A pressure injury is localized damage to the skin and underlying soft tissue usually over a bony prominence or related to a medical or other device.
Normal capillary refill is 16-33 mmHg.
Ischemia occurs with prolonged pressure >33 mmHg:
- Ischial tuberosity: >100 mmHg during sitting
- Sacral region: 40-60 mmHg in supine
- Trochanteric region: 70-80 mmHg in lateral position
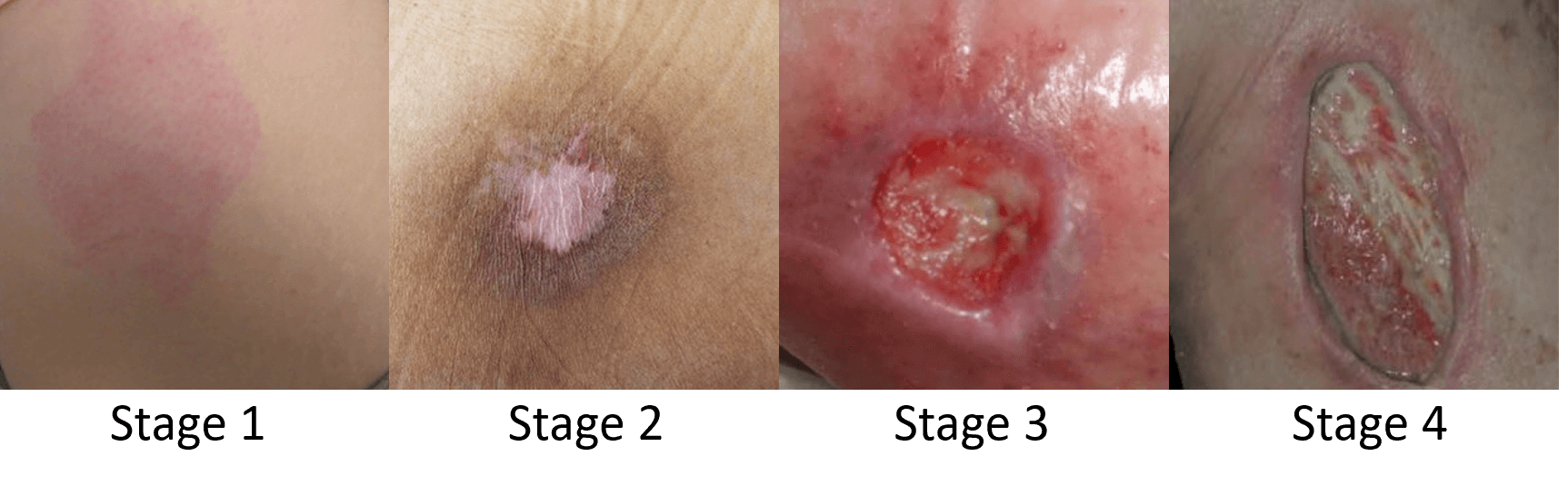
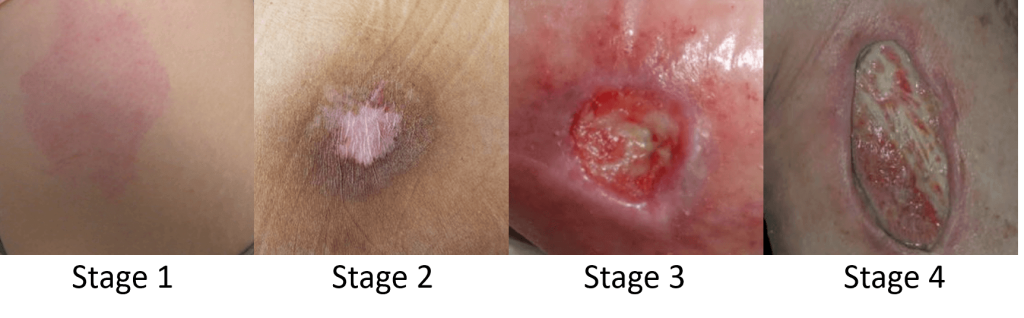
NPIAP Classification or Staging
| Grade | Description | Management |
| I | Non-blanchable redness | Protective dressing |
| II | Partial thickness loss of skin | Moist dressing; cleanse the wound |
| III | Full thickness skin loss – fat visible | |
| – No necrotic tissue | Moist to absorbent dressing Cleanse the wound | |
| – Necrotic tissue | Debridement (sharp if advancing cellulitis or autolytic/enzymatic/mechanical if non-urgent) Then, moist to absorbent dressing; cleanse the wound | |
| IV | Full thickness skin loss – bone, tendon, muscle visible | |
| – No necrotic tissue | Moist to absorbent dressing Cleanse the wound | |
| – Necrotic tissue | Debridement (sharp if advancing cellulitis or autolytic/enzymatic/mechanical if non-urgent) Then, moist to absorbent dressing; cleanse the wound |
Use topical antibiotics for local infection.
Patients who are at risk of pressure/bed sores
Mnemonic: Pressure Sores Are Not Much Fun
- Position change: restricted
- Sensation: impaired
- Activity: bedridden or chairbound
- Nutrition: poor
- Moisture: incontinence
- Friction shear: difficult transfers due to contractures/spasticity
Patients meeting 3 or more of the above requires intervention for bed sore prevention.
Reference: Maffeo, R. (1998). Clinical Notebook A quick mnemonic for predicting pressure sores in ED patients. Journal of Emergency Nursing, 24(5), 418–419. doi:10.1016/s0099-1767(98)70009-1
Pressure/Bed sore Prevention
Mnemonic: NO ULCERS
- Nutrition and fluid status
- Observation of skin
- Up and walking or assist with position changes
- Lift, don’t drag
- Clean skin and continence area
- Elevate heels
- Risk assessment
- Support surfaces