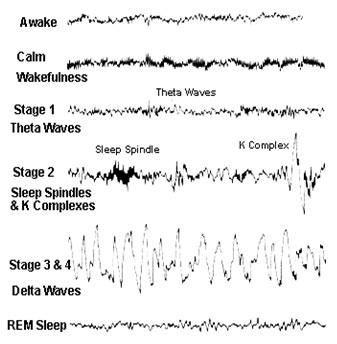
Mnemonic: BATS Drink Blood – in sleep
1. Awake with eyes open: Beta wave (highest frequency and lowest amplitude)
2. Awake with eyes closed: Alpha wave (synchronized brain activity)
3. NREM/Slow wave/Orthodox sleep (70-80%):
- Stage 1 (light sleep): Theta waves
- Stage 2 (intermediate): Sleep spindles and K-complex
- Stage 3 and 4 (deep sleep): Delta waves (lowest frequency and highest amplitude)
4. REM/Paradoxical sleep (20-30%): Beta waves
Order in which frequency decreases and amplitude increases: BAT Drink
- Beta wave: >14 Hz, low amplitude
- Alpha wave: 8-13 Hz, high amplitude
- Theta wave: 4-7 Hz, high amplitude
- Delta wave: 3-5 Hz, maximum amplitude