Structure
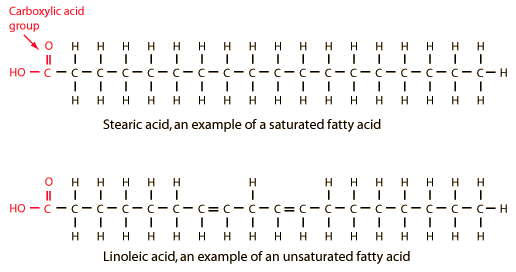
- Saturated fatty acid: Single bond (“S” for saturated and single bond)
- Unsaturated fatty acid: Double bond(s), i.e. “D” for Double bonds, Decreased melting temperature and Decreased atherosclerotic risk (by decreasing LDL)
- Trans-fatty acid: Unsaturated fatty acid which act like saturated fatty acid (hydrogenation of unsaturated fatty acid)
Nomencleture:
C 16:0 = Palmitic acid (16 C with 0 double bonds)
C 18:2 (9,12) = Linoleic acid (18 C with 2 double bonds at 9th and 12th C position)
Omega “x” = Total number of carbon atoms – Farthest double bond from the carboxylic acid side.
C 18:2 (9,12) = Omega 6 (18-12 = 6)
Saturated fatty acids (-ic)
Number of carbon atom increases by 2 in the order of albhabets – LMnoPqrS
L is the 12th letter, hence, has 12 carbon atoms.
- Lauric acid: 12 C
- Myristic acid: 14 C
- Palmitic acid: 16 C
- Stearic acid: 18 C
Unsaturated fatty acids (-eic or -nic)
A. Monounsaturated fatty acid (MUFA):
- C 16:1 (9) = Palmitoleic acid (omega 7)
- C 18:1 (9) = Oleic acid (omega 9)
B. Polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA):
Humans lack the ability to introduce double bonds in fatty acids beyond carbons 9 and 10, as counted from the carboxylic acid side. Hence, they become essential fatty acids:
- Linoleic acid: C 18:2 (9,12) = omega 6 (precurosor of arachidonic acid)
- Maximum in safflower oil
- Alpha – Linolenic acid: C 18:3 (9,12,15) = omega 3 (reduce risk of cardiovascular disease)
- Found in cold water fish, nuts
- Gamma – Linolenic acid: C 18:3 (6, 9, 12) = omega 6
Phospholipids and Glycolipids
- Glycero-phospho-lipids = Glycerol + Phosphate + Fatty acid
- Phosphatidylcholine (Lecithin): cell membrane
- Dipalmitoyl lecithin: surfactant
- Phosphatidyl insoitol: second messengers
- Diphosphatidyl glycerol (Cardiolipin): inner mitochondrial membrane (maintain ETC and antigenic – cross react with antibodies against treponema pallidum)
- Shingo-phospho-lipids = Ceramide (Sphingosine + Fatty acid) + Phosphate, e.g. Sphingomyelin (myelin in nervous tissue)
- Glyco-sphingo-lipids = Ceramide (Sphingosine + Fatty acid) + Carbohydrate, e.g. Cerebrosides, Globosides, Gangliosides
- Neutral:
- Cerebroside (Ceramide + Monosaccharide): In brain and peripheral nerve (Galactocerebroside, Glucocerebroside)
- Globoside (Glucocerebroside + Additional monosaccharide)
- Acidic (negatively charged):
- Gangliosides (Globoside + NANA i.e. N-acetyl neuraminic acid) = Ganglioside (ganglionic cells of CNS, particulary at nerve endings)
- Sulfatides (Galactocerebroside + Sulfate) = Nerve tissue (myelin) and kidney
- Neutral:
- Galacto-lipids = Glycerol + Galactose + Fatty acid
Ceramide is synthesized from Serine amino acid in endoplasmic reticulum.