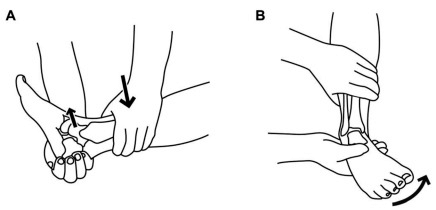
Anterior Drawer Test
Assesses: Anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL)
Position: Knee joint in flexion and ankle in 10-15 degrees plantar flexion
Maneuver: The examiner exerts a downward force on the tibia while simultaneously attempting to “lift up” the foot while grasping behind the heel.
Interpretation: A significant difference from the unaffected side (>2 mm) or dimpling of the anterior skin (suction or dimple sign) is considered positive.
Source: Polzer H, Kanz KG, Prall WC, Haasters F, Ockert B, Mutschler W, Grote S. Diagnosis and treatment of acute ankle injuries: development of an evidence-based algorithm. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2012 Jan 2;4(1):e5. doi: 10.4081/or.2012.e5. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PMID: 22577506; PMCID: PMC3348693. (CC BY-NC 3.0)
Talat Tilt Test
The patient is positioned in sitting or supine lying with the knee in full extension. The examiner stabilizes the distal leg with one hand while the other hand holds the heel with the ankle:
a. Assess Anterior talofibular ligament: Plantar flexion – inversion
b. Assess Calcaeno-fibular ligament: Neutral position – inversion
c. Assess Posterior talofibular ligament: Dorsiflexion – inversion
d. Assess Deltoid ligament: Plantar flexion – eversion
e. Assess Syndesmotic (high ankle) sprain: Dorsiflexion – eversion
The lateral ankle ligaments consist of:
1. Anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL)
2. Calcaneofibular ligament (CTFL)
3. Posterior talofibular ligament (PTFL)
Involvement in sprains: ATFL > CFL > PTFL
CFL is the only extra-capsular ligament among these 3.
Grading or Classification of Lateral ankle sprains:
| Grade | Hematoma/swelling/tenderness | Anterior drawer test | Talar tilt test | Anatomic lesion | Stability | Treatment |
| 1 | Positive | Negative | Negative | Incomplete tear of ATFL | Stable | PRICE, NSAID, Early weight bearing and Exercise for range of motion |
| 2 | Positive | Positive | Negative | Complete tear of ATFL Incomplete tear of CFL | Unstable | Semirigid ankle brace and Supervised rehabilitation; Surgery for chronic instability |
| 3 | Positive | Positive | Positive | Complete tear of ATFL Complete tear of CFL | Unstable | Same as for grade 2 |
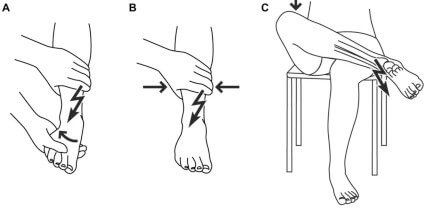
Tests for Ankle syndesmosis
Source: Polzer H, Kanz KG, Prall WC, Haasters F, Ockert B, Mutschler W, Grote S. Diagnosis and treatment of acute ankle injuries: development of an evidence-based algorithm. Orthop Rev (Pavia). 2012 Jan 2;4(1):e5. doi: 10.4081/or.2012.e5. Epub 2011 Dec 14. PMID: 22577506; PMCID: PMC3348693. (CC BY-NC 3.0)
Ankle syndesmosis consists of 4 ligaments:
1. Anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL)
2. Posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL)
3. Interosseous ligament (IOL)
4. Deltoid ligament
The 3 ligaments other than deltoid ligament is often referred to as lateral ligament.
Interpretation: Positive if pain is reproduced in the area of syndesmosis
Maneuvers:
- External rotation test: Tibia is fixed with one hand and external rotation stress is applied to ankle with other
- Squeeze test: Tibia and fibular are squeezed above the midpoint of calf
- Crossed leg test: The patient is seated and the tested leg is crossed at the junction of middle and distal 3rd (pivot point) upon the non-injured knee and a downward force is applied by the patient or examiner on the medial aspect of the knee on the tested side
Grading of syndesmotic injuries:
| Grade | Clinical | X-ray | Anatomic lesion | Stability | Management |
| 1 | Pain upon palpation of AITFL | Normal | Incomplete tear of lateral ligaments | Stable | Non-operative |
| 2 | + Positive external rotation and squeeze test | Normal | Complete tear of AITFL and IOL | Stable/Unstable | Non-operative/Operative |
| 3 | All tests positive | >2mm medial clear space widening and/or widened syndesmosis | Complete injury to lateral ligaments (AITFL, IOL, PITFL) and deltoid ligament avulsion | Unstable | Operative |
Thank you for this detailed overview of ligament tests for ankle injuries! I found the explanations quite helpful, especially the visual aids that accompany the descriptions of each test. It’s great to have a comprehensive resource like this for understanding ankle injuries better. Looking forward to more posts on related topics!