Meniscal tears are best seen on T1-weighted, gradient-echo and proton-density images. The menisci are low intensity on all sequences.
Morphologies
| Meniscal tear morphology | Description | MRI appearance |
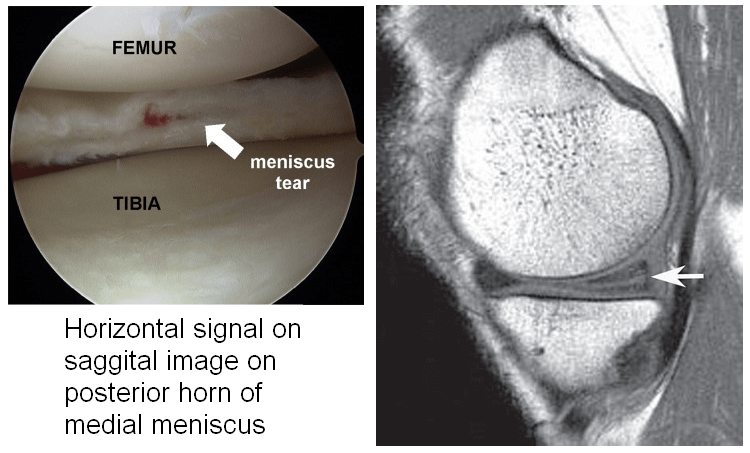
| Horizontal | Separates meniscus into superior (femoral) & inferior (tibial) fragments | Primarily horizontal signal on sagittal images |
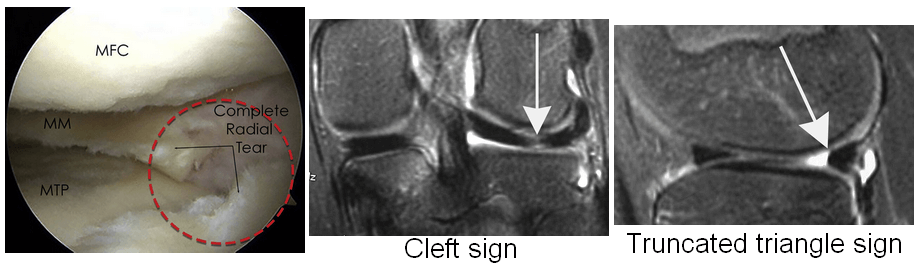
| Vertical radial | Splits central margin of meniscus | Vertical signal oriented perpendicular to the curvature of the meniscus (Cleft sign & Truncated triangle sign) |
| Vertical longitudinal | Extends along length of meniscus; separates meniscus into inner & outer fragments | Vertical signal oriented parallel to the curvature of the meniscus |
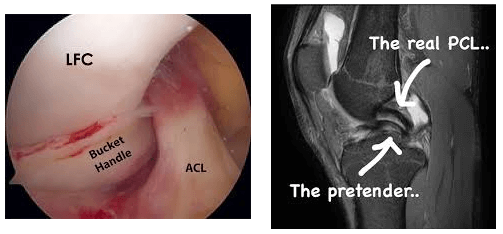
| Bucket handle | Subtype of the longitudinal tear in which the displaced central fragment resembles a bucket handle | “Double PCL sign” – displaced fragment often seen parallel to the PCL in the intercondylar notch on sagittal images |
| Complex | Combination of multiple planes; commonly horizontal & radial | Characteristics of each tear type or fragmented/macerated |
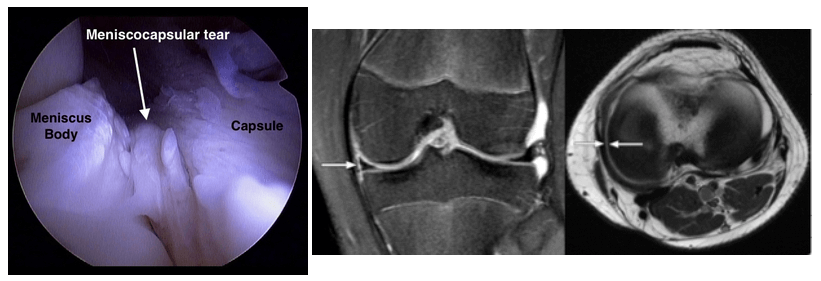
| Meniscocapsular separation | Rupture of meniscus-capsule junction | Increased signal between the edge of the meniscus & the capsule |
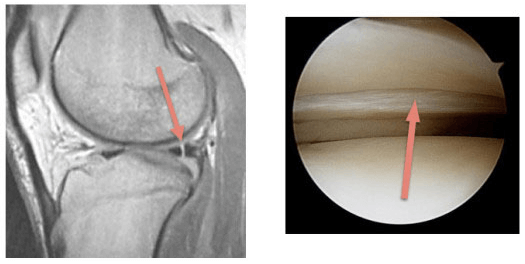
Grading
- Grade 1: Degenerative process – focal, globular intrasubstance increased signal
- Grade 2: Degenerative process – horizontal, linear intrasubstance increased signal
- Grade 3: Meniscal tear – increased signal extends to or communicates with at least 1 articular surface
- Grade 4: Complex tear/macerated meniscus