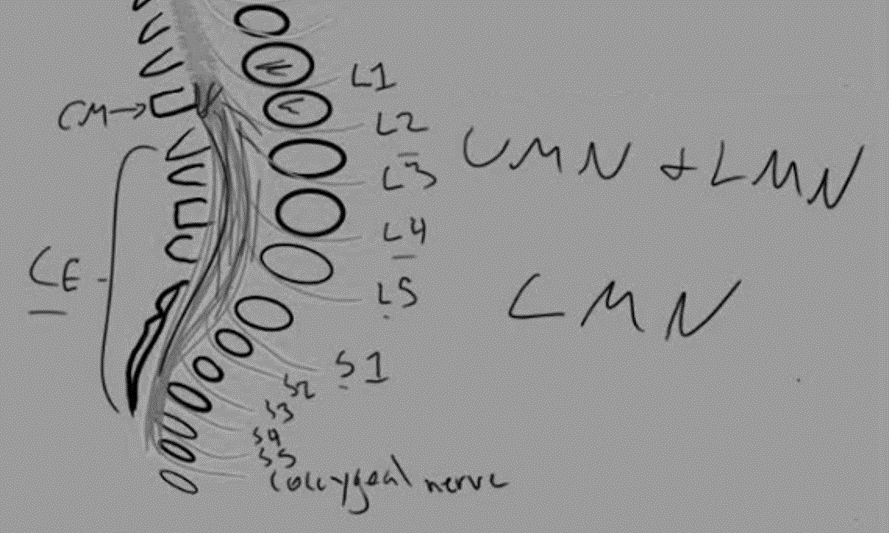Definitions Condition Vertebral level of injury Neurological level of injury ISNCI level of injury Conus Medullaris Syndrome (CMS) T12-L2 T12-S5 T11 Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES) L3-L5 L3-S5 L2 Anatomy The spinal cord ends as a tapered structure called the conus medullaris at the level of L2–L3 disc in the neonate…
Tag: Emergency medicine
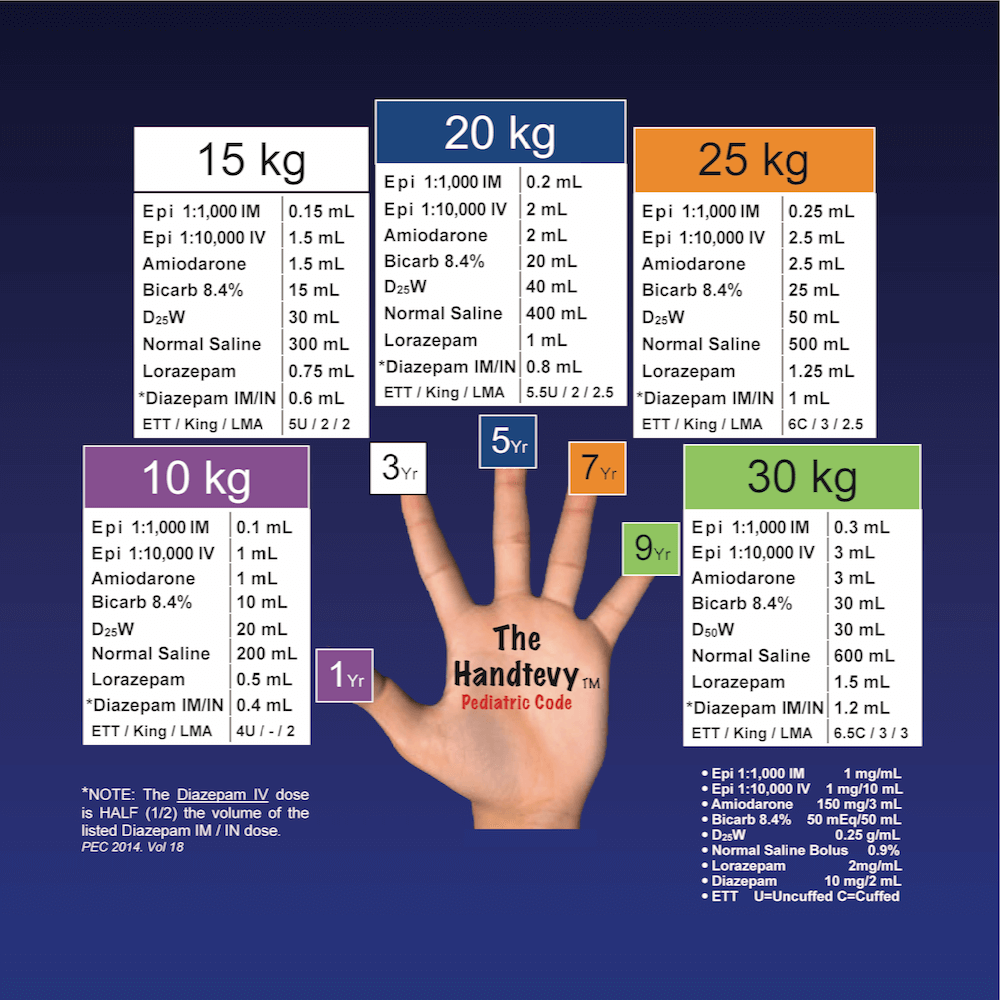
Handtevy Method : Emergency Drug Dose by Age
To obtain the correct weight for each age, assign each finger a chronological odd number starting with 1, representing the age in years. Now, using the same fingers, count in the multiples of 5, starting with 10 to obtain the corresponding ideal body weight in kilograms. For the even ages,…

Differential Diagnoses of Older patient’s fall : Mnemonic
Mnemonic: CATASTROPHE 1. Caregiver and housing (information on the circumstances of present fall and falls history) 2. Alcohol (including withdrawal) 3. Treatment (medications, recently added or stopped, compliance) 4. Affect (depression or lack of initiative) 5. Syncope (any episode of fainting) 6. Teetering (dizziness) 7. Recent illness 8. Ocular problems…

