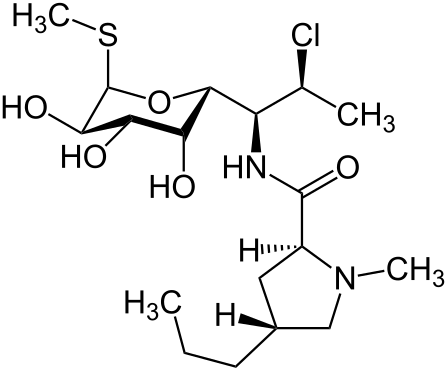
Class: Lincosamide
Mechanism of action: Binds 50S subunit of ribosome and inhibits translation – bacteriostatic (Remember the mnemonic: buy AT 30 & CELLS at 50)
Spectrum: Gram positive and Anaerobes
Mnemonic: PAST
- Penicillinase producing Staphylococci
- Anaerobes (Bacteroides, Clostridium, Fusobacterium)
- Streptococci (Viridans, Pyogenes, Pneumoniae)
- Toxoplasma
Uses:
Mnemonic: PAST
- Peritonitis, Pelvic abscess, Prophylaxis in dentistry
- Aspiration pneumonia, Acne, Anaerobic infections
- Septic abortion, Staphylococcus aureus infection (musculoskeletal infections)
- Toxoplasmosis
Adverse effects:
Mnemonic: PAST
- Pseudomembranous colitis
- Abdominal pain
- Skin (rashes, urticaria), Skeletal muscle paralysis (high dose and long-term use)
- Toxic megacolon