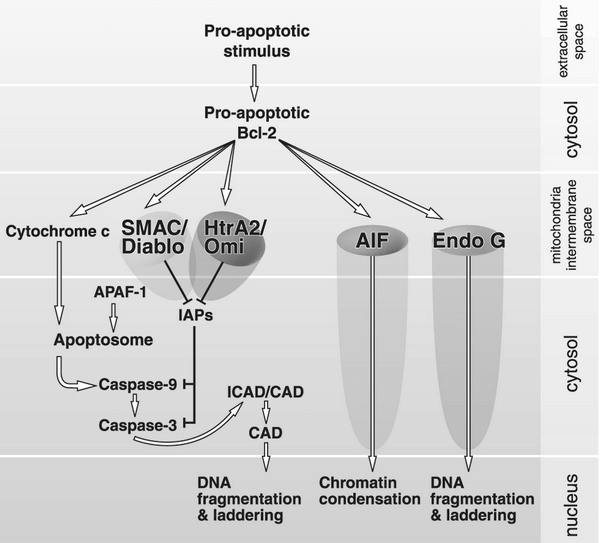
Caspases (Pro-apoptotics) Initiator caspases: Executioner caspases: 3 and 7 Pro-apoptotic genes Mnemonic: “B” followed by a vowel Anti-apoptotic genes Mnemonic: Contains “L” or “XL” Other: Inhibitor of Apoptosis (XIAP) How all these genes and molecules work together to complete apoptosis? Find it here.
Tag: General concepts
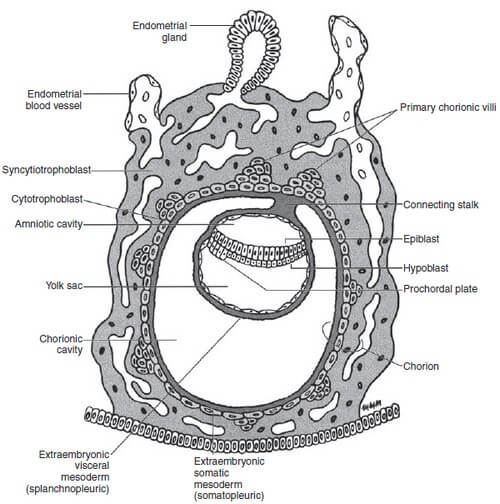
Embryology Week 2: Rule of Twos
Starting from Day 8, blastocyst progressively invades into the endometrial stroma and there is formation of: 2 layers in Trophoblast: 1. Inner mononulcear Cytotrophoblast (Cellular) Mitotic figures are found in the cytotrophoblast – hence generate primary chorionic villi into the syncytiotrophoblast. 2. Outer multinucleated Syncytiotrophoblast (Syncytium – cells have fused) Mitotic…
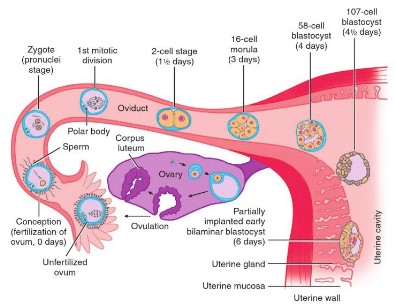
Embryology Week 1: Cleavage to Implantation
Following events occur in the zygote formed in the week zero of development: Cleavage Approximately 24 hours after fertilization the zygote begins with the first cleavage division. Series of mitotic divisions of the zygote (occurs in fallopian tube) to form small daughter cells called blastomeres. Characteristics of cleavage in humans:…
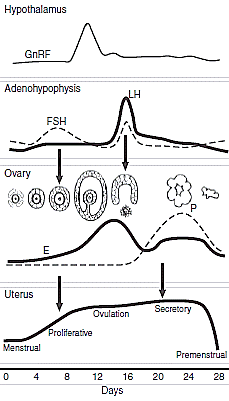
Embryology Week 0: Gametogenesis, Ovulation and Fertilization
Gametogenesis – formation of gametes from primitive germ cells Spermatogenesis, begins at puberty and occurs in seminiferous tubules (spermiogenesis occurs in sertoli cells). One spermatogenesis takes an average of 74 days to complete. Oogenesis Stages Spermatogenesis Migrate at 6th week of development 1. Primordial Germ Cells / PGCs (46, 2n) – epiblast…