Organophosphorous poisononing : Mnemonic Approach
A. Muscarinic overstimulation: Mnemonic: DUMBBBELS Diarrhea/Diaphoresis Urination Miosis Bronchorrhea Bronchospasm Bradycardia Emesis Lacrimation Salivation B. Nicotininc overstimulation (NMJ and Sympathetic ganglia): Mnemonic: Monday, Tuesday, Wednesday, Thursday, Friday (MTWThF) Mydriasis/Muscle cramps Tachycardia Weakness Twitching Hypertension/Hyperglycemia Fasciculations C. Nicotinic overstimulation in CNS: Mnemonic: Five Cs Confusion Consternation (anxiety) Convulsions Coma CVS and…
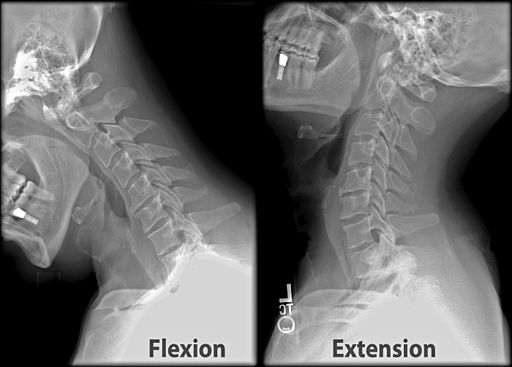
C-spine X-ray : Mnemonic Approach
Mnemonic: ABCDEF For images of the particular Cervical spine (C-spine) X-ray findings and views mentioned below, please refer to the links at the end of the article or use web-search. Adequacy Skull base, C1-C7 and upper T1 must be visible 3 views: True lateral, AP, Odontoid (Open mouth) +/- Swimmer’s…
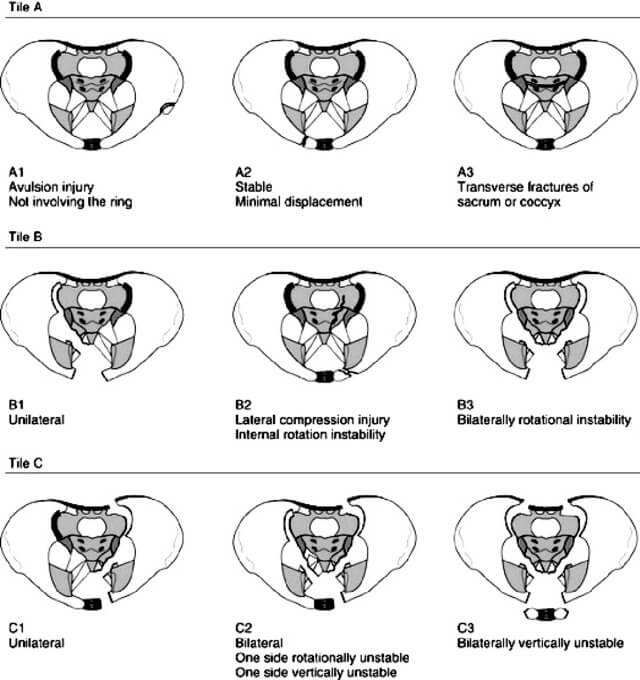
Pelvic Fracture Classification and Management : Simplified
