History: Hand dominance and occupation? Injury? Pain? Paresthesia? Impaired function? Swelling? Position: Place the patient’s hands on pillow Look: SEATS a. Shape or Deformity: – Wrist: Radial deviation: RA Ulnar deviation and flexion deformity: Spastic hemiplegia (CP) Wrist drop (also finger drop): Radial nerve injury Prominent dorsal ulnar and radial…

Mendelian Inheritance : Basis of Genetics
Some important terminologies Gene: a functional part of the DNA molecule of a chromosome which directs the synthesis of a specific polypeptide chain. Allele (allelomorph): alternative form of a gene found at the same locus on a pair of homologous chromosomes. Homozygous: the presence of two identical alleles at a…
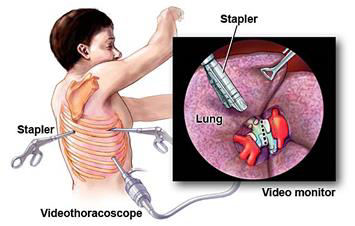
Text Presentation on Empyema Thoracis
A) INTRODUCTION Empyema (aka Empyema Thoracs or Empyema of the chest) is an accumulation of pus in the pleural space that occurs when an infection spreads from the lungs. It comes from the Greek word empyein, which means : pus–producing (suppurates). Empyema itself is not a disease but it is actually a condition complicated by another disease….
Approach to hypertension in pregnancy
Hypertension in pregnancy is one of the major cause of maternal, fetal and neonatal mortality and morbidity in both the developing and developed nations. About 10-15% of pregnancies are accompanied by hypertension and if these are detected early and effective interventions are performed, the prognosis is good. A. HISTORY FOR…
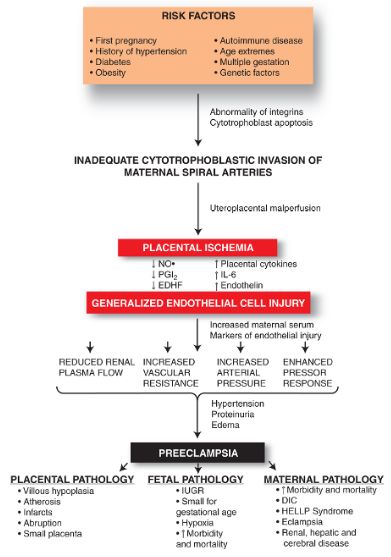
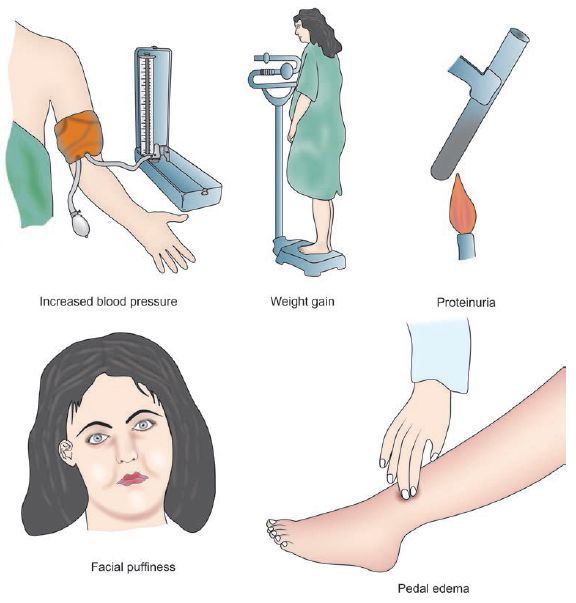
Hypertensive Disorders in Pregnancy – Basics
Hypertensive disorders in pregnancy is a term that encompass wide range of blood pressure related disorders during pregnancy like gestational hypertension, pre-eclampsia, eclampsia, etc. Blood pressure in Normal Pregnancy: During middle trimester, due to the reduction in Systemic Vascular Resistance (SVR) and Arterio-venous (AV) shunting within the uterus and intervillous…
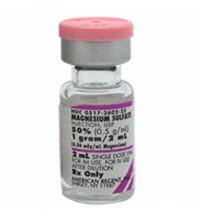
Pritchard regimen (MgSO4) in PIH
Pre-eclampsia is a disorder of pregnancy, characterized by hypertension (BP > 140/90 mmHg measured 2 times with interval ≥ 6 hours) and proteinuria (urinary excretion of ≥ 0.3 gm protein/24 hour specimen or 1+ in dipstick) after the 20th weeks of gestation in a previously normotensive and non-proteinuric woman. Pre-eclampsia…
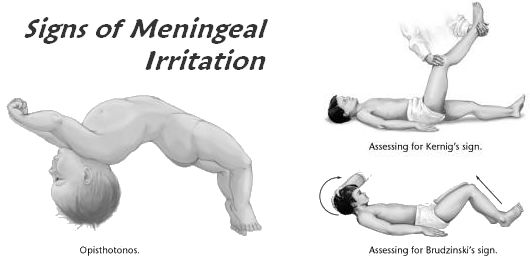
Meningeal signs
Meningitis refers to the inflammation of leptomeninges and underlying subarachnoid cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Meningism or meningismus is a morbid state characterized by a meningitic syndrome (a triad of headache, photophobia and nuchal rigidity) without intracranial inflammation. Some authors, have also used the term “meningism” or “meningismus” to describe the characteristic signs…
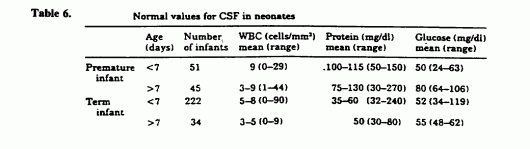
Practical Procedures : Lumbar Puncture (LP)
Synonyms: Spinal tap Definition: Puncture of subarachnoid space in the lumbar region of the spinal cord to withdraw cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) for diagnostic or therapeutic purpose or inject drugs for anesthetic purpose. Indications: A. Diagnostic: CNS infections: Bacterial, viral, fungal, parasitic or TB meningitis Subarachnoid hemorrhage Carcinomatosis meningitis (CNS involvement…
