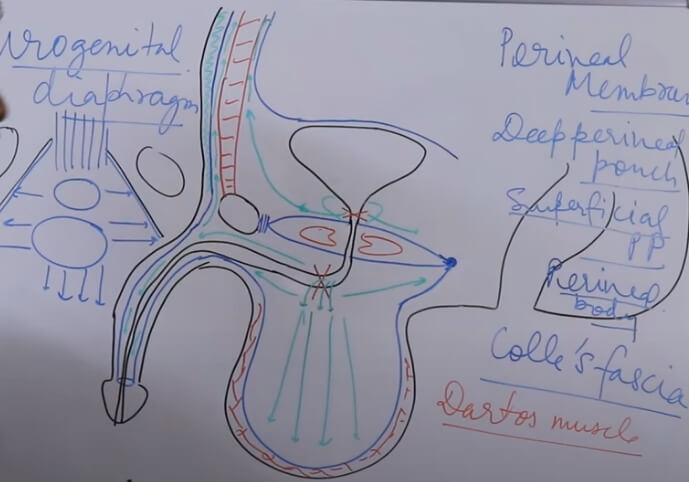
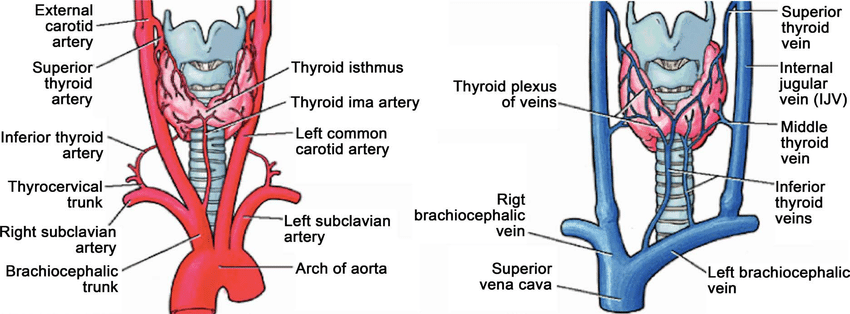
Penile Layers
Mnemonic: ABCD (from inside to outside)
1. Albuginea (tunica albuginea): Envelopes 3 corporal bodies (2 cavernosa and 1 spongiosum)
2. Buck’s fascia: Separates corpora cavernosa from corpus spongiosum; separates superficial and deep dorsal veins of the penis
- Corpora cavernosa
- Forward continuation of crura
- Corpus spongiosum:
- Continuation of bulb of penis
- Encloses spongy/penile urethra
- Suspensory ligament: attachment to pubic bone maintains penile position during erection
3. Colle’s fascia: Continuous with Scarpa’s fascia of abdomen and Dartos fascia of scrotum
- Fundiform ligament: It springs from the lower part of the linea alba and splits into 2 lamellae, which enclose the proximal part of the body of penis and after that connect on its urethral aspect together with the septum of scrotum.
4. Dermis (skin)
Nerve Supply of Penis
Sensory and Motor:
Mnemonic: PID
- Motor: Pudendal nerve (S2-S4)
- Sensory: Ilio-inguinal nerve, Dorsal nerve of penis
Autonomic innervation:
- Parasympathetic (muscle relaxation) via S2-S4: Pointing (erection)
- Sympathetic (muscle contraction) via T11-L2: Shooting (ejaculation)
Scrotum and Testis Layers
Mnemonic: Some Dirty Englishmen Called It Testis (Outside to Inside)
| Layer | Derived from anterior abdominal wall |
| 1. Skin | Skin |
| 2. Dartos muscle/fascia | Superficial fascia |
| 3. External spermatic fascia | External oblique aponeurosis |
| 4. Cremasteric muscle/fascia | Internal oblique |
| 5. Internal spermatic fascia | Transversalis fascia |
| 6. Tunica vaginalis (parietal and visceral) | Peritoneum |
| 7. Tunica albuginea – septates testis into lobules |
Since the testes are originally retroperitoneal organs, the lymphatic drainage is to the lumbar and para-aortic nodes, along the lumbar vertebrae. This is in contrast to the scrotum, which drains into the nearby superficial inguinal nodes.
Carcinomas confined to testes thus never result in inguinal lymphadenopathy and are surgically removed via and inguinal incision.
