Unique features of stomach in relation to TNM cancer classification
1. Cancer penetrates the muscular propria and invades the ligaments (gastrohepatic and gastrocolic, i.e. lesser and greater omentum respectively) subserosally without breeching the serosa. Gastric cancer invasion of the lesser and greater omentum is T3, not T4. Perforation of the visceral peritoneum is required to be T4.
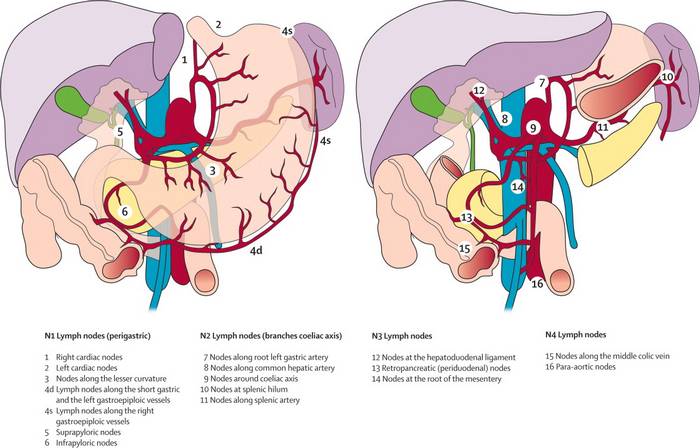
2. In other sites of GI tract, regional lymph nodes are beyond the serosa. But, in stomach the lymph nodes are located within the serosa. It is the only anatomic site in which positive nodes (T1 N1) are still stage I, assigned to IB. In view of the fact that regional lymph node metastasis usually begins in early period of gastric cancer, regional lymph node dissection should be recommended as part of curative resection.
3. Adding subscript numbers to T and N categories together correlates with stage.
4. The nodal categories are unique: N1, 1 to 2 nodes; N2, 3 to 6 nodes; and N3a 7–15 nodes, N3b has × 16 nodes, >15 nodes. In comparison to many digestive system sites where N1 encompasses all nodal categories, the stomach is the most elaborate.
Study Surgical Anatomy of Stomach for better understanding of Gastric Carcinoma.
TNM Classification of Gastric Carcinoma
Primary Tumor (T)
Stomach is a hollow tube, and like in other gastrointestinal tumors – T staging is dependent upon the depth of invasion.
- T1: Mucosal and Submucosal
- a – Mucosal (lamina propria or muscularis mucosae)
- b – Submucosal
- T2: Muscularis propria
- T3: Subserosal without invasion of visceral peritoneum or adjacent structures (can involve gastrohepatic, gastrocolic ligaments and omentum subserosally)
- T4: Serosal or Adjacent structures
- a – Serosa (Visceral peritoneum)
- b – Adjacent structures
Regional Lymph Nodes (N)
N staging is done based on number of involvement of nodes.
- N1: 1-2
- N2: 3-6
- N3: ≥7
- a – 7 to 15
- b – >15
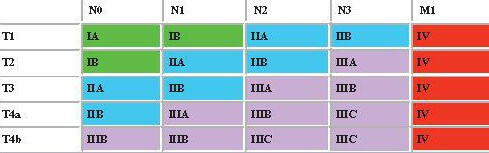
AJCC Staging of Gastric Carcinoma
- M1 is a separate stage = Stage IV
- Both T and N progression determines Stage group I-III
- Subscript addition of T+N determines stage and substage progression; T4a applies to this but T4b is either IIIB or IIIC:
- Stage IA = 1 = T1N0
- Stage IB = 2 = T2No or T1N1
- Stage IIA = 3 = T3N0 or T2N1 or T1N2
- Stage IIB = 4 = T4(a)N0 or T3N1 or T2N2 or T1N3
- Stage IIIA = 5 = T4(a)N1 or T3N2 or T2N3
- Stage IIIB = 6 = T4(a)N2 or T3N3
- T4b +/- N1 = Stage IIIB
- Stage IIIC = 7 = T4(a)N3
- T4b N2/N3 = Stage IIIC