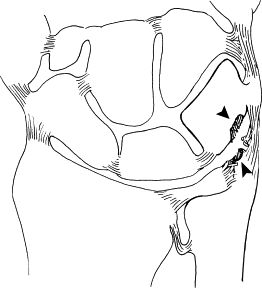
Definition: Impaction of triquetrum against the ulnar styloid causing chondromalacia, synovitis and ulnar-sided wrist pain
Pathology:
- Normal anatomy: Meniscus homologue will be interposed between tip of ulnar styloid and triquetrum
- Ulnar styloid impaction syndrome:
- Early: Soft tissue erosion
- Late: Contact of ulnar styloid tip with triquetrum resulting in degeneration
Etiology:
- Reduced stylo-triquetral distance (bringing styloid to triquetrum or brining triquetrum to ulnar styloid)
- Dynamic styloid prominence based on ligamentous laxity, instability or loading activities
- Combination of both
Clinical features:
1. Asymptomatic
2. Ulnar-sided wrist pain, aggravated by wrist extension and specific positioning (having hands on hip or back pockets)
3. Potential history of trauma to distal radius or ulna, surgery to carpus, generalized ligamentous laxity or other features suggestive of a disturbance to normal wrist mechanics at the lunotriquetral interval
4. Examination:
- Point tenderness over ulnar styloid tip
- Ruby’s ulnar styloid provocation test: This is performed with patient’s elbow resting on the examiner’s table and the forearm initially in neutral rotation. The dorsiflexed wrist is rotated into full supination decreasing the distance between the styloid process and triquetrum and also makes ulnar variance negative (differentiating from ulno-carpal impaction of the ulnar head against lunate). Reproduction of pain with the maneuver is considered as positive provocation.
Diagnosis:
Long ulnar styloid radiographically + Ruby’s ulnar styloid provocation test
Standard PA X-ray:
- Ulnar styloid process >6 mm
- Ulnar styloid process index (USPI) >0.21 ± 0.07
- The USPI is defined as (styloid length − ulnar variance)/width of the ulnar head.
- Ulnar styloid capitate ratio (SCR) >0.18 ± 0.05 (stronger correlation than USPI)
- Degenerative changes including cystic changes in the triquetrum and distal ulna in early stages before degenerative ulnar-sided progression ensues
Dynamic fluoroscopic assessment and 3D CT: used to confirm impingement
MRI (for late stage): focal subchondral sclerosis and chondromalacia of styloid tip as well as proximal triquetral chondromalacia
Treatment:
1. Non-operative:
- Wrist splinting
- Activity modification
- Analgesia +/- Steroid injection
2. Operative:
- Partial ulnar styloid resection (open or arthroscopic) – preserving TFCC attached to the base of styloid
- Co-existing ulnar head impaction: Ulnar shortening procedure