Zero Position
Zero position is the position during elevation in coronal or sagittal plane or in any plane where:
- There is no further rotation, active gliding of joint surfaces and circumduction
- The mechanical axis corresponds to the anatomical axis of the shaft
- Gliding, rotation and “breast-stroke” movements become identical
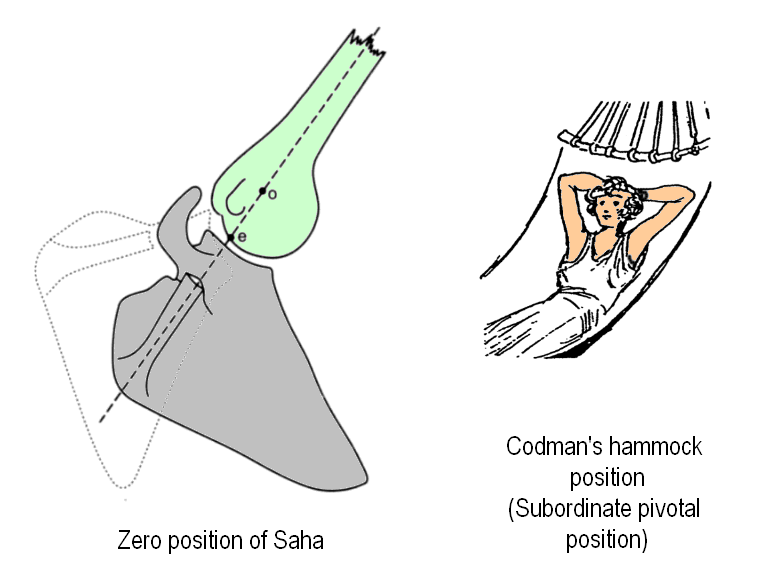
Zero position of shoulder
The humerus is elevated to about 165° with individual variations and is in the newly acquired scapular plane (around 45° anterior to the coronal plane).
The humeral shaft axis roughly is in alignment with the scapular spine in this position.
This is the relative position of scapula and humerus which is seen in fast-moving quadrupeds to give stability to the joint.
Codman’s subordinate pivotal position
Codman’s hammock position and Saha’s zero position concept are not different.
Codman pointed out a position when lying on a hammock with hands clasped behind the head. In this position, the arm is elevated and externally rotated with the clavicle slightly elevated and the shoulder close to maximum elevation.
The deltoid, supraspinatus and infraspinatus all are relaxed, and the humerus aligns with the scapular spine.
In this position, the joint is locked posteriorly as far as dorsal motion is concerned, but lateral motion is still possible if the humerus is rotated.
Clinical uses of Zero position
- Treatment of dislocations
- Treatment of unimpacted abduction fractures of the surgical neck
- Treatment of epiphyseal separations
- Treatment of upper fourth shaft fractures
References:
- SAHA AK. [Zero position of the glenohumeral joint: its recognition and clinical importance]. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 1958 Apr;22(4):223-6. PMID: 13534237; PMCID: PMC2413634.
- The Shoulder – Function and Clinical Aspects (Katsuya Nobuhara)