthmic spondylolisthesis High grade…
Tag: Musculoskeletal system
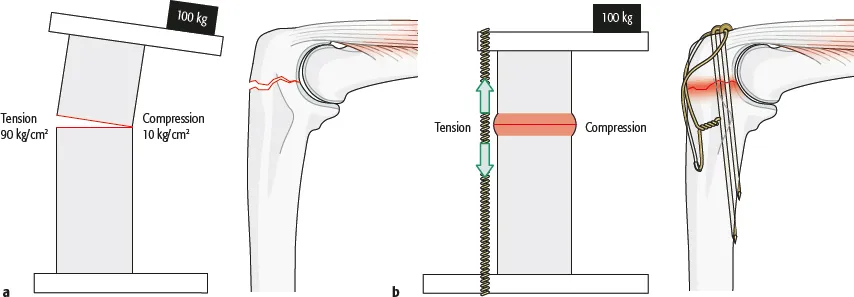
Tension Band Wiring (TBW)
Tension Band Principle A tension band is any device placed on the tension side of an eccentrically loaded fracture that converts tensile load into compressive load. The convex side of the bone is under tension whereas the concave side is under compression. For a tension band to work, the fracture…
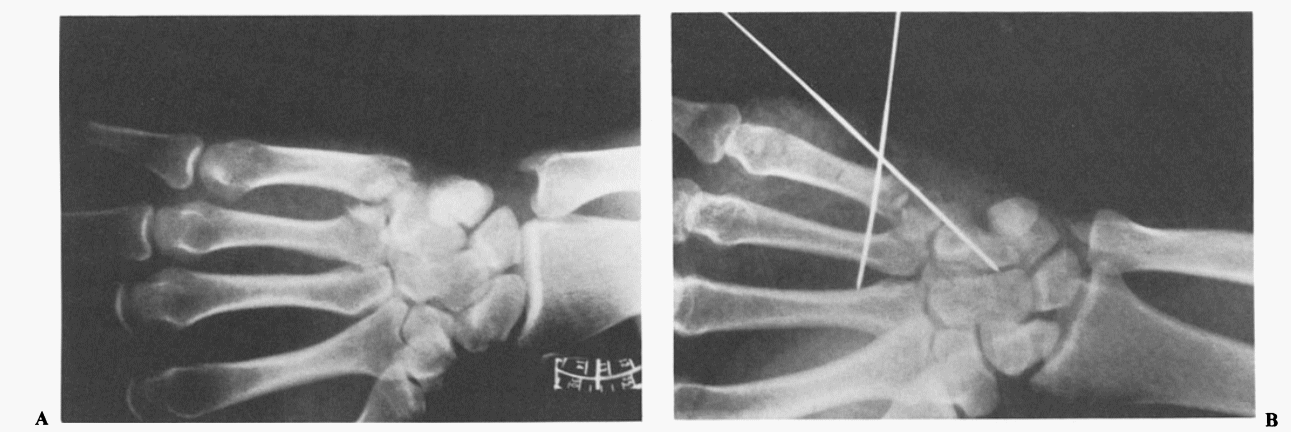
Reverse or Baby or Mirrored Bennett’s Fracture
Definition: The fracture-dislocation at the base of the fifth metacarpal analogous to Bennett’s fracture of the thumb Mechanism of injury: Muscle pull and displacement: Consequences of unreduced fracture-dislocation: Possible associations: X-ray views: Treatment: 1. Closed reduction and internal fixation with K-wires 2. Open reduction and internal fixation with K-wires or…
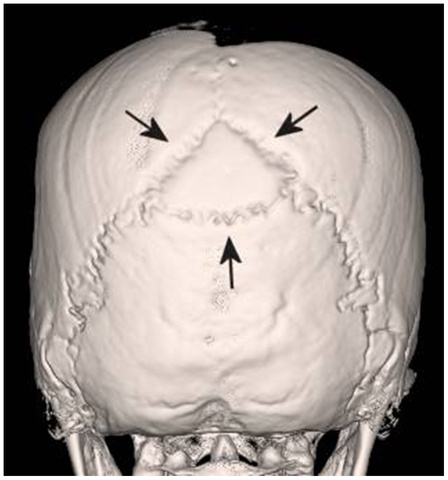
Wormian Bones
