Origin
Type II alveolar cells/pneumocytes (small but numerous) and Lamellar bodies (appear in Type II pneumocytes at around the 20th week of gestation)
Type I alveolar cells (large and covers 95% alveoli) are squamous cells and involved in gas exchange process.
Recycling
- 90% is reprocessed (through endocytosis); average time for turnover is around 10 hours.
- CPAP can prevent excessive loss of surfactant drainage into airways by decreasing depth and length of respiration.
Composition
- Phophatidylcholine (70-80%) and phosphatidylglycerol (5-10%)
- Phosphatidylinositol, Phosphatidylserine,Phosphatidylethalomine (10%)
- Other lipids (10%); 2% surfactant lipids
- Surfactant Proteins- SP-A, SP-B, SP-C, SP-D (5-10%)
Functions
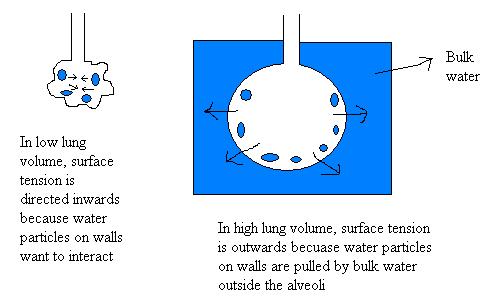
Law of Laplace (P = 2γ/r) states that the pressure difference between the inside and the outside of an elastic sphere (“Laplace pressure or transmural pressure”) is inversely proportional to the radius. Here, γ represents the surface tension.
Surfactant lowers the surface tension by interspersing between the water molecules lining the alveoli. It lowers the surface tension of smaller alveoli more than that of large alveoli. This prevents the smaller alveoli from collapsing and emptying their air contents into the larger alveoli.
In the absence of surfactant, to expand the alveoli, the transpulmonary pressure will have to be increased to -28 cm H2O, and this would lead to a net pressure gradient acting outwards. However, since surfactant reduces the surface tension and thus reduces the required transpulmonary pressure, the net pressure gradient acts inwards maintaining the alveolar interstitium relatively dry.
Factors Affecting Surfactant maturation
1. Glucocorticoids: Intrinsic cortisol accelerates surfactant maturation. Dexamethasone administered increases expression of beta-adrenergic receptors with resultant increase in surfactant production.
2. Beta- adrenergic Drugs: Terbutalline and Formeterol increase cAMP and increase production and secretion of Surfactant.
3. Thyroid Hormones: T4 has enhancing property on lung maturation and surfactant secretion however, it does not cross placenta.
4. Prolactin: It is under study. However low prolactin has been seen in infants with RDS.
5. Epidermal growth factor: Has shown to increase SP-A and L:S ratio in non-human models.
6. Fibroblast pneumocyte factor: under study
7. Insulin: delays the maturation of alveolar type II cells and decrease the production of saturated Phosphatidylcholine. It inhibits the expression of SP-A gene.
8. Testosterone: delays the lung maturation through its action on lung fibroblast.
Errors of Surfactant Metabolism
1. Polymorphism of SP-A expression: predisposition to sever RSV infection and increase risk for BPD.
2. SP-B polymorhism: RDS
3. SP-C deficiency: Interstitial Lung disease
4. SP-D deficiency: Alveolar accumulation of lipids and proteins.