Causes of SIADH Mnemonic: SIADH Diagnosis and Diagnostic Criteria Mnemonic: SOD-IUN TEA
Tag: Internal medicine

Peptic Ulcer (Johnson) Classification
Mnemonic: 1. 1 is Less 2. 2 is Two 3. 3 is Pre- 4. 4 is Door 5. 5 is 5 letter (NSAID) Type Mnemonic Location Acid hypersecretion Complications Surgery I (55%) Less Lesser curvature No Bleeding uncommon Distal gastrectomy with BI, BII or RY GJ anastomosis II (20%) Two…
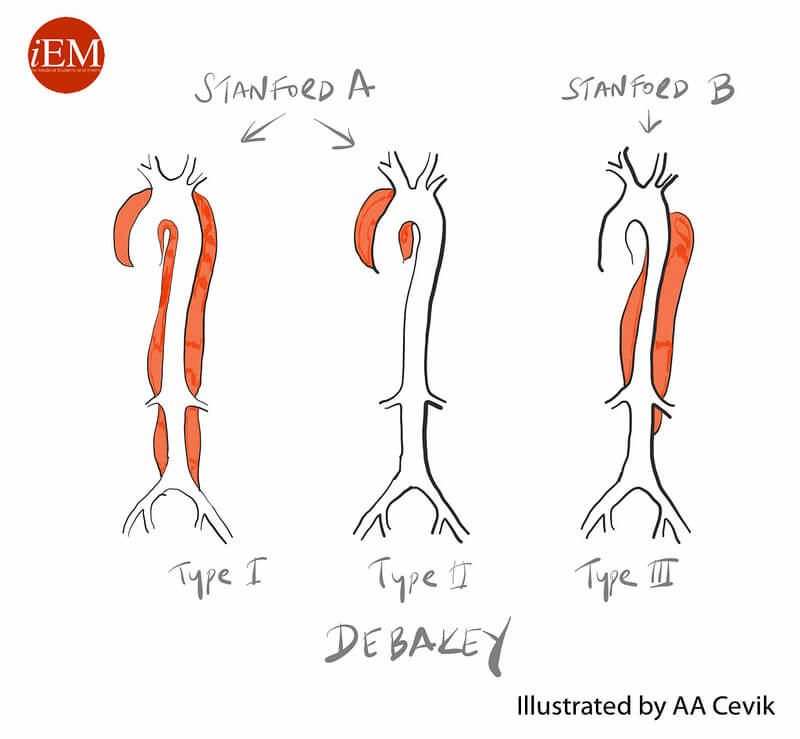
Aortic dissection
Risk factors Mnemonic: ABCDE Pathophysiology Intimal tear allows blood to enter between intima-media space creating a false lumen. Blood may propagate proximal or distal to tear. Clinical features Investigations Classification and Management Stanford DeBakey Description Frequency Management Mnemonic: BAD Mnemonic: A for A; B for B A (Ascending aorta involved)…
Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) : Mnemonic Approach
Rome IV Criteria for IBS Mnemonic: 1, 2, 3 Recurrent abdominal pain on average: Criteria fulfilled for the last 3 months with symptom onset at least 6 months prior to diagnosis Alarm findings (Red flags) Mnemonic: ALARMING Additional diagnostic testing Mnemonic: Rule out 4 “C” 1. Carcinoma 2. Celiac disease…
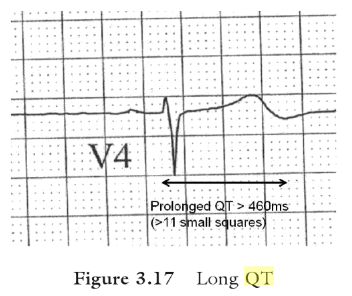
Prolonged QT Interval : Mnemonics
Normal QT Interval Duration: 0.3-0.44 s (0.46 s for women); tends to increase as the heart rate decreases Bazett’s formula for corrected QT interval (QTc): QTc = QT/ √RR Prolonged QT Interval Duration: >0.44 s (men) and >0.46 s (women) Can lead to: Polymorphic VT (Torsades de pointes) Causes: Mnemonic:…
Pheochromocytoma : Mnemonics
Pheochromocytoma is a catecholamine-producing tumor arising from chromaffin cells of the sympathetic nervous system derived embryologically from the primitive neural crest cells. Sites: Clinical features Mnemonic: 5 H or 7 P’s 5 H 7 P Hypertension Paroxysmal rise in pressure (BP) Headache Pain (headache) Hyperhidrosis Perspiration (hyperhidrosis) Hyperglycemia Pallor Hypermetabolism…
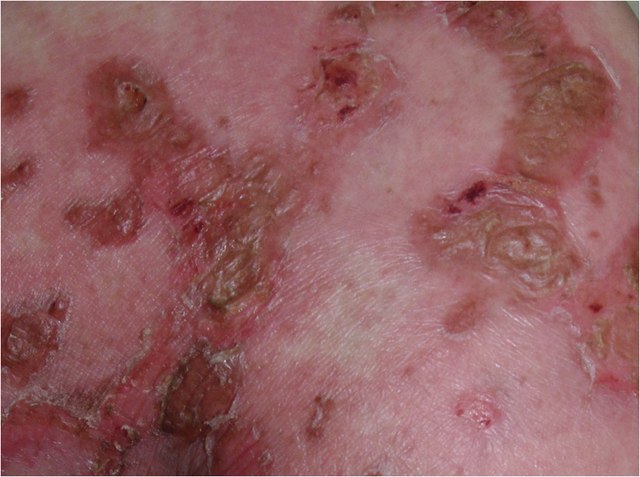
Glucagonoma : 6 D’s
Glucagonoma is an alpha-cell tumor of pancreas. Mnemonic: 6 D’s 1. Diabetes 2. Dermatitis (Necrolytic migratory erythema) 3. Declining weight 4. Diarrhea 5. Deep vein thrombosis 6. Dilated cardiomyopathy
ABG Interpretation Made Easy
Normal values Step 1: pH Step 2: pCO2 Step 3: HCO3- Step 4: Determine compensation If there is metabolic acidosis or alkalosis, determine if there is appropriate respiratory compensation: No respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 = Measured pCO2 Respiratory compensation: Expected pCO2 ≠ Measure pCO2 Step 5: Delta ratio ΔAG /…
