Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disease of white matter that occurs due to interaction of genetic factors with unknown environmental factors. It is characterized by the pathological triad of inflammation, demyelination and gliosis. It is diagnosed using McDonald’s criteria. My mnemonic for clinical features and treatment of multiple sclerosis is: MULTIPLE SCLEROSIS.
Motor: UMNL
Mental function (Higher mental function): Mild cognitive changes, apathy, inattention, depression, euphoria
Uhthoff’s phenomenon: worsening of symptoms on exposure to heat (hot water bath) or exercise, and occurs due to conduction block
Lhermitte’s sign
Trigeminal neuralgia
Internuclear ophthalmoplegia and optic neuritis
Incontinence (bowel and bladder involvement)
Pulfrich effect: may occur when conduction latencies between the eyes are unequal, resulting in a sense of disorientation in moving traffic
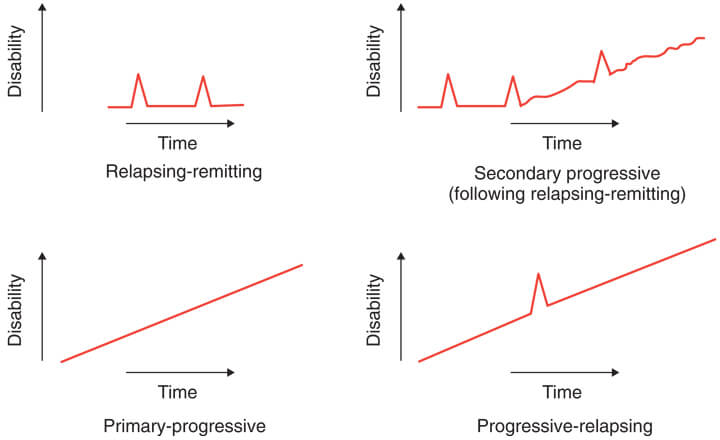
Lesions disseminated in time and space: Dissemination in time indicates involvement of more than one area of CNS dysfunction. All events occurring within 30 days of an event are considered to be part of a single event. Dissemination of space indicates involvement of more than one area of the CNS.
Exacerbations and remissions
Sensory: Posterior column involvement
Cerebellar signs
Language: Dysarthria
Evoked potential: prolongation
Ruled out if: LMN lesions, peripheral nerve involvement, prominent cortical signs, early dementia and extrapyramidal signs
Oligoclonal bands in CSF electrophoresis
Steroids for acute exacerbation
Immunotherapy (Disease modifying drugs): ABC MN – Avonex (IFN β1a), Betaseron (IFN β1b), Copaxone (Glatiramer), Mitoxantrone and Natalizumab
Symptomatic management with baclofen (for spasticity) and anticholinergics (for spastic bladder)

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.