Wormian bones are abnormal ossicles that develop from extra ossification centers within the cranium. They are most frequently located in the lambdoid suture or the coronal suture, and have been seen in the fontanelles, particularly the posterior fontanelle. Commonest Cause Idiopathic (Anatomic variant) Other Causes Mnemonic: PORK CHOPS 1. Pyknodyostosis…
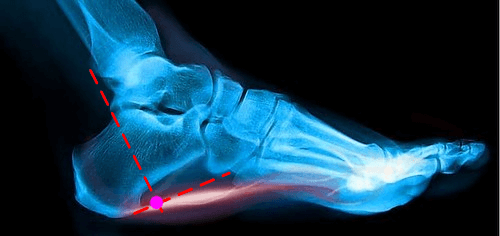
Plantar fasciitis : Injection Technique
Anatomy Plantar fascia arise from medial and lateral tubercles on the inferior surface of calcaneus. The lesion is invariably found at the medial head. Intersection technique 1. Position: Supine with knee flexed and hip externally rotated (figure of 4) 2. Landmark: Point of intersection of a line drawn parallel to…
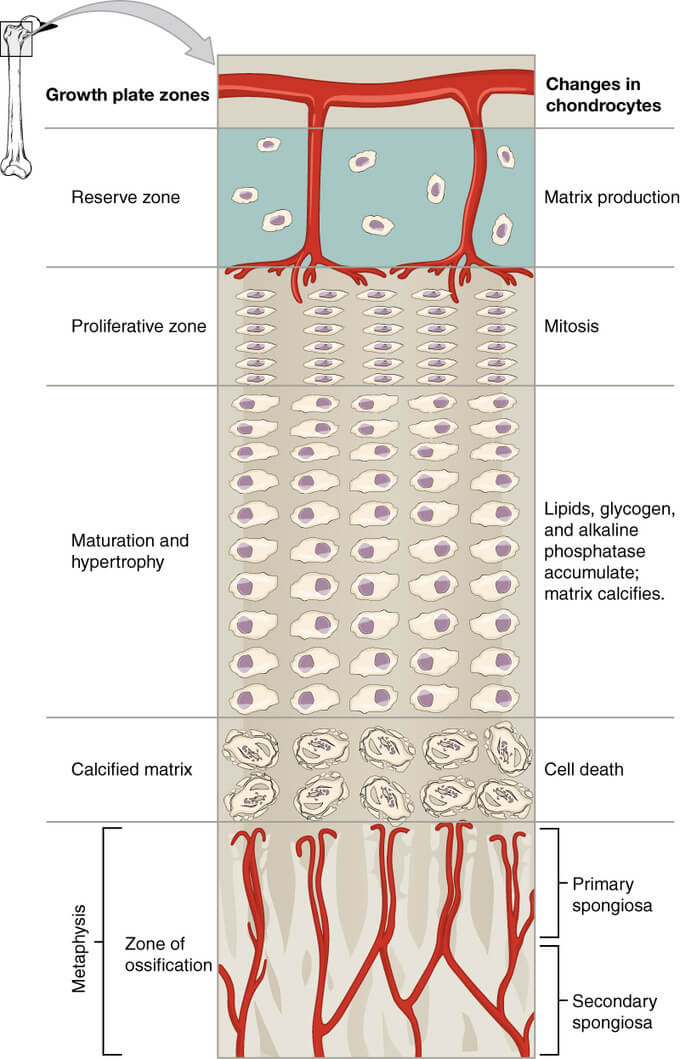
Anatomy of Physis (Growth Plate)
Periphery of physis: The physis is connected to the epiphysis and metaphysis peripherally via: Blood supply of physis: There are three sources of blood supply to the physis: the epiphyseal, metaphyseal, and perichondral circulations. Zones of physis: Zones Characteristics Functions Blood supply Diseases Epiphysis Epiphyseal artery Multiple Epiphyseal Dysplasia (MED) Physis 1….
