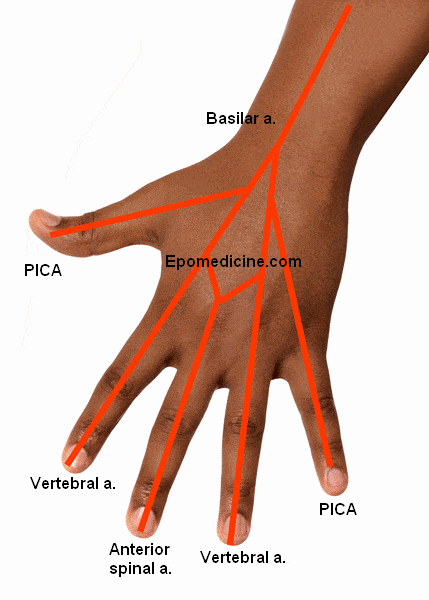
Vertebral Artery I use the analogy of hand to remember the vertebral artery and it’s branches: Origin: Branch of subclavian arteries Course: Ascends through transverse foramina on C6 through C1 and enters posterior fossa through foramen magnum Continue up the ventral surface of medulla Converge at the ponto-medullary junction to form…
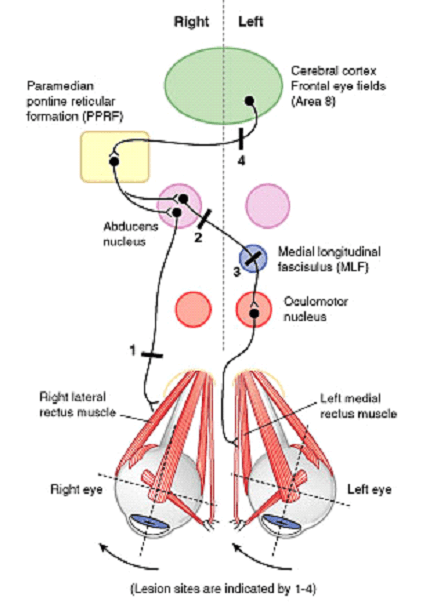
Horizontal Conjugate Gaze Pathway
Components of Pathway For both eyes to look at a side: Contralateral Frontal Eye Field (Brodmann area 8) Ipsilateral PPRF (Paramedial Pontine Reticular Formation) Ipsilateral CN VI Nucleus Contralateral Medial Longitudinal Fasciculus (MLF) Contralateral CN III Nucleus Horizontal Conjugate Gaze Pathway Lesions of Conjugate Gaze Pathway Abducens (CN VI) nerve:…
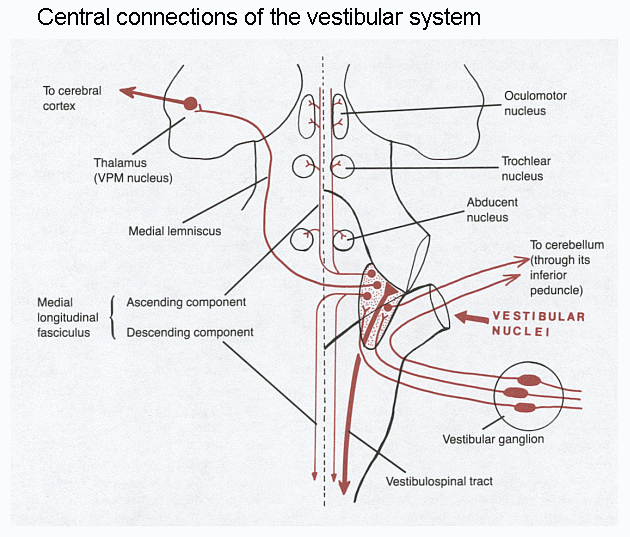
Vestibular Pathway Simplified
Vestibule and Sensory receptors Location: Medial to tympanic membrane and Posterior to Cochlea Sensory receptors 1. Macula: Present in otolith (calcium carbonate crystals) organs – saccule (anteriorly) and utricle (posteriorly) Both are connected by corresponding ducts, which together will form endolymphatic duct, this passes through a bony canal (the vestibular…
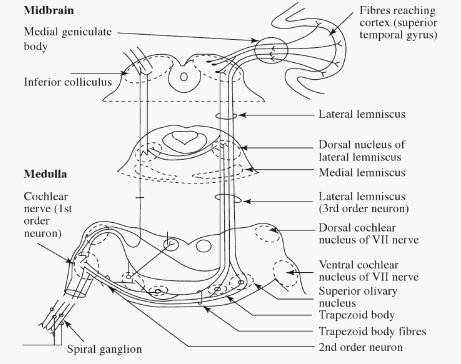
Auditory Pathway Mnemonic
Auditory Pathway Component Mnemonic E.C.O.L.I.M.A Ascending from peripheral to central the components are: Ear receptors (Hair cells) in Cochlea and Eighth Cranial nerve (CN VIII) Cochlear nucleus Superior Olivary nucleus Lateral lemniscus Inferior colliculus Medial geniculate body Auditory cortex Explanation of the Mnemonic Ear receptors and Eighth cranial nerve (Organ…
