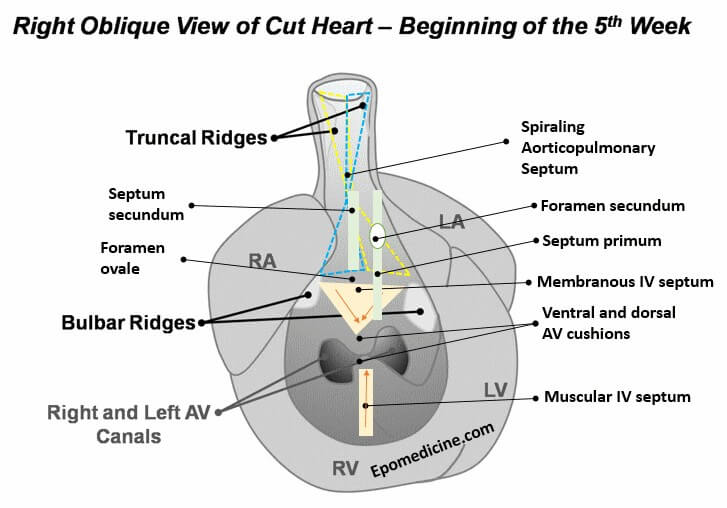
Heart Tube At the beginning of 4th week of development, heart is a continuous and valveless linear tube that resembles a chicken hung upside-down. It consists of 5 embryonic dilatation, that are destined to be the inflow and outflow tract and compartments of the hear without septum and valves. From cranial…
Tag: Anatomy
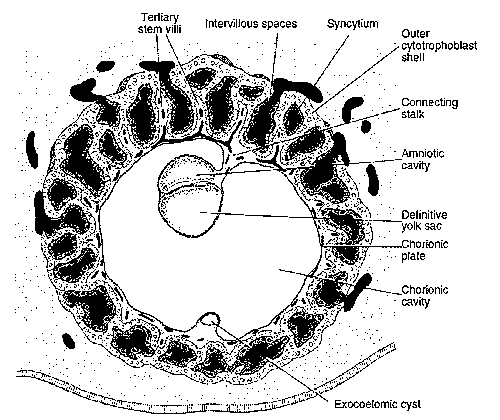
Embryology Week 3: Trimalinar Germ Disc
In the Week 2, we had a bilaminar germ disc with 2 cavities (amniotic cavity and yolk sac) suspended in the chorionic (extraembryonic cavity) by a connecting stalk (future umbilical cord). In the 3rd week, the embryo will have 3 germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm) following a process called…
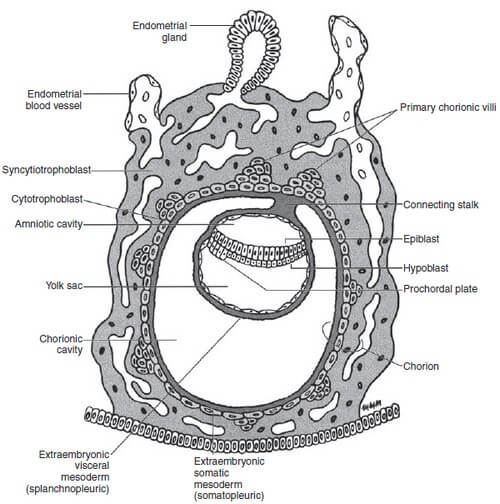
Embryology Week 2: Rule of Twos
Starting from Day 8, blastocyst progressively invades into the endometrial stroma and there is formation of: 2 layers in Trophoblast: 1. Inner mononulcear Cytotrophoblast (Cellular) Mitotic figures are found in the cytotrophoblast – hence generate primary chorionic villi into the syncytiotrophoblast. 2. Outer multinucleated Syncytiotrophoblast (Syncytium – cells have fused) Mitotic…
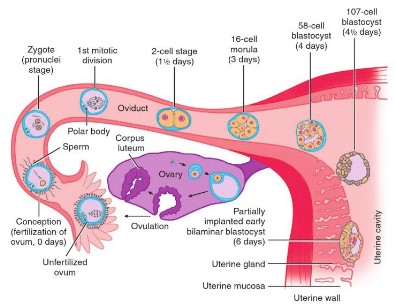
Embryology Week 1: Cleavage to Implantation
Following events occur in the zygote formed in the week zero of development: Cleavage Approximately 24 hours after fertilization the zygote begins with the first cleavage division. Series of mitotic divisions of the zygote (occurs in fallopian tube) to form small daughter cells called blastomeres. Characteristics of cleavage in humans:…
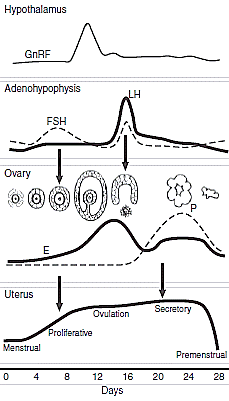
