In children, the growth plate (physis) is a zone of cartilate situated between the epiphysis and the metaphysis of long bones. Cartilage is weaker than bone and thus is a common site of fracture.
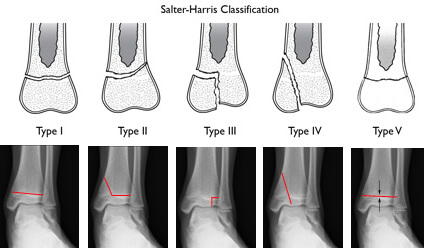
The Salter-Harris classification consists of 5 different types of growth plate fractures based on the location of the injury. In general, the higher the number, the worse the prognosis.
Mnemonic: SALTeR
- Slipped or Straight through
- Above
- Low
- Through everything
- Rammed
Epiphyseal plate is always involved as it is a classification for physeal fracture.
Salter Type I fractures (Slipped or Straight through): fracture plane passes through the growth plate without involving the bones
Salter Type II fractures (Above): commonest; metaphysis + epiphyseal plate; thurston-holland sign or corner sign (metaphyseal chip)
Salter Type III fractures (Low): epiphyseal plate + epiphysis
Salter Type IV fractures (Through everything): Metaphysis + Epiphyseal plate + Epiphysis
Salter Type V fractures (Rammed): Crush injuries to the epiphyseal plate; rarest; often missed diagnosis; most common in the knee and ankle.
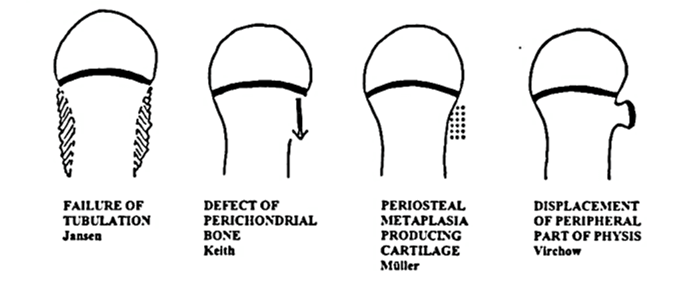
Rang and Ogden Additions:
- Type VI: Perichondral ring injury
- Type VII: Epiphysis & Articular cartilage injury (Osteochondritis Dissecans)
- Type VIII: Metaphyseal injury
- Type IX: Periosteum injury
There exist also complex multiplanar injuries of the physis, epiphysis and metaphysis, not categorized by Salter and Harris. Triplane fracture in ankle is an example.