Types
Most common cancer: Metastases
Primary lung cancer:
| Type | Frequency | Location | Association | Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Small (oat) cell carcinoma | 15% | Sentral (central) | Smoker | Neuroendocrine differentiation (Kulchitsky cells) Aggressive (disseminate early – lymphadenopathy) Paraneoplastic syndrome (ACTH, ADH, Antibodies – Lambert eaton) Inoperable Chemosensitive |
| Adenocarcinoma | 40% | Peripheral | Non-smoker (most common) | k-Ras, EGFR, ALK mutations Nodule/mass Hypertrophic osteoarthropathy (clubbing) Bronchio-alveolar subtype (pneumonia-like): Excellent prognosis, apparent “thickening” of alveolar walls |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | 25% | Sentral (central) | Smoker (most common) | Hilar mass Obstruction Cavitation Calcium (PTHrP) Keratin pearls and intracellular bridge |
| Large cell carcinoma | 10% | Peripheral | Smoker | Poor prognosis Pleomorphic giant cells |
| Carcinoid tumor | 2% | Central | Non-smoker | Excellent prognosis Mass effect Carcinoid sydrome (rare) Chromogranin A + |
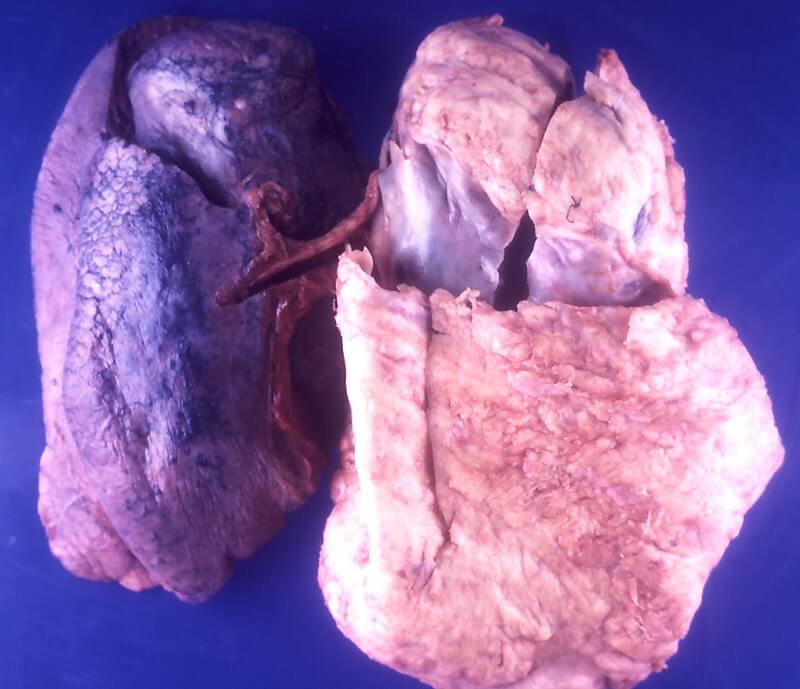
Growing rate (Doubling time)
Mnemonic: SmS LA
- Small cell carcinoma: 30 days
- Squamous cell carcinoma: 90 days
- Large cell carcinoma: 120 days
- Adenocarcinoma: 150-180 days
Management
1. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): Chemotherapy +/- Radiotherapy
2. Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC):
- Stage I, II, IIIA: Surgical resection +/- Chemo-radiotherapy
- Stage IIIB, IV: Chemo-radiotherapy
- >1 lobe involvement (ipsilateral or contralateral)
- 2 sides local nodes involvement (contralateral mediastinal/hilar)
- Mediastinal structure invasion
- Distant lymph node metastases
- Distant metastases
Contra-indications to lung surgery:
- SVC obstruction
- FEV1 <1.5
- Malignant pleural effusion
- Vocal cord paralysis
Awesome mnemonic thank you 🙏🏾