Male Urethra
Mnemonic: Pet My Beautiful Pig (Proximal to Distal)
| Portion | Segment | Length | Features |
| 1. Posterior (lined by transitional columnar epithelium) | Prostatic | 3 cm | Widest and most dilatable |
| – Iliac lymph nodes | Membranous | 2 cm | Shortest, narrowest and least dilatable |
| – Injury = Deep extravasation of urine (extraperitoneal/into deep perineal pouch) | |||
| 2. Anterior (lined by pseudostratified columnar epithelium; distal-most portion by squamous epithelium) | Bulbar | ||
| – Inguinal lymph nodes | Penile/Spongy | 16 cm | Longest |
| – Injury = Superficial extravasation of urine (intraperitoneal/into superficial perineal pouch) |
Spermatic Cord
Sperm Ejaculation Pathway
Mnemonic: SEVEN UP
- Seminiferous tubules
- Epididymis
- Vas deferens
- Ejaculatory ducts
- None
- Urethra
- Penis
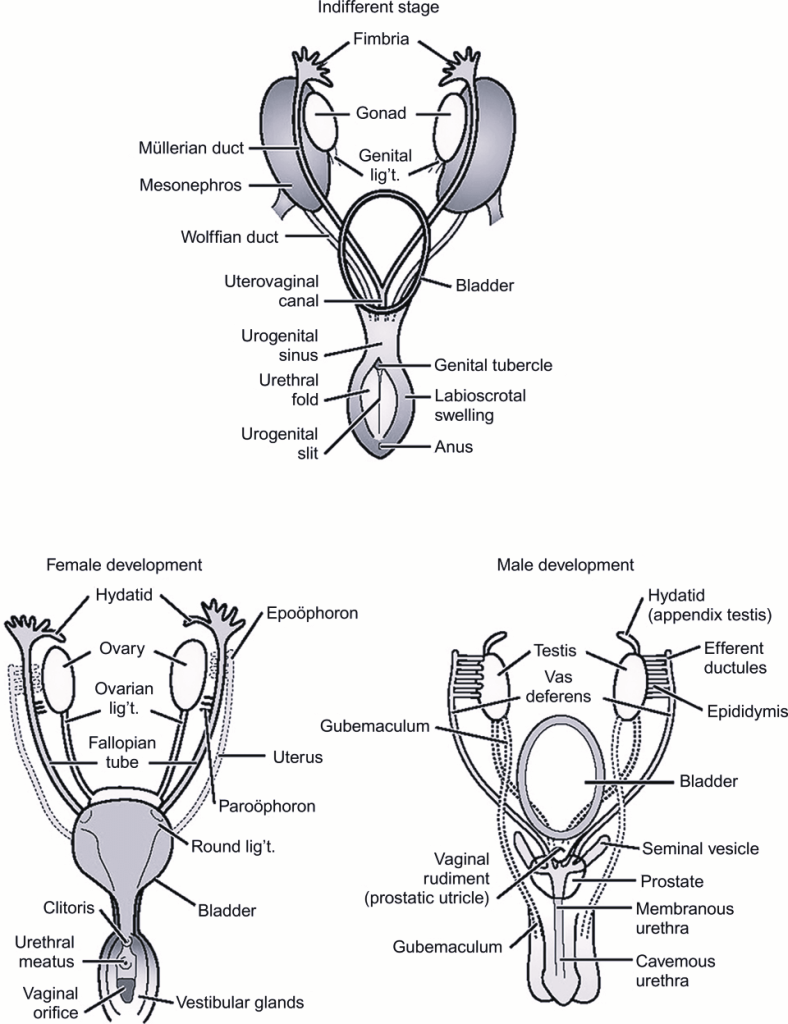
Derivatives of Embryonic Genital Structures
| Embryonic structure | Male | Female |
| Indifferent gonad | Testis | Ovary |
| Cortex | Ovarian follicles | |
| Medulla | Seminiferous tubules Rete testis | Medulla Rete ovarii |
| Gubernaculum | Gubernaculum testis | Ovarian ligament Round ligament of uterus |
| Mesonephric tubules | Ductuli effernetis Paradidymis Abberant ductules Ductus epididymis Ductus deferens Ureter, pelvis, calyces and collecting systems | Epoophoron Paraoophoron Duct of epoophoron Duct of paraophoron Ureter, pelvis, calyces and collecting systems |
| Mesonephric duct | Appendix of epididymis Ejaculatory duct & seminal vesicle | |
| Paramesonephric duct | Appendix of testis Prostatic utricle | Hydatid of Morgagni Fallopian tubes Uterus Vagina (upper) |
| Genital tubercle | Penis | Vestibule Clitoris |
| Urogenital folds | Ventral (under) aspect of penis – penile urethra | Labia minora |
| Labioscrotal swellings | Scrotum | Labia majora |