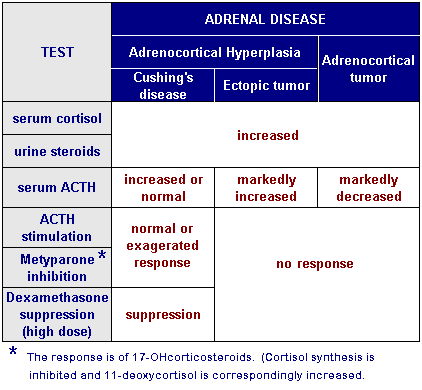
The Dexamethasone Suppression Test (DST) is based on the principle of negative feedback exerted by steroids on pituitary gland’s ACTH secretion.
Negative feedback with exogenous steroid works if the cause is excessive ACTH secretion from pituitary:
1. Cushing’s disease (pituitary ACTH dependent Cushing’s syndrome): Excessive ACTH secretion by pituitary adenoma
2. Depression and stress: Excessive ACTH secretion from pituitary in response to increased hypothalamic CRH
3. Obesity: IGF-1 mediated inhibition of hepatic 11β-HSD1 resulting in decreased peripheral conversion of cortisone to cortisol. Hence, pituitary ACTH secretion is increased due to loss of normal negative feedback.
Negative feedback with exogenous steroid will not work if:
1. ACTH is secreted from a different source in body (Ectopic ACTH secretion)
2. Adrenal tumors autonomously secrete steroids (Primary Cushing syndrome, i.e. ACTH independent)
ACTH:
1. High in ACTH dependent causes (Inferior petrosal sinus ACTH is high if ACTH is produced by pituitary, i.e. Cushing’s disease)
2. Low (due to negative feedback) in ACTH independent (Adrenal) cause.
This much understanding is enough to understand the Dexamethasone suppression test. Let’s interpret the results of DST:
Overnight Dexamethasone Suppression Test:
Dexamethasone is given at 11-12 PM.
- Low dose: 1 mg
- High dose: 8 mg
Plasma cortisol is measuret at 8 AM next morning.
Note: Traditionally, Dexamethasone Suppression Test was performed over 2 days with multiple doses of Dexamethasone. Studying different textbooks may create confusion. Here, we are discussing about the overnight dexamethasone suppression test.
1. Suppressed with low dose DST:
- <2 mcg/dl: Normal
- 2-5 mcg/dl: Obesity, Depression or Stress
2. Suppressed with high dose DST: Plasma cortisol suppresses >50% baseline
- Piuitary cause (Cushing’s disease)
Mnemonic: Suppressed with high dose DST – Higher level problem i.e. pituitary
3. Not suppressed with high dose DST:
- Ectopic ACTH secretion
- Adrenal cause, i.e. ACTH independent (Primary Cushing’s syndrome)
4. To differentiate the cause using ACTH measurement:
Low ACTH (<5 mcg/dl): Adrenal cause
- Next step: Adrenal CT or MRI
High ACTH (>15 mcg/dl): ACTH dependent cause
- Petrosal (IPSS)/Peripheral ACTH >3: Pituitary cause (Cushing’s disease)
- Next step: MRI pituitary
- Petrosal (IPSS)/Peripheral ACTH <3: Ectopic ACTH secretion
- Next step: Octreotide scintigraphy and Chest and upper abdominal CT