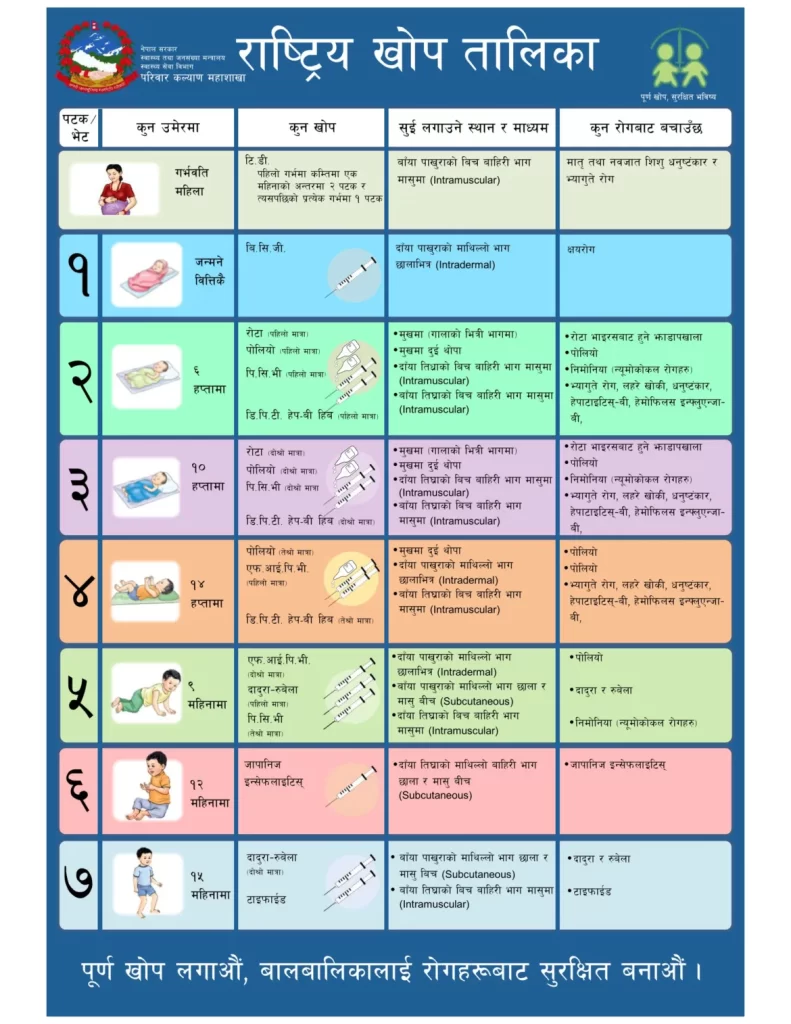
There should be at least 7 contacts of children (At birth, 6,10,14 weeks, 9, 12, 15 months) to health center to fully immunize as per national immunization programme of Nepal.
Previously, 11 antigens were provided through national immunization program. Recently, rotavirus vaccine and fIPV (fractional IPV) has been added.
Nepal is polio free since 2010 and has switched to bOPV (bivalent) from tOPV (trivalent) since April 17 2016 (Baisakh 5 2073).
| S.N | Vaccine | Age of administration | Dose | Route of administration | Protect against |
| 1. | BCG (Bacillus Calmette Guerin) | At birth | 1 | Intradermal | Tuberculosis |
| 2. | Pentavalent Vaccine (Diphtheria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Hepatitis B and Hemophilus influenza B) | 6, 10 and 14 weeks | 3 | Intramuscular | Diphtheria, pertussis,Tetanus, Hepatitis B and Haemophilus Influenza B |
| 3. | OPV ( Oral Polio Vaccine) | 6, 10 and 14 weeks | 3 | Oral | Polio |
| 4. | PCV (Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine) | 6, 10 weeks and 9 months | 3 | Intramuscular | Pneumococcal diseases (Meninges, ear and chest infections) |
| 5. | Rotavirus vaccine | 6, 10 weeks | 2 | Oral | Rota virus diarrhea |
| 5. | fIPV (Fractional Injectable polio vaccine) | Child under 1 year (14 weeks and 9 months, 2 doses) Child under 5 years (Missed dose): 2 doses should be separated by 8 weeks | 2 | Intramuscular | Polio |
| 6. | MR (Measles – Rubella) | 9 and 15 months | 2 | Subcutaneous | Measles and Rubella |
| 7. | JE (Japanese Encephalitis) | 12 months | 1 | Subcutaneous | Japanese Encephalitis |
| 8. | Typhoid vaccine | 15 months | 1 | Intramuscular | Typhoid |
Td (Tetanus diphtheria) for expecting mothers – 2 doses, 1 months apart.
Summary of Injection sites
| BCG | Intradermal | Upper left arm |
| DTP | Intramuscular | Outer mid-thigh |
| OPV | Oral | Mouth |
| HepB | Intramuscular | Outer mid-thigh |
| Measles | Subcutaneous | Upper left arm |
| Yellow fever | Subcutaneous | Upper right arm |
| Tetanus toxoid | Intramuscular | Outer, upper arm |
| Hib | Intramuscular | Infants — Outer mid-thigh |
| Older children — Upper arm | ||
| Japanese encephalitis | Subcutaneous | Upper arm |
| Meningococcal | Subcutaneous | Upper arm |
| Typhoid | Intramuscular | Outer-mid-thigh |
WHO recommendations for interrupted or delayed (missed) routine immunizations as updated on April, 2019:
https://www.who.int/immunization/policy/Immunization_routine_table3.pdf

The dose of rota vaccine and opv
The dose of rotarix is 1 ml and that of OPV is 2 drops.
Could you please tell me which PCV is given to Kid in Nepal Government Hospital.
Is it Prevenar 13 or Synflorix. I must know because I have taken two doses in Nepal. Now
I am in India, so they are asking me to confirm it.
Prevenar is PCV-13 and Synflorix is PCV-10. The vaccine Nepali children receive, PCV-10, protects against 10 pneumococcal serotypes.
Thanks for your valuable information.
Hi Epomedicine,
Thanks for you valuable information.
My son has taken two doses of PCV from Nepal government hospital. Currently I am staying in Bangalore. As per Nepal Vaccination table, 3rd should should be taken in 9 months. According to Indian vaccination schedule, they are giving PCV booster in 15 months. Kindly suggest me when it would be better to take PCV-10 Booster (Synflorix) as 3rd PCV for my son. Now he is already 1 year old.
The PCV immunization strategy of Nepal is 2P+1 dose, i.e. 2 primary dose at 6 wks and 10 wks and a booster dose at 9 months. This can vary according to the country. For a 2P+1 schedule with PCV-10, WHO has given following recommendations:
1. 2 primary doses should ideally be completed by 6 months, starting as early as 6 weeks of age with a minimum interval of 8 weeks between doses.
2. One booster dose should be given between 9-15 months of age. In this schedule, the booster does of pneumococcal vaccine may be given along with measles vaccine and Vitamin A supplementation.
https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/90378/WHO_IVB_13.09_eng.pdf
Studies found that use of a 2+1 PCV schedule with booster at age 9 months in a resource-poor setting improved antibody persistence through early childhood without compromising antibody responses in early infancy.
Thanks for you kind information.
Thanks for valuable information ….❤
Is rotavirus vaccine use in Nepal ?
Under the GAVI aid, more than 3,00,000 has entered Nepal. Government has planned to start its use after June 29 (Asar 15). About 6,20,000 infants will be immunized with the vaccine.
Are these vaccines given free of cost? If not, do the prices differ?
which rotavirus vaccine is currently used? Rotarix® or Rotateq®?