FIGO has published a new classification for ovarian cancer. These new cancer staging rules will be incorporated into the 8th Edition of the UICC TNM Classification of Malignant Tumours, which is thought to be effective from 2017.
Cancer of the ovary has 3 major stages (I, II and III) and each stage is divided into A, B with or without C reflecting the T stage. Stage IV is divided into A and B reflecting M stage.
As the regional lymph nodes for the ovaries are outside the capsule, involvement of nodes correspond to peritoneal invasion by the primary tumor, i.e. T3=N1.
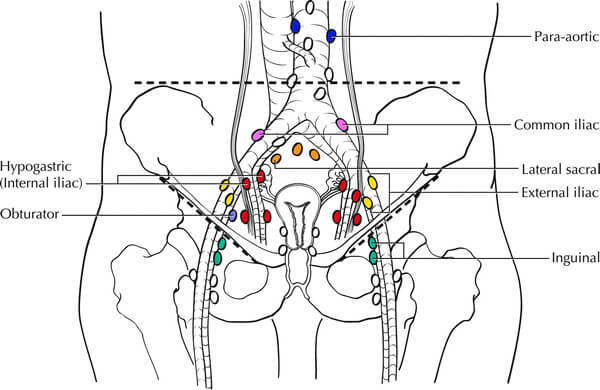
Sentinel nodes: Obturator and Internal Iliac nodes
Regional nodes: Para-aortic, Inguinal, External iliac, Renal hilar (left) and Paracaval (right)
Juxtaregional nodes: Common iliac, hypogastric and lateral sacral nodes
FIGO and TNM Staging
Stage I (T1) – Limited To Ovaries
- A: 1 Ovary (capsule intact) or Fallopian tube
- B: Both ovaries (capsule intact)
- C: Capsule ruptured
- 1 – Surgical spill
- 2 – Capsule ruptured before surgery or tumour on surface of ovary or tube
- 3 – Malignant cells in ascites or peritoneal washings
Stage II (T2) – Pelvic extension below pelvic brim or Primary peritoneal carcinoma
- A: Uterus, fallopian tubes, ovary (ies)
- B: Other pelvic tissues
Stage III (T3 and/or N1) – Beyond Pelvis and/or Lymph nodes
- A: Retroperitoneal nodes only and/or Microscopic peritoneal metastases
- 1 – Retroperitoneal lymph nodes only, i.e. T1/2 N1
- 2 – Microscopic peritoneal metastasis, i.e. T3a
- B: Macroscopic peritoneal metastasis ≤2 cm, i.e. T3b
- C: Peritoneal metastasis >2 cm, i.e. T3c
Stage IV (M1) – Distant Metastases
- A: Pleural effusion positive cytology
- B: Parenchymal metastases
Note:
Implants on liver capsule: Stage III
True liver parenchymal metastases: Stage IV
5 year survival by Stage of Ovarian Cancer
The 5-year survival rate in descending order is:
- 80% for stage I disease
- 50% for stage II disease
- 30% for stage III disease
- 8% for stage IV disease.
Several other factors can affect prognosis such as histologic type, tumor grade, amount of residual disease after surgery, etc.