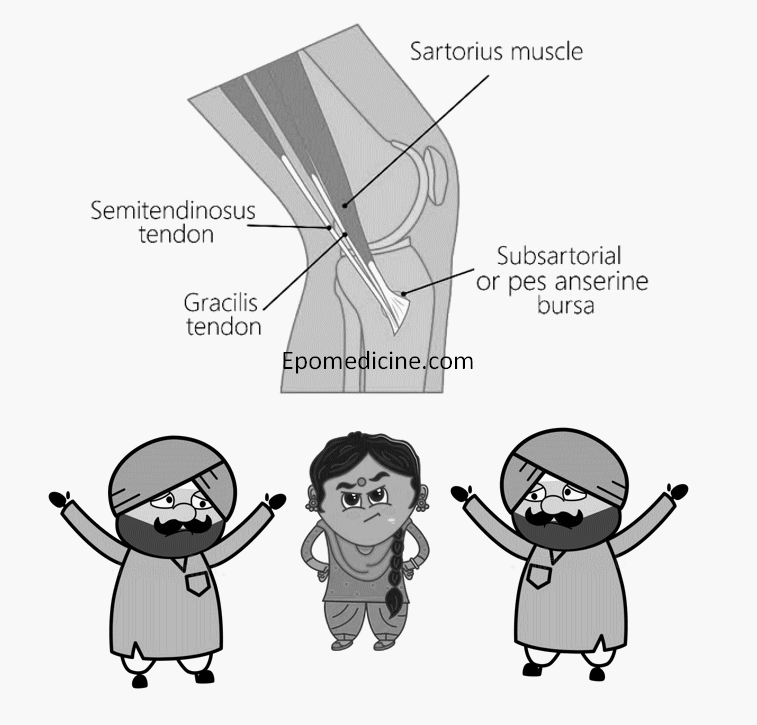
Pes Anserinus is composed of the combination of tendinous insertions of the sartorius, gracilis and semitendinosus muscles (guy ropes muscles) which attaches to the medial side of tibia to generate a “goose’s foot” like appearance. These three muscles are mainly flexors of the knee but also have a role in internal rotation of the tibia. It lies superficial to the distal tibial insertion of medial collateral ligament (MCL). Pes anserinus bursa lies between MCL attachment and pes anserinus tendons.
Mnemonic: a Girl between 2 Sardars
This is a mnemonic similar to “a Lady between 2 Majors” which implies for the muscles around the radial groove. From anterior to posterior, the tendons of pes anserinus are:
- Sartorius
- Gracilis
- Semitendinosus
Mnemonic: FOT
The order of the innervation of these muscles from anterior to posterior:
- Sartorius: Femoral nerve
- Gracilis: Obturator nerve
- Semitendinosus: Tibial nerve
Mnemonic: ART
There origins in order can be remembered:
- Sartorius: ASIS
- Gracilis: Ramus (ischiopubic ramus)
- Semitendinosus: Tuberosity (ischial tuberosity)
The conjoined tendon attaches to the proximal medial tibia 42 mm +/- 7 mm below tibial plateau, distal and medial to tibial tuberosity. Saphenous nerve exits between the sartorius and gracilis as it pierces the deep fascia.