Embryology Week 0: Gametogenesis, Ovulation and Fertilization
Gametogenesis – formation of gametes from primitive germ cells Spermatogenesis, begins at puberty and occurs in seminiferous tubules (spermiogenesis occurs in sertoli cells). One spermatogenesis takes an average of 74 days to complete. Oogenesis Stages Spermatogenesis Migrate at 6th week of development 1. Primordial Germ Cells / PGCs (46, 2n) – epiblast…
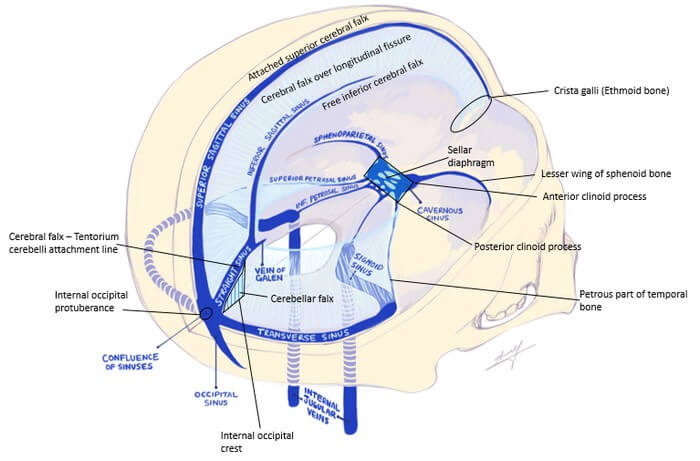
Dural Reflections and Venous Sinuses
Dura mater (pachymenix) is the outer meningeal layer consisting of: Dural Reflections These are the infoldings formed by the inner meningeal layer reflecting away from the fixed periosteral dural layer. Two vertical reflections – Separate the right and left hemisphere Two horizontal reflections Dural Venous Sinuses 1. Superior sagittal sinus:…
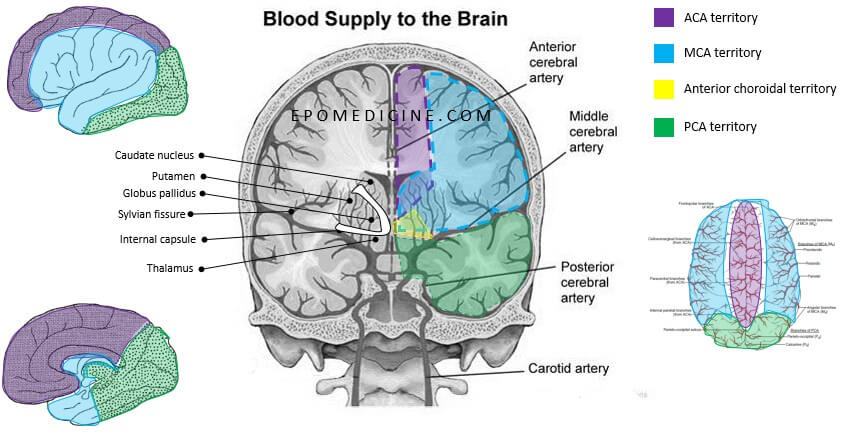
Circle of Willis and Forebrain Blood Supply
We have already discussed earlier on the intracranial course of Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) and Circle of Willis formation with the help of a simple mnemonic. General Concepts of Blood Supply of Brain and Spinal Cord 1. Spinal cord, Hind-brain and Mid-brain: Veterbro-basilar system 2. Forebrain: Circle of willis which…
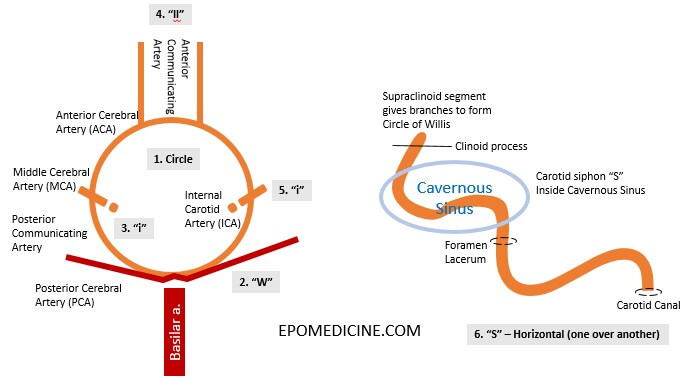
Circle of Willis – Mnemonic and Drawing
Circle of Willis is an important arterial communication that supplies the forebrain (telencephalon, diencephalon and optic vesicle) and often frequently tested in the exams. Circle of Willis receives blood from: Here, we will learn a mnemonic to draw the circle of willis and intracranial course of Internal Carotid Artery (ICA)….