Subtle differences in the morphology and functions of macrophages develop as a result of the influence of a particular microenvironment. Appearance of macrophages to histologists have been described as a kind of mythological Proteus, “a creature who had the power of changing his appearance at will”. The life-span of these fixed tissue macrophage is 2-4 months.
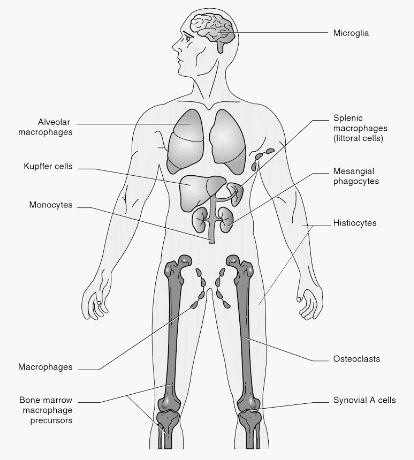
Central nervous system: Microglia, Gitter cells (Microglia after phagocytosis of infectious material and cellular debris)
Connective tissues: Histiocytes
Bone: Osteoclasts
Skin and mucosa: Langerhans cells
Joints: Synovial A cells
Lung: Pulmonary Alveolar Macrophages (PAM), Dust cells, Type II Macrophages
Liver sinusoids: Kupffer cells
Lymph node and red pulp of spleen: Littoral cells
Bone marrow: Reticulum cells
Kidney: Mesangial cells
Placenta: Hofbauer cells (Villous or fetal macrophages)
Peritoneal cavity: Peritoneal macrophages
Intestine: Lamina propria macrophages
Peyer’s patch: LysoMac
Other named macrophages:
- Foam cell: Atherosclerosis & Niemann-Pick disease
- Foamy macrophage: Whipple disease
- Gaucher cell: Gaucher disease
- Heart failure cells (Hemosiderin laden macrophages in lungs): Pulmonary edema
- Anitschkow cells: Rheumatic fever
- Epitheloid/Giant cell: Granuloma
- Warthin-Finkeldey cell: Measles
- Reed-Sternberg cell: Hodgkin’s lymphoma
- Langhan’s giant cell (Horse-shoe pattern): Tuberculosis
- Touton gian cell: Xanthomas, Fat necrosis, Xanthogranulomatous inflammation, Dermatofibroma
References: