Proximal humerus
Insertion of Rotato Cuffs
Mnemonic: SIT-S
a. Greater tubercle: Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Teres minor
b. Lesser tubercle: Subscapularis
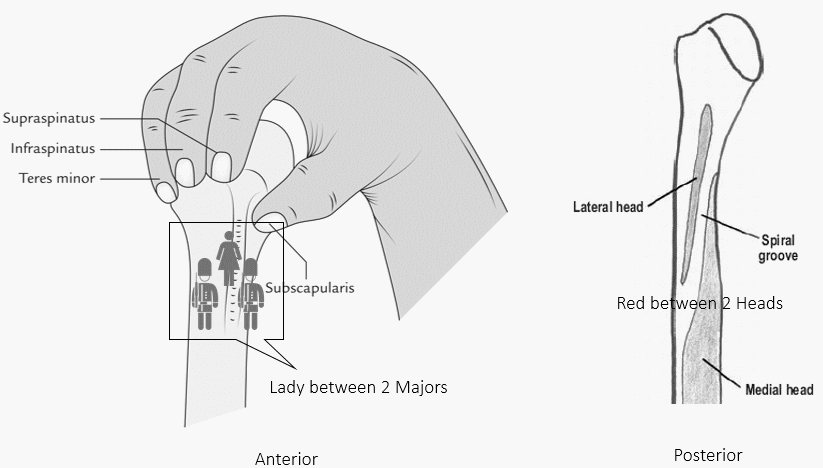
Attachment of Other muscles
Anteriorly and posteriorly the muscles attach on each side of the depressions (groove and sulcus).
a. Anteriorly: Insertion of 3 muscles
Mnemonic: Lady between 2 Majors
- Crest of greater tubercle: Pectoralis major
- Intertubercular sulcus or Bicipital groove (between greater and lesser tubercle): Lattisimus dorsi (Tendon of long head of biceps passes through this grrove)
- Crest of lesser tubercle: Teres major
b. Posteriorly: Origin of 2 muscles
Mnemonic: Red between 2 Heads
- Radial groove: Radial nerve
- Superior to radial groove: Lateral head of triceps
- Inferior to radial groove: Medial head of triceps
c. On Proximal Shaft:
Mnemonic: CD
- Medial side: Coracobrachialis
- Lateral side: Deltoid
Scapula
a. Medial border: Insertion of 3 muscles
Mnemonic: SLR – all supplied by nerves from ROOT of brachial plexus
- Anteriorly: Serratus anterior (Long thoracic nerve)
- Posteriorly:
- Superiorly: Levator scapulae (Dorsal scapular nerve)
- Inferiorly: Rhomboids – minor superior to major (Dorsal scapular nerve)
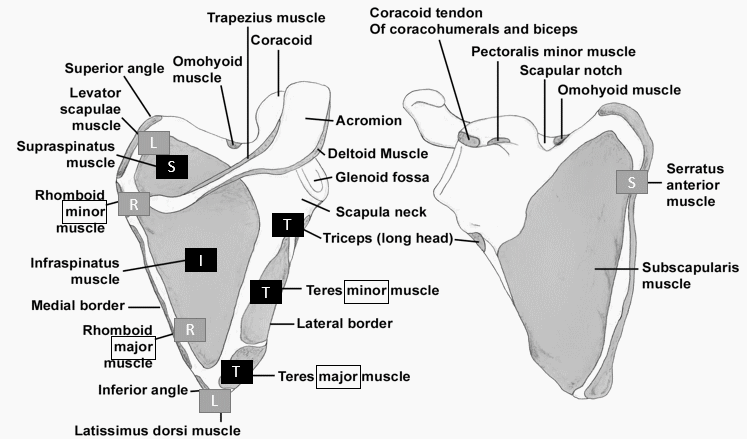
b. Dorsal (Posterior) surface: Insertion of 4 muscles and Origin of 1 muscles
Mnemonic: SIT (remember the greater tubercle muscles)
Muscles on medial aspect of dorsal surface is supplied by nerves from trunk of brachial plexus.
