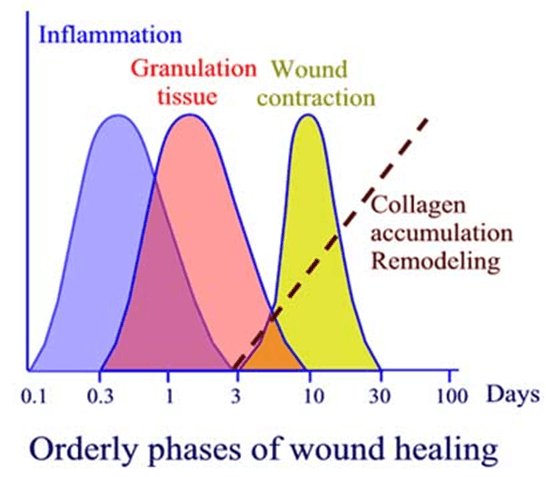
1. Haemostasis (immediate): In response to exposed collagen, platelets aggregate at the wound and degranulate, releasing inflammatory mediators. Clotting and complement cascades activated. Thrombus formation and reactive vasospasm achieve haemostasis.
2. Inflammation (0-3 days): Vasodilatation and increased capillary permeability allow inflammatory cells to enter wound, and cause swelling. Neutrophils amplify inflammatory response by release of cytokines; reduce infection by bacterial killing; and debride damaged tissue. Macrophages follow and secrete cytokines, growth factors, and collagenases. They phagocytose bacteria and dead tissue and orchestrate fibroblast migration, proliferation, and collagen production.
3. Proliferation (3 days-3 weeks): Fibroblasts migrate into the wound and synthesize collagen. Specialized myofibroblasts containing actin cause wound contraction. Angiogenesis is stimulated by hypoxia and cytokines and granulation tissue forms
4. Remodelling (3 weeks-1 year): Re-orientation and maturation of collagen fibres increases wound strength.
Reference: Oxford Handbook of Clinical Surgery
Points to remember:
Maximum collagen production occurs at 20 days
Maximum wound strength at 3 to 6 months