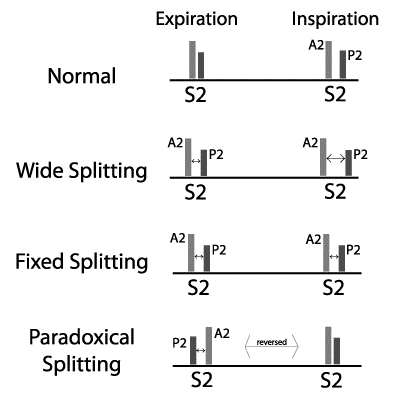
In the chapter of cardiac cycle, we have discussed the mechanism of production of heart sounds and their physiologic splitting. First Heart Sound (S1) Mechanism Closure of atrioventricular valves. It is best appreciated in mitral and tricuspid area of chest for respective components. Loud S1 Slamming a door from a…
Tag: Cardiovascular system
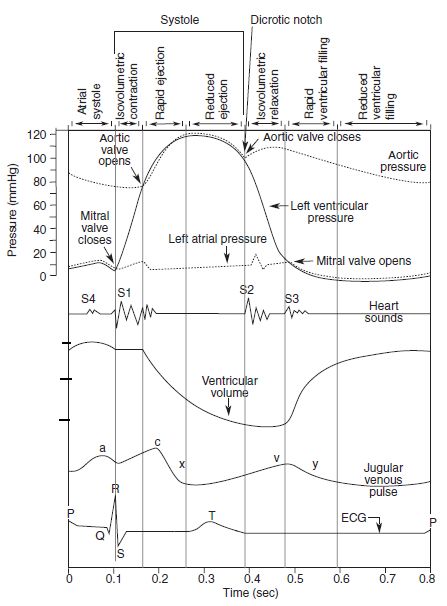
Cardiac Cycle – Summary and Wigger’s Diagram
Cardiac Cycle Opening and closing of valves When the valve opens, different compartments act as a single chamber (atrio-ventricle or aorto-ventricle). For a blood to flow, pressure in “giver” must be higher then that in “receiver”. Pressure difference opens or closes the valve: Role of atrial contraction in Ventricular filling…
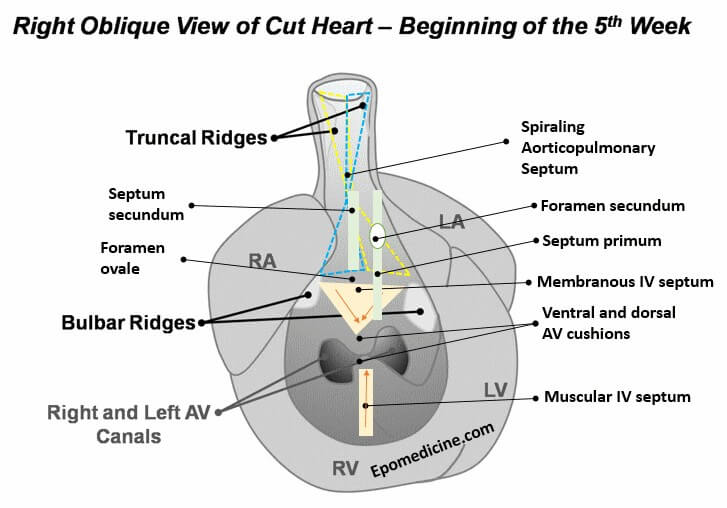
Heart Development – Embryology Made Easy
Heart Tube At the beginning of 4th week of development, heart is a continuous and valveless linear tube that resembles a chicken hung upside-down. It consists of 5 embryonic dilatation, that are destined to be the inflow and outflow tract and compartments of the hear without septum and valves. From cranial…
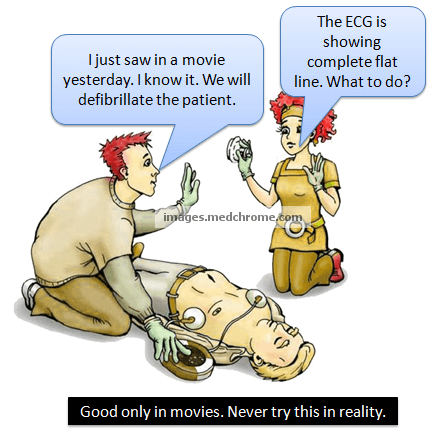
Why to not defibrillate Asystole ?
What is asystole? Asystole is a state of no cardiac electrical activity. It is seen as a “flat-line” in ECG monitor. However, other possible causes of flat-line should be ruled out before calling it asystole. They are: Loose or disconnected ECG leads Loss of power to ECG monitor Once, asystole…
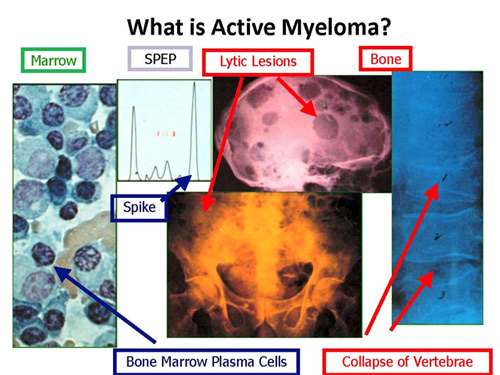
Multiple Myeloma : Quick Approach
Plasma cell dyscrasia refers to an abnormal proliferation of plasma cells that usually secrete a monoclonal immunoglobulin. A) CLINICAL FEATURES Features vary among various conditions: Mnemonic: CRAB Infection 1. Calcium increased: Hypercalcemia Nephrocalcinosis and
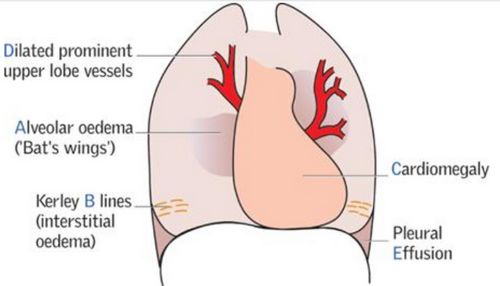
Cardiac (Heart) Failure Made Easy (Pathophysiology and Diagnosis)
DEFINITION OF CARDIAC FAILURE It is a state in which there is: a. Forward failure: inability of heart to maintain cardiac output sufficient to meet the metabolic demands of peripheral tissues AND/OR b. Backward failure: ability to do so with elevated filling pressure PATHOGENESIS OF CARDIAC FAILURE 1. Myocyte loss…

Pulsus Paradoxus – Clinical Examination
Synonyms: Paradoxical pulse, Paradoxic pulse, Reversed Bernheim sign Definition of Pulsus Paradoxus There is normal physiological fall in Blood pressure upto 10 mmHg during inspiration. Pulsus paradoxus is the exaggeration of this normal decline in blood pressure more than 10 mmHg during inspiration. The “paradox” refers to the fact that…
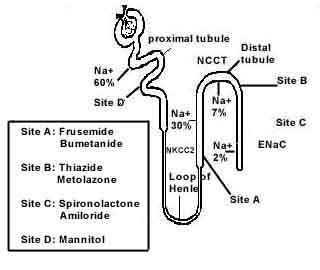
Approach to a Child with Edema
Before beginning the clinical approach to a child with edema, it is necessary to understand the basics of fluid compartments, starling forces and technique of eliciting edema. Life threatening causes of Edema: Generalized: Cardiac disease Congestive Heart Failure Pericardial effusion Renal disease Nephrosis Nephritis Hepatic failure Localized: Allergic reaction with…