- Above spine of scapula (supraspinous fossa): Supraspinatus (Suprascapular nerve)
- Below spine of scapula (infraspinous fossa): Infraspinatus (Suprascapular nerve)
- On lateral border: 3 Ts
- Teres minor
- Below Teres minor: Teres major (minor superior to major)
- Above Teres minor (Infraglenoid tubercle): Origin of Triceps long head
Lattisimus dorsi also originates on inferior angle of scapula dorsally.
c. Anterior (Ventral) surface: Subscapular fossa (Subscapularis)
d. Around Glenoid fossa: 2 long heads
- Supraglenoid tubercle: Long head of biceps
- Infraglenoid tubercle: Long head of tricpes
e. Coracoid process:
- Tip: Coracobrachialis, Biceps short head
- Superior surface: Pectoralis minor
f. Spine of scapula and Acromion:
- Upper lip of spine of scapula and medial margin of acromion: Trapezius insertion
- Inferior lip of spine of scapula and lateral margin of acromion: Deltoid origin
Clavicle
Acromion continues with lateral clavicle through acromioclavicular joint. Spine of scapula, Acromion and Clavicle forms an arc.
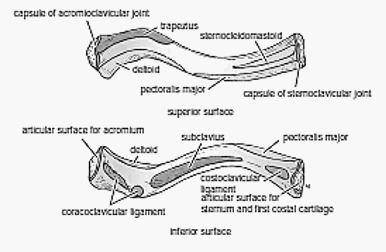
a. Lateral 1/3 of clavicle:
- Anterior border: Deltoid origin
- Posterior border: Trapezius insertion
b. Medial 1/3 of clavicle:
- Anterior surface: Pectoralis major
- Superior surface: Sternocleidomastoid
- Inferior surface: Subclavius
| Muscle | Origin | Insertion | Action | Innervation |
| Trapezius | a. Superior: Occipital protuberance, nuchal line, ligamentum nuchae b. Middle: Spinous process of T1-T5 c. Inferior: Spinous process of T6-T12 | a. Lateral calvicle b and c. Acromion and spine of scapula | a. Elevates scapula + Upward rotation of glenoid b. Retracts (adducts) scapula c. Depress scapula + Upward rotation of glenoid | Cranial nerve XI; C2-C4 |
| Levator scapulae | Transverse process of C1-C4 | Superior medial scapula | Elevates and adducts scapula | Dorsal scapular nerve; C3-C5 |
| Rhomboids | Ligamentum nuchae and spinous process of C7-T5 | Medial scapular border | Retracts scapula | Dorsal scapular nerve; C4-C5 |
| Latissimus dorsi | a. Superficial: Spinous process of T7-T12 (beginning from level of inferior angle of scapula) b. Iliac: Posterior 1/3 of iliac crest c. Costal: Ribs 9-12 d. Scapular: Inferior angle of scapula | Biccipital groove | Arm internal rotation, adduction and extension | Thoracodorsal nerve; C6-C8 |
| Serratus anterior | Ribs 1-8 | Anterior medial scapula | Protracts and Upwardly rotates scapula | Long thoracic nerve; C5-C8 |
| Deltoid | a. Clavicular: Lateral 1/3 clavicle b. Acromial: Acromion c. Spinal: Spine of scapula | Deltoid tuberosity of humerus | a. Flexion and internal rotation of arm b. Abduction of arm from 15-90 degrees c. Extension and external rotation of arm | Axillary nerve; C5-C6 |
| Pectoralis major | a. Clavicular head: Anterior medial clavicle b. Sternocostal head: Lateral border of sternum, Superior 6 costal cartilages, Fascia of external oblique muscle | Crest of greater tubercle | Arm adduction and internal rotation | Lateral and medial pectoral nerves; C5-T1 |
| Pectoralis minor | Just lateral to costal cartilage of ribs 3-5 | Coracoid process | Medial pectoral nerve; C8, T1 | Stabilizes scapula |
| Supraspinatus | Supraspinous fossa of scapula | Greater tubercle of humerus | Assists deltoid and initiates arm abduction | Suprascapular nerve; C4-C6 |
| Infraspinatus | Infraspinous fossa of scapula | Greater tubercle of humerus | Arm external rotation | Suprascapular nerve; C5-C6 |
| Teres minor | Lateral border of scapula | Greater tubercle of humerus | Arm external rotation | Axillary nerve; C5-C6 |
| Subscapularis | Subscapular fossa | Lesser tubercle of humerus | Arm internal rotation | Upper and lower subscapular nerves; C5-C6 |
| Teres major | Inferior angle of scapula | Crest of lesser tubercle | Arm internal rotation and adduction | Lower subscapular nerve; C5-C6 |
Internal rotators of arm are supplied by nerves from the CORDS of the brachial plexus.