Before proceeding to this topic, it would be wise to go through the topics listed below: Tile/AO Classification Tile classification divides pelvic fractures into three basic types according to stability based on the integrity of the posterior sacroiliac complex. Here is a mnemonic that can be used to remember tile…
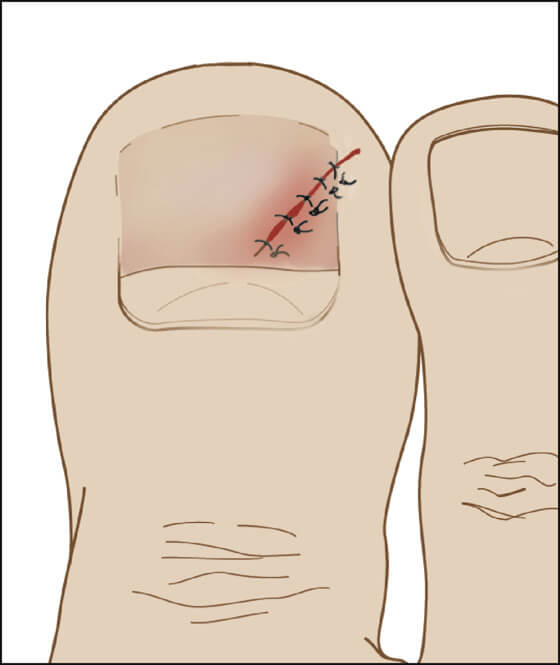
Nail Bed Injuries : Van Beek Classification and Management
Clinically, the Van Beek classification system denominates 5 principal nail bed injuries, subclassified by location within the nailbed (involving either the sterile and/or germinal matrix, respectively) and the extent of injury. Germinal Matrix Injury GI: Small subungual hematoma proximal nail (<25%) GII: Germinal matrix laceration, large subungual hematoma (>50%) GIII:…

Dog bite wounds : Primary closure or Delayed closure?
A study of 50 dog bite wounds revealed that the commonest colonizing: Aerobic micro-organisms are: Pasteurella (50%), Streptococcus (46%), Staphylococcus (46%), Neisseria (32%), and Corynebacterium (12%), Eikenella corrodens (2%) Anaerobic micro-organisms are: Fusobacterium nucleatum (16%), Bacteroides tectus (14%), Prevotella heparinolytica (14%), Propionibacterium acnes (14%), Prevotella intermedia (8%), Peptostreptococcus anaerobius (8%),…