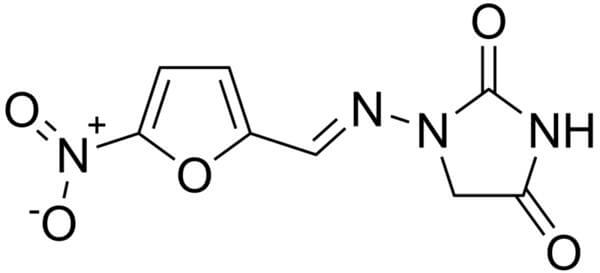
Recently, a wound swab culture and sensitivity reported an E.coli sensitive to Nitrofurantoin. But will it really be helpful in the wound infection? Without a doubt, literatures claim that the sole use of the drug is in the treatment of Urinary Tract Infection (UTI), as after oral or intravenous (i.v.)…
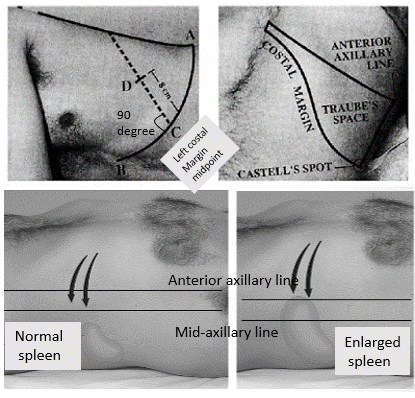
Percussion of Spleen
Traube’s semilunar space Borders: Superiorly: Left 6th rib superiorly Laterally: Left midaxillary line or Left anterior axillary line Inferiorly: Left costal margin Method: Patient’s position: supine with left arm slightly abducted. Percuss: from medial to lateral Interpretation: Resonance (Normal) and Dullness (Splenomegaly) Also: Pleural effusion or mass in stomach may…
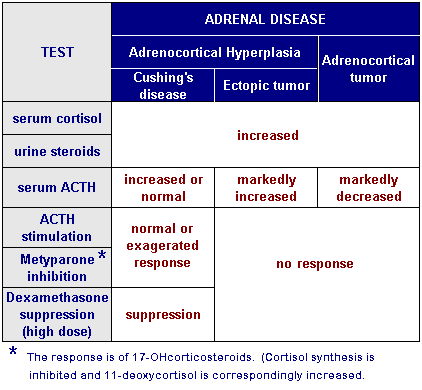
Understanding Dexamethasone Suppression Test
The Dexamethasone Suppression Test (DST) is based on the principle of negative feedback exerted by steroids on pituitary gland’s ACTH secretion. Negative feedback with exogenous steroid works if the cause is excessive ACTH secretion from pituitary: 1. Cushing’s disease (pituitary ACTH dependent Cushing’s syndrome): Excessive ACTH secretion by pituitary adenoma…
Cholangiocarcinoma (Bile Duct Cancer) – Quick Review
This article is in response to the request made by a reader in the comment section. Today, we will try to simplify the biliary tree cancers. Classification of Cholangiocarcinoma Second-order bile ducts act as the separation point between intrahepatic and extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. A. Inhtrahepatic – 10 to 20% B. Extrahepatic…
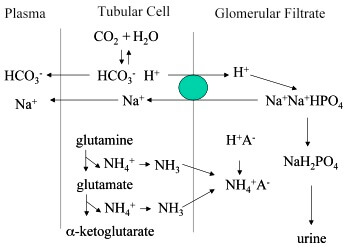
Most Important Urinary Buffer: Phosphate or Ammonia?
