ADME is the 4-letter acronym used to describe pharmacokinetics:
- Absorption – Entering the body
- Distribution – Moving about the body
- Metabolism – Changing within the body
- Excretion – Leaving the body
ABCD is another 4-letter acronym used to describe pharmacokinetics:
- Administration – factor related to dosing and adherence
- Bioavailability – fraction of administered drug reaching systemic circulation
- Clearance – volume of plasma cleared of drug per unit time (active drug leaving the systemic circulation)
- Distribution – to the site(s) of action
The most important pharmacokinetic parameters from a dosing point of view are:
- The clearance (CL) – determines the maintenance dose-rate
- The volume of distribution (Vd) – determines the loading dose (LD)
- The half-life (t½) – determines the time to steady state and the dosing interval
Vd = Volume of distribution
D = Dose
Co = Concentration in plasma
CL = Clearance
kE = Elimination constant
t1/2 = Half life
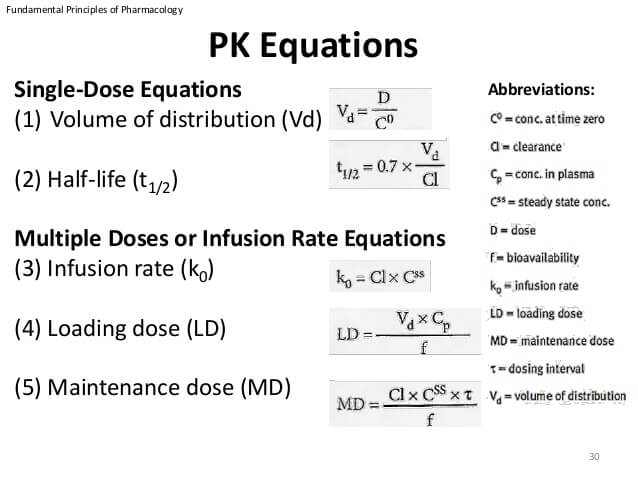
In the mnemonics below, equations can be created by inserting “=” after the 1st word and “/” before the last word.
Mnemonic: ViDeo = DOwnloader/CONverter
Vd = D/Co
Also, Loading dose = Vd X Concentration targeted
E.g. To achieve a target Cp of 1.5 µg/L for digoxin (Vd = 500 L) –
LD (µg) = 500 (L) X 1.5 (µg/L) = 750 µg
Mnemonic: ViDeo = CLear/KlEar
Vd = CL/kE
E.g. A 2,000 mg dose with a concentration of 600 mg/L has a clearance of 0.05 L/hr. What is the elimination rate constant (KE)?
Vd = CL/kE = 0.05/kE
Also, Vd = D/Co = 2000/600
i.e. 0.05/kE = 2000/600
kE = 0.05 X 600/2000 = 0.015 hr
| Vd | Compartment | Drug types |
| Low | Intravascular | Large/charged molecules; plasma protein bound |
| Medium | ECF | Small hydrophilic molecules |
| High | All tissues including fat | Small lipophilic molecules, especially if bound to tissue protein |
Mnemonic: HalfLife = Learnt To make ViDeo CLear
A very common assumption is that it takes about 5.5 half lives to completely clear a drug from the body. Steady state is a dynamic equilibrium in which drug concentration stays constant (ie, rate of drug
elimination = rate of drug administration).
t1/2 = ln(2) Vd/CL = 0.7 Vd/CL
E.g. In the above case, if we need to calculate t1/2 –
t1/2 = 0.7 X Vd/CL or 0.7/kE = 0.7/0.015 = 46.7 hr
Maintenance dose calculation:
Clearance of theophylline is 2.8 L/hr and Target concentration is 10 mg/L. What is the TDS maintenance dose?
Dosing rate = CL X Target concentration = 2.8 X 10 = 28 mg/hr
Maintenance dose = Dosing rate X Dosing interval = 28 X 8 = 224 mg
If the bio-availability is <1, divide by bioavailability (F). Suppose, if the bioavailability of theophylline is 0.8. Then,
Maintenance dose = 224/0.8 = 280 mg
In renal or liver disease, maintenance dose is decreased and loading dose is usually unchanged.