a. Pectoralis major: Lateral and medial pectoral nerves (from lateral and medial cords)
b. Latissimus dorsi: Thoracodorsal nerve (from posterior cord)
c. Teres major: Lower subscapular nerve (from posterior cord)
d. Subscapularis: Upper and lower subscapular nerve (from posterior cord)
Learn the Anatomy of Brachial Plexus: https://epomedicine.com/medical-students/brachial-plexus-simplified/
Shoulder Muscles by Action
a. Forward flexion: Deltoid (anterior fibers), Pectoralis major (clavicular fibers), Coracobrachialis, Biceps
b. Extension: Deltoid (posterior fibers), Teres major, Teres minor, Latissimus dorsi, Pectoralis major (sternocostal fibers), Triceps (long head)
c. Horizontal adduction: Pectoralis major, Deltoid (anterior fibers)
d. Horizontal abduction: Deltoid (posterior fibers), Teres major, Teres minor, Infraspinatus
e. Abduction: Deltoid, Supraspinatus, Infraspinatus, Subscapularis, Teres minor, Long head of biceps (if arm laterally rotated first – trick movement)
f. Adduction: Pectoralis major, Latissimus dorsi, Teres major, Subscapularis
g. Internal rotation: Pectoralis major, Deltoid (anterior fibers), Latissimus dorsi, Teres major, Subscapularis
h. External rotation: Infraspinatus, Deltoid (posterior fibers), Teres minor
i. Elevation of scapula: Trapezius (upper fibers), Levator scapulae, Rhomboids (major and minor)
j. Depression of scapula: Serratus anterior, Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor, Latissimus dorsi, Trapezius (lower fibers)
k. Protraction (forward movement) of scapula: Serratus anterior, Pectoralis major, Pectoralis minor, Latissimus dorsi
l. Retraction (backward movement) of scapula: Trapezius, Rhomboid major, Rhomboid minor
m. Scapular upward rotation: Trapezius (upper fibers), Serratus anterior
n. Scapular downward rotation: Levator scapulae, Rhomboids, Pectoralis minor
Important Muscular Spaces of Shoulder
The 3 important spaces – triangular space, quadrangular space and triangular interval exists between the 3 “T” muscles attaching on lateral border of dorsal scapula and the humerus.
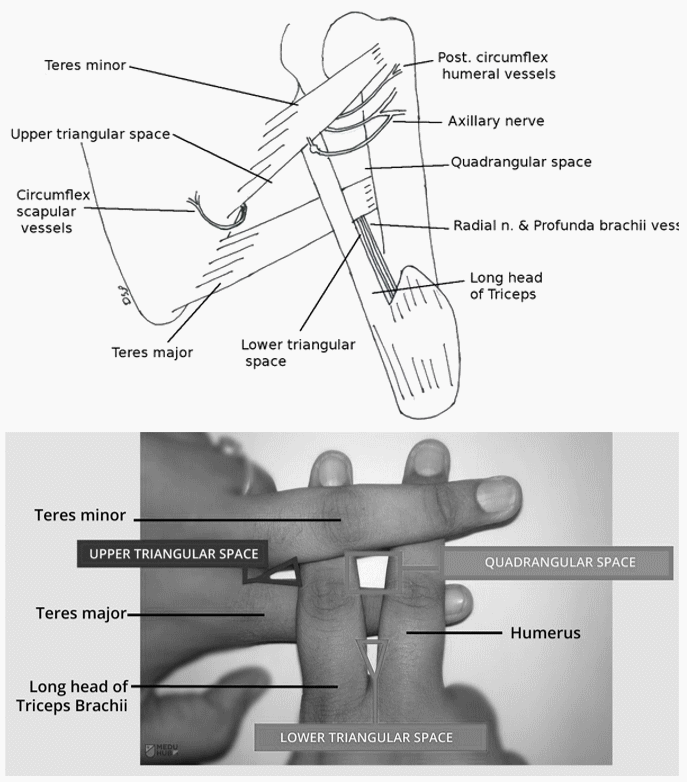
Mnemonic: Interlock the 2 fingers of both hands as shown in the fingure above. 2 fingers oriented upwards represent Humerus and Triceps long head. 2 fingers oriented laterally represent Teres minor and Teres major. Remember that all these 3 muscles attach on the lateral border of dorsal scapula. Also remember ‘minor superior to major’.
a. Quadrangular space:
- Borders
- medial: long head of triceps
- lateral: humeral shaft
- superior: teres minor
- inferior: teres major
- Contents
- posterior humeral circumflex artery
b. Triagnular space:
- Borders
- inferior: teres major
- lateral: long head of triceps
- superior: lower border of teres minor
- Contents
- scapular circumflex artery
c. Triagnular interval (Lower triangular space):