There are multiple choice questions (mcq) which asks: What is the most important urinary buffer? And the choices include both the phosphate and ammonia. Different textbooks on physiology and biochemistry have different opinions. Some say that the most important is Phosphate and the others say Ammonia is more important. So,…
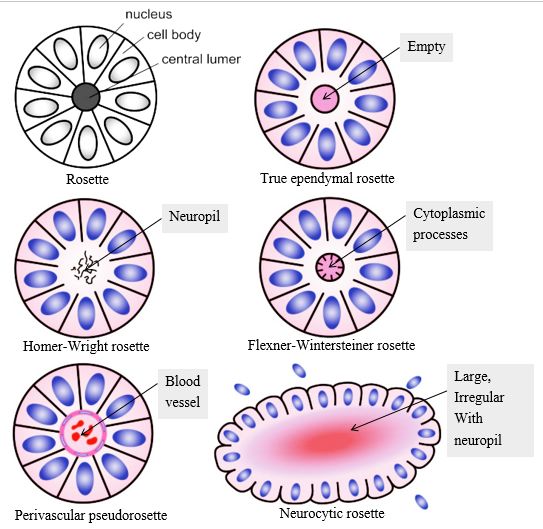
Rosettes in Pathology
Rosette refers to a decoration or pattern resembling a rose. In pathology, rosette refers to aa halo or “spoke-wheel” arrangement of cells around a central structure especially in neoplasms of neuroblastic or neuroectoderma origin. The central structure can be: a. Empty lumen: True ependymal rosette Well differentiated ependymomas (minority of cases)…
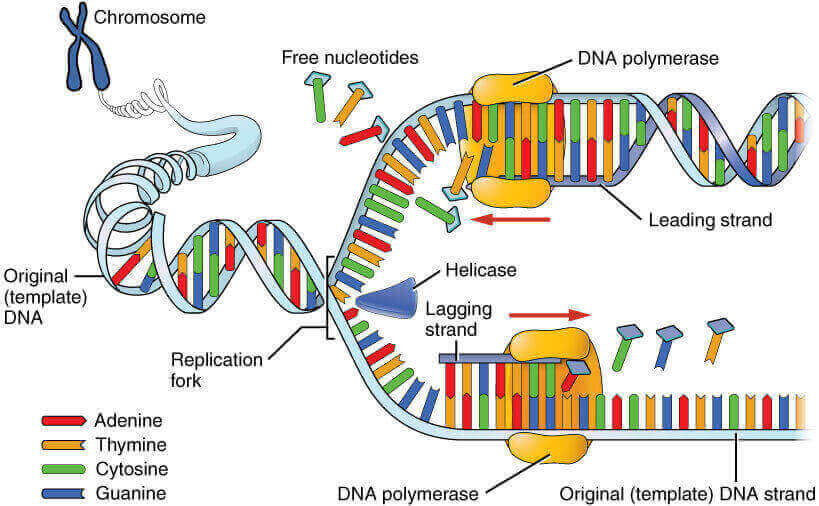
DNA Replication Explained With Zipper Model
Imagine DNA as a zipper Prokaryotic DNA as a zipper with single slider (single origin of replication) and Eukaryotic DNA as a zipper with two sliders (multiple origin of replication). Zipper teeth: Purines and pyrimidine bases Complementary teeth pair: Complementary base pairs attached by hydrogen bonds Top stops: Origin of…
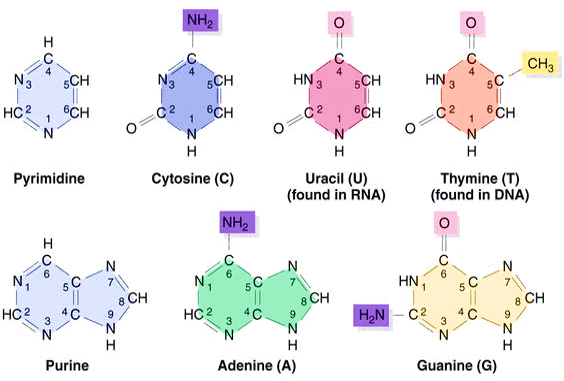
Purine and Pyrimidines : Structure, Synthesis and Metabolism
Purines and Pyrimidines Bases Purines = 2 rings Adenine Guanine Hypoxanthine (Deaminated Adenine) Adenine to Hypoxanthine deamination is mediated by Adenosine deaminase which is decreased in Autosomal recessive SCID. Accumulated dATP inhibit ribonucleotide reductase leading to deficient synthesis of other deoxyribonulceotide precursors for DNA synthesis. Xanthine (Deaminated Guanine) Mnemonics: Pure…