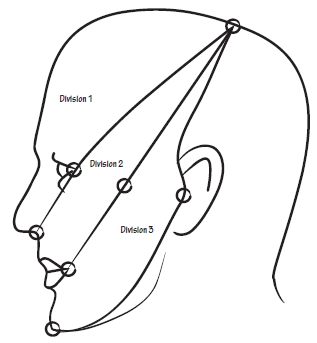
Trigeminal Nerve Simplified
Course of Trigeminal Nerve and Trigeminothalamic Pathway Mandibular (CN V3) Division of Trigeminal Nerve Maxillary (CN V2) Division of Trigeminal Nerve Ophthalmic (CN V1) Division of Trigeminal Nerve Sensory Map Of Trigeminal Nerve on Face Area of Ophthalmic division: Line joining – Just behind the top of head Corner of eyes…
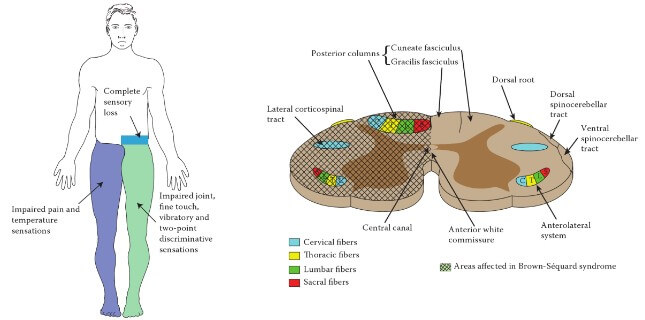
Brown-Sequard Syndrome – Anatomical Basis
Definition of Brown Sequard Syndrome Neurological syndrome resulting from spinal cord hemisection (damage to one lateral half of spinal cord). Causes of Brown Sequard Syndrome Penetrating trauma Spinal fractures Spinal dislocation Disc herniation Vasculitis Radiation induced injury Clinical Manifestations and Anatomical Basis of Brown Sequard Syndrome 1. Damage of Corticospinal…
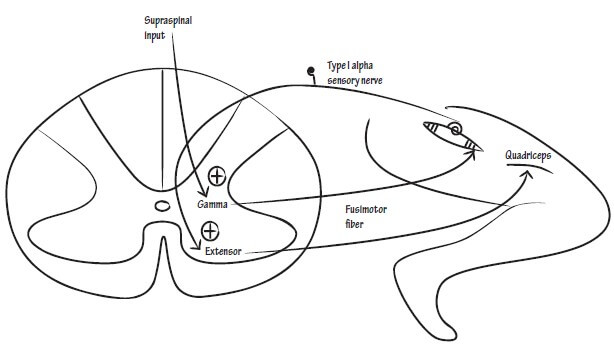
Lower Motor Neuron Lesion (LMNL) – Anatomical Basis
The anatomical basis of Upper Motor Neuron Lesion (UMNL) has already been discussed earlier. Similarly, we will explain the anatomical basis of clinical syndrome of Lower Motor Neuron Lesion (LMNL). A. Ipsilateral involvment: Lower motor neuron comprises of motor neurons in the anterior neurons and the fibers originating from them,…
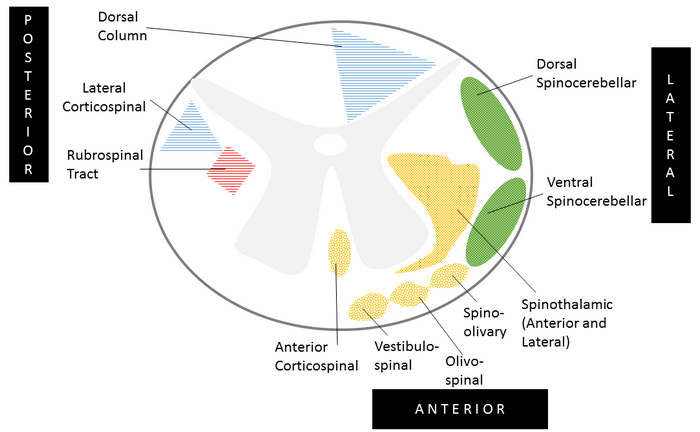
Spinal Tracts Simplified
Organization of Ascending and Descending Tracts in Spinal Cord A. 2 Posterior Tracts: The fibers of these tracts cross to the opposite side at the level of medulla: B. 2 Lateral Tracts: The fibers of these tracts remain on ipsilateral side: C. 2 Anterior Tracts: The fibers of these tracts…