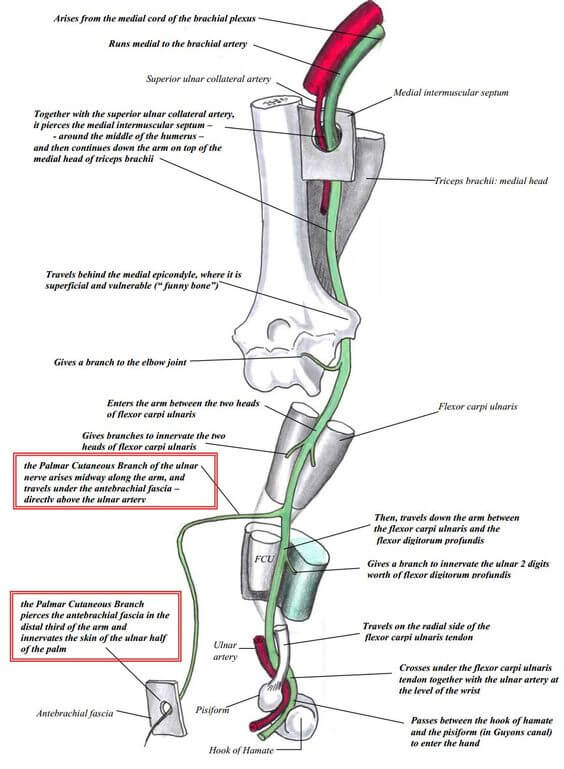
Origin: C(7), C8, T1 (medial cord of Brachial plexus)
Course:
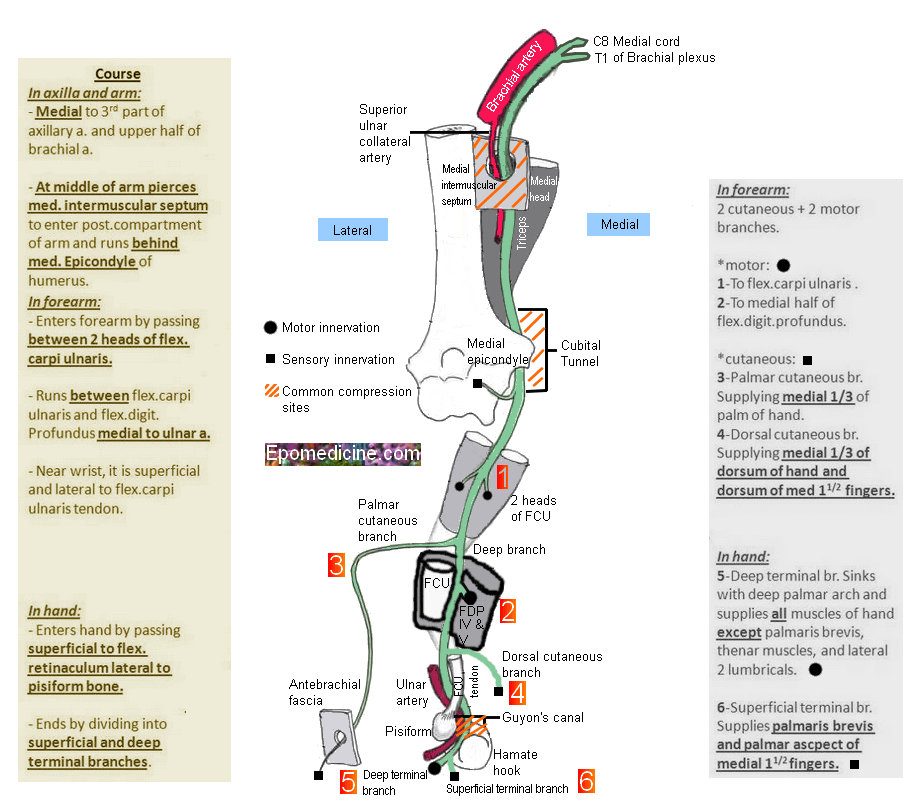
- Axilla: Medial to axillary artery and lateral to axillary vein (between axillary artery and vein)
- Arm: Medial to brachial artery and pierces medial intermuscular septum at mid-upper arm and continues over medial head of triceps (arcade of Struthers in 50%, i.e. arch between medial intermuscular septum and medial head of triceps) – no branch in arm
- Elbow:
- Behind medial epicondyle (postcondylar groove between medial epicondyle and olecranon; anconeus epitrochlearis muscle bridges it in 10% cases)
- Cubital tunnel (1st segment – aponeurosis between tendinous part of 2 heads of FCU that tenses on elbow flexion; thick in 75% i.e. Osborne band and 2nd segment between and under 2 muscular heads of FCU)
- Forearm: Descends between flexor carpi ulnaris and flexor digitorum profundus, medial to ulnar artery; distally no cover (between FCU medially and FDS laterally)
- Dorsal ulnar cutaneous nerve (branches 5-10 cm above wrist crease)
- Palmar ulnar cutaneous nerve (barnches 5-10 cm above wrist crease)
- Wrist: Superficial to Flexor retinaculum and pass through Guyon’s canal (between pisiform and hook of hamate) and bifurcates into deep motor branch and superficial sensory branch on distal part of guyon’s canal
- Hand: Hypothernar muscles, Intrinsics and Digital nerve
Motor innervation:
1. Forearm: Flexor carpi ulnaris (weakness of ulnar deviation and flexion of wrist), Medial half of flexor digitorum profundus (branches near the elbow)
2. Hand: branches near wrist
- Hypothenar muscles: Palmaris brevis, Abductor digiti minimi, Flexor digiti minimi, Opponens digiti minimi (Atrophy of hypothenar eminence)
- Thenar muscles: Adductor pollicis (Froment’s sign or Book test), Deep head of flexor pollicis brevis
- 4 palmar interossei (Card test – loss of adduction of fingers)
- 4 dorsal interossei (Egawa test – loss of abduction of fingers)
- Medial 2 (3rd and 4th) lumbricals (Ulnar claw hand – hyperextension at MCP joint and flexion and IP joint of ring and little fingers)
Sensory innervation: Palmar branch at forearm and Digital branch at wrist (Guyon’s canal)
- Palmar: Hypothenar area and medial 1 and 1/2 fingers
- Dorsal: Medial 2 and 1/2 except tip of middle finger and lateral 1/2 tip of ring finger
Clinical correlation:
1. Ulnar paradox: Ulnar nerve injury at elbow produces less intense clawing than occurs after injury of ulnar nerve at wrist because of the paralysis of FDP to ring and little finger (flexion is brought only by FDS).
2. Entrapment around elbow:
- Arcade of Struthers (fascia extending from medial intermuscular septum to medial head of triceps)
- Medial intermuscular septum
- Exostosis or osteophytes of medial epicondyle
- Cubital tunnel & Osborne’s ligament (fascial band between 2 heads of FCU)
- Anconeus epitrochlearis (accessory muscle)
3. Ulnar tunnel syndrome: Entrapment ulnar neuropathy in Guyon’s canal
- Hypoesthesia in medial 1 and 1/2 fingers, and weakness of intrinsic muscles of hands and clawing of 4th and 5th fingers (ability to flex wrist is unaffected and there is no radial deviation of hand).