Organization of Ascending and Descending Tracts in Spinal Cord
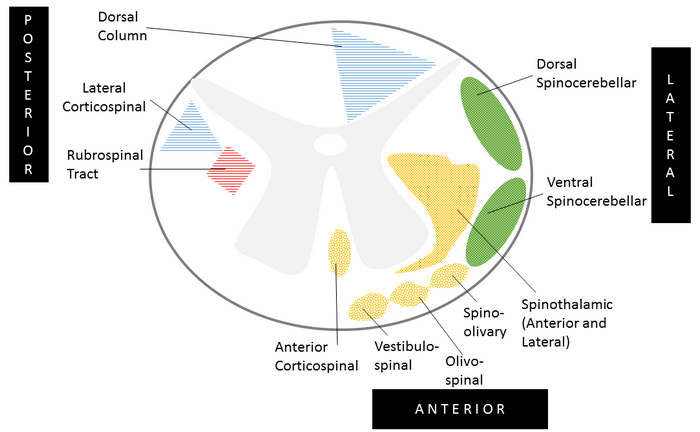
A. 2 Posterior Tracts:
The fibers of these tracts cross to the opposite side at the level of medulla:
- Dorsal column (Cross at medulla)
- Fasciculus gracilis
- Fasciculus cuneatus
- Lateral corticospinal tract (Cross at medulla)
B. 2 Lateral Tracts:
The fibers of these tracts remain on ipsilateral side:
- Dorsal spinocerebellar tract (Do not cross)
- Ventral spinocerebellar tract (Crosses 2 times to lie on ipsilateral side)
- 1st crossing in the spinal cord
- 2nd crossing in the cerebellum
C. 2 Anterior Tracts:
The fibers of these tracts cross at the level of spinal cord:
- Anterior corticospinal tract
- Anterior and Lateral spinothalamic tract
D. Extrapyramidal tracts:
- Rubrospinal tract (Cross at midbrain)
- Vestibulospinal tract: Uncrossed
- Reticulospinal tract: Uncrossed
- Olivospinal tract: Uncrossed
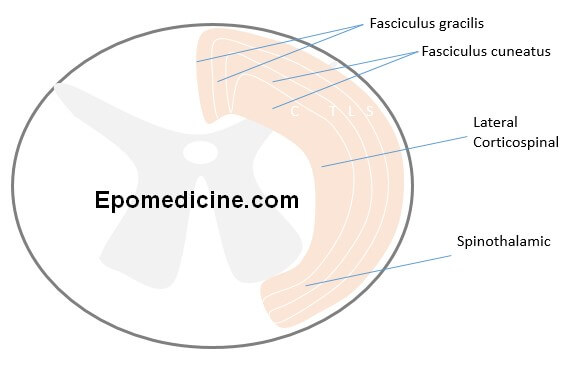
Now, look at the somatotropic arrangement of the various tracts:
- Fasciculus gracilis: lower limbs
- Fasciculus cuneatus: upper limbs
- Corticospinal tract: upper limbs medially and lower limbs laterally
- Spinothalamic tract: upper limbs medially and lower limbs laterally
Ascending tracts:
| Tracts | Function |
| Lateral spinothalamic | Pain, Temperature |
| Anterior spinothalamic | Light (crude) touch |
| Dorsal column | Fine touch, proprioception, 2 point discrimination |
| Spinocerebellar | Movement and position mechanisms |
| Spinotectal | Afferent information for spino-visual reflexes and brings about movement of the eyes and head toward the source of the stimulation |
| Spinoreticular | Deep and chronic pain |
| Spino-olivary | Conveys information to the cerebellum from cutaneous and proprioceptive organs |
Descending tracts:
| Tracts | Functions |
| Lateral corticospinal | Fine motor (controls distal musculature) Modulation of sensory functions |
| Anterior corticospinal | Gross and postural motor function (proximal & axial musculature) |
| Rubrospinal | Motor function Facilitates the activity of flexor muscles and inhibits the activity of extensor or antigravity muscles |
| Vestibulospinal | Postural reflexes Facilitates the activity of extensor muscles and inhibits the activity of flexor muscles in association with the maintenance of balance |
| Reticulospinal | Modulation of sensory transmission Modulation of spinal reflexes Influence voluntary movements and reflex activity |
| Tectospinal | Reflex head turning Concerned with reflex postural movements in response to visual stimuli |
| Descending autonomic | Modulation of autonomic functions Controls sympathetic and parasympathetic functions |
| Medial longitudinal fasciculus | Coordination of head & eye movements |