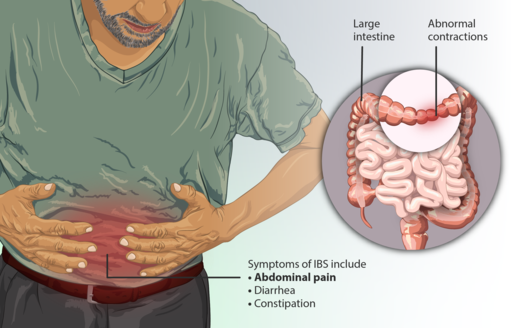
When we look from lateral side, the veins on each side form a “W” shaped arrangement.
Each corner of the “W” is prolonged upward into the scalp, and downward into the neck. Remember the 3 verticla stems of letter “W”:
- 1st stem (in face): Facial vein
- 2nd stem (behind mandible, in front of ear): Retromandibular vein
- 3rd stem (behind ear): Posterior auricular vein
The two diagonal stems branching from the middle stem represents anterior and posterior division of retromandibular vein.
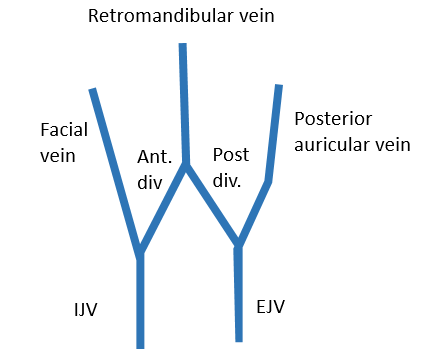
Superficial temporal vein + Maxillary vein = Retromandibular vein
Posterior auricular vein + Posterior division of retromandibular vein = External jugular vein (EJV)
Facial vein + Anterior division of retromandibular vein = Common facial vein (drains in Internal Jugular Vein – IJV)
Deep connection of Facial vein
- Facial vein drains pterygoid plexus (pterygoid venous plexus drains deep veins) via deep facial vein.
- Pterygoid plexus has connection with cavernous sinus through the emissary veins.
How does facial vein communicate with the cavernous sinus ?
Through 3 deep connections:
- Superior ophthalmic vein
- Inferior ophthalmic vein
- Pterygoid plexus
Always remember!!! Facial veins are valveless.