‘Z-effect’ and ‘Reverse Z-effect’ are complications relating to differential migration of screws that arise from fixation of unstable proximal femoral fractures with Proximal Femoral Nail (PFN) having 2 interlocking head screws. The 4 patterns of unstable intertrochanteric fracture hip are:
- Disrupted calcar femorale/posteromedial cortex
- Reverse oblique: angulated proximal medial to distal lateral
- Transverse trochanteric or transtrochanteric (fracture exits lateral cortex)
- Subtrochanteric extension
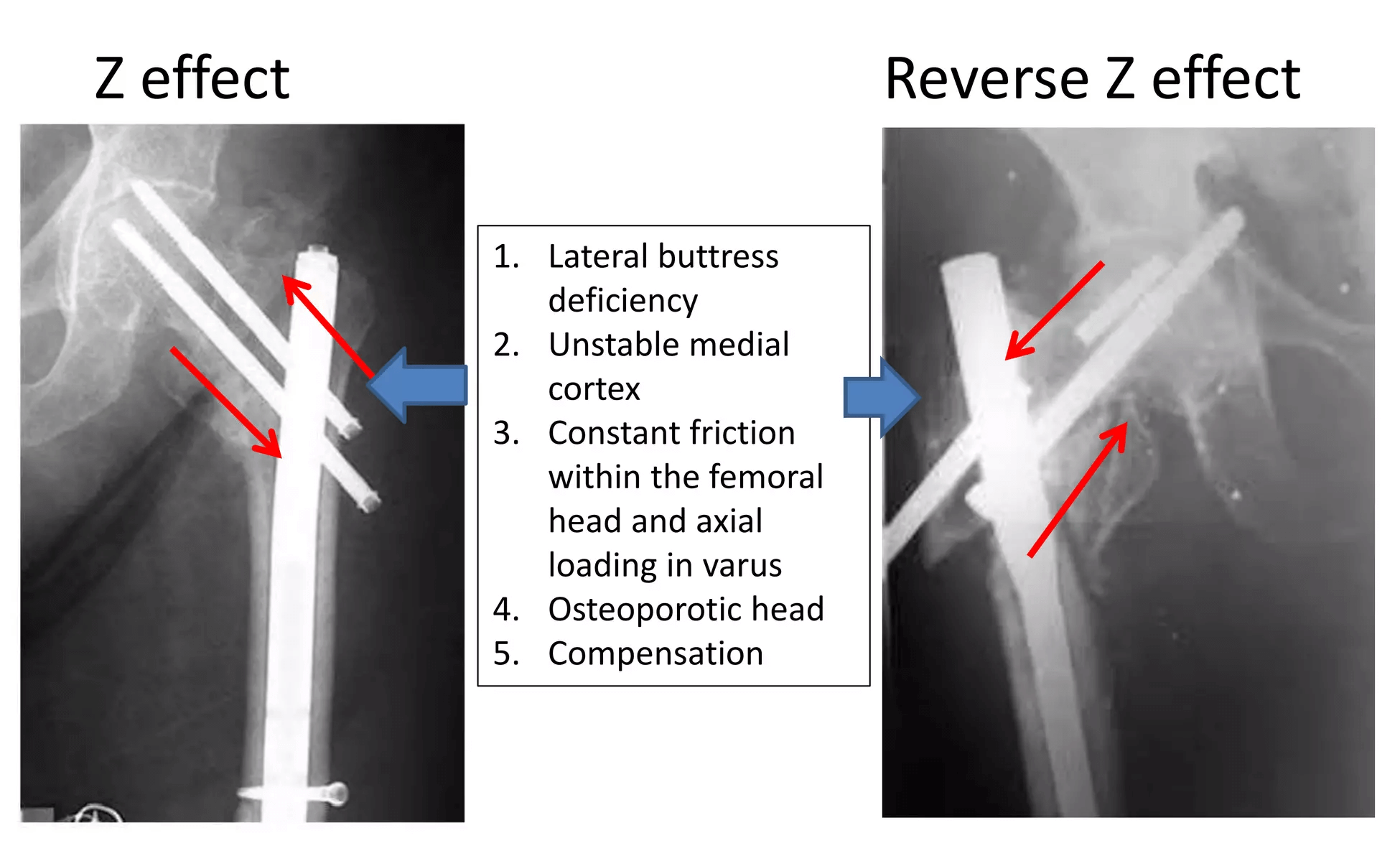
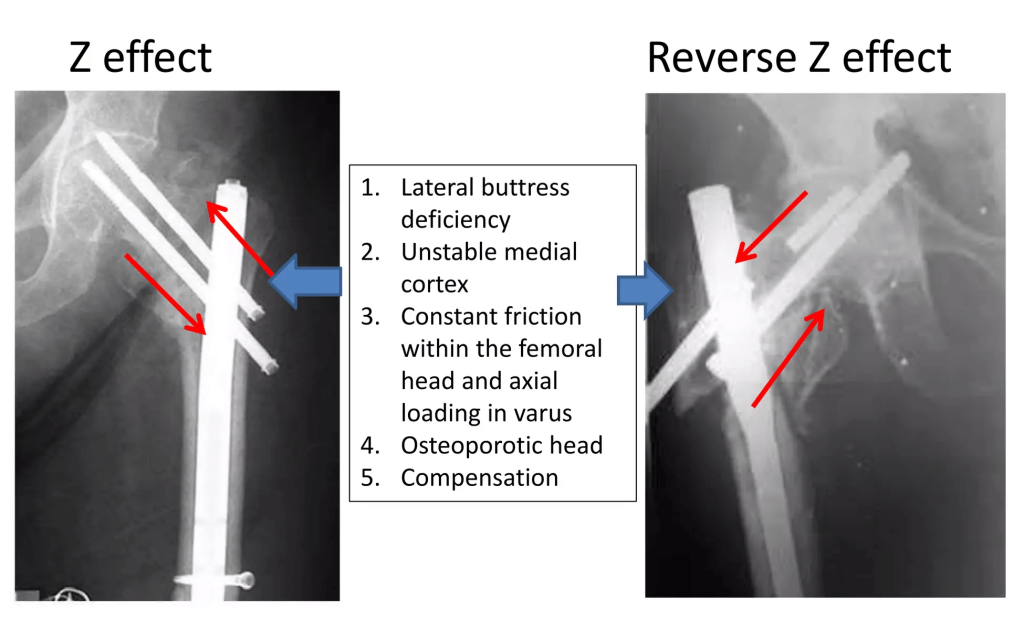
Z-effect: The Z-effect involves the lateral migration of the lag screw, varus collapse and perforation of the femoral head by the superior derotation screw.
Reverse Z-effect: The reverse Z-effect involves the lateral migration of the superior derotation screw accompanied by the medial migration of the lag screw.
In practice, sometimes only one screw actually migrates, and the fracture undergoes an accommodation process that may lead to the perforation of the femoral head by the screw that remains in the normal position.
Possible causes:
1. Strauss EJ, et.al.: Significant medial cortex comminution that are prone to varus collapse (mismatch between the compressive strengths of femoral head and femoral neck)
2. Weil YA, et.al.: Deficient lateral buttress and unstable calcar pattern
3. Poor bone quality
Reference: Siddiqui, Y.S., Khan, A.Q., Asif, N., & Sherwani, M.A. (2019). Modes of failure of proximal femoral nail (PFN) in unstable trochanteric fractures. MOJ Orthopedics & Rheumatology.