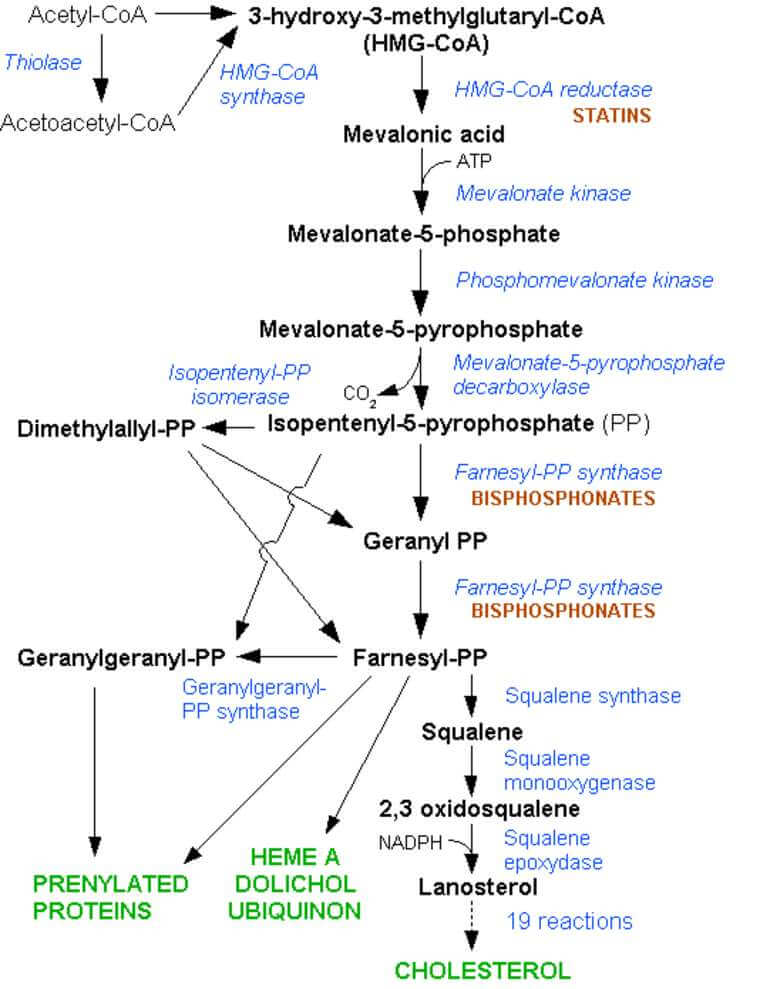
Cholesterol Synthesis Mnemonic
Liver as a hub of cholesterol metabolism All nucleated cells have the capacity to synthesize cholesterol from acetyl-CoA (like most biological lipids). 90% of synthesis occurs in liver and intestine. The cholesterol biosynthesis pathway involves enzymes that are in the cytoplasm, microsomes (ER), and peroxisomes. Liver obtains cholesterol from 3…
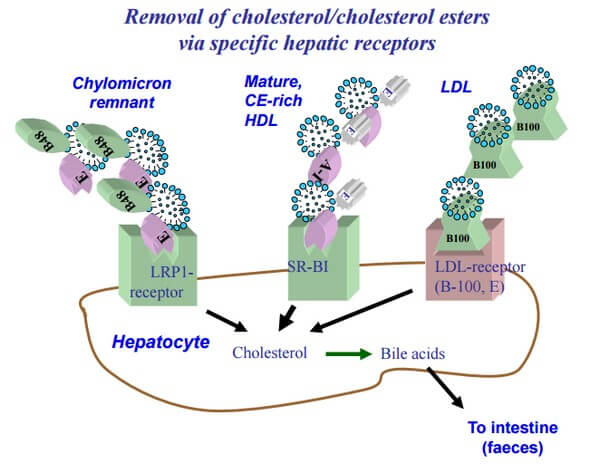
Lipoprotein Metabolism Simplified
Lipoproteins Composition of Lipoproteins: Non-polar core – mainly triglycerides and cholesteryl esters Single surface layer – amphipathic phospholipids and cholesterol Apoprotein or Apolipoprotein Class Abbreviation Density Protein Lipid content Electrophoretic mobility Chylomicrons CM lowest lowest highest (exogenous triacylglycerol) don’t migrate Very low density lipoproteins VLDL .. .. .. (endogenous triacylglycerol)…

Inheritance of Disease – Mnemonics
Lets work with some generalizations 1. X-linked dominant, mitochondrial and Y-linked conditions are rare. You need to remember them. 2. Usually inherited in autosomal dominant pattern are: Mostly mutations in non-enzymatic structural proteins (e.g. collagen, fibrillin, cytoskeletal proteins of RBC) or in membrane receptors (e.g. LDL receptor) Diseases due to diminished…
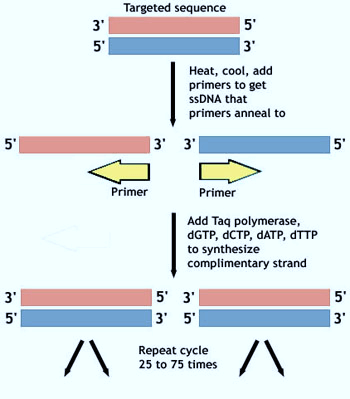
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Made Easy
What is Polymerase Chain Reaction ? It is a process of artificial DNA replication (amplification of a selected part of DNA). As the name suggests: Polymerase: It requires DNA polymerase for extending the added primers to complete DNA replication. Chain Reaction: PCR is run in cycles. The number of molecules…