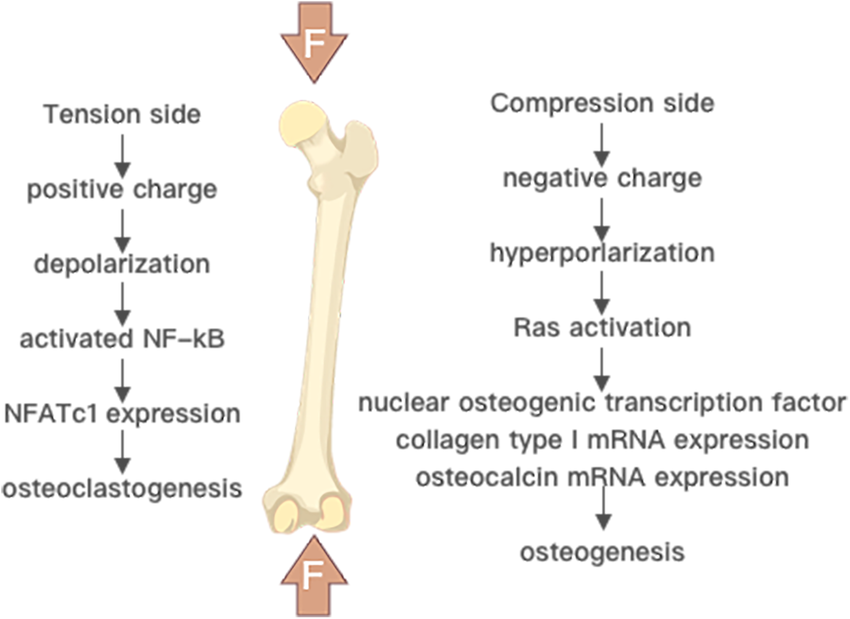
Wolff’s law and Hueter-Volkmann law
Bone remodeling involves the removal of mineralized bone by osteoclasts followed by the formation of bone matrix through the osteoblasts that subsequently become mineralized. There are 2 prominent concepts of bone remodelling: 1. Hueter-Volkmann law or Delpech’s law: It states that bone growth in the skeletally immature is inhibited in…
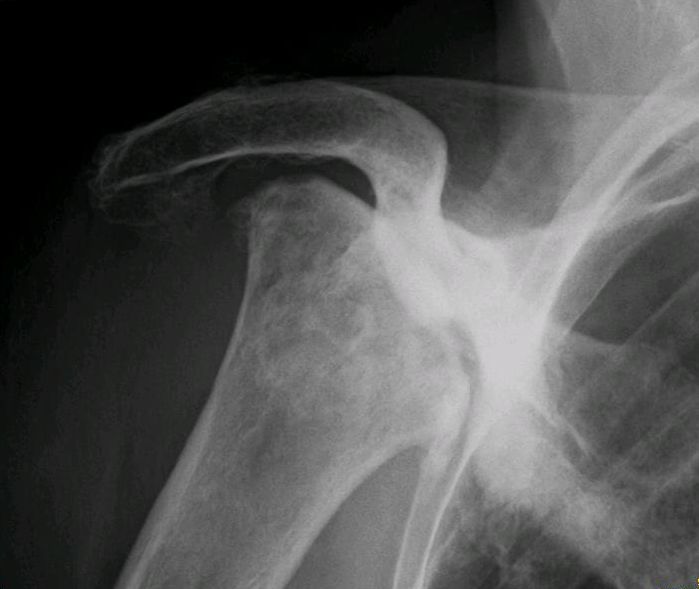
Avascular Necrosis (Osteonecrosis) of Various Bones : Stages and Management
Propensity Stages and Management Stages Hip (modified Ficat-Arlet) Shoulder (Cruess) Lunate (Lichtman) Knee (Koshino) Scaphoid (Herbert and Lanzetta) Management 0 – Silent + NWB joints – Immobilization, NSAIDs WB joints – a. Realignment osteotomyb. Core decompression +/- bone grafting or MSC therapy I – Suggestive clinically and MRI + +…