Order of decreasing wavelength
Mnemonic: CHyNa PuRE
The laser tissue interaction can be remembered in the reverse order using the mnemonic ACiDiTy.
- Carbon dioxide (CO2): 10600 (photoThermal)
- Holmium YAG: 2100 (photoDisruption)
- Nd:YAG: 1064 (photoDisruption)
- Pulsed dye laser: 585-600 (photoChemical)
- aRgon green: 514 (photoChemical)
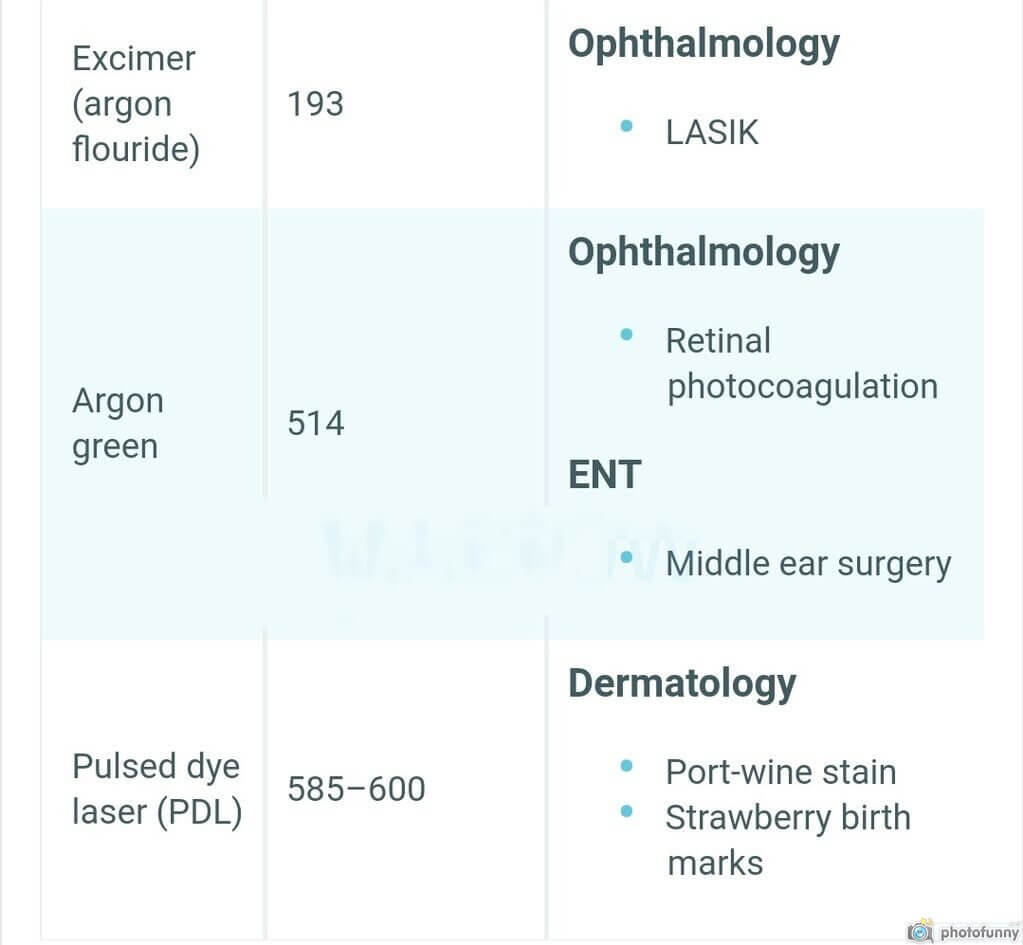
- Excimer: 193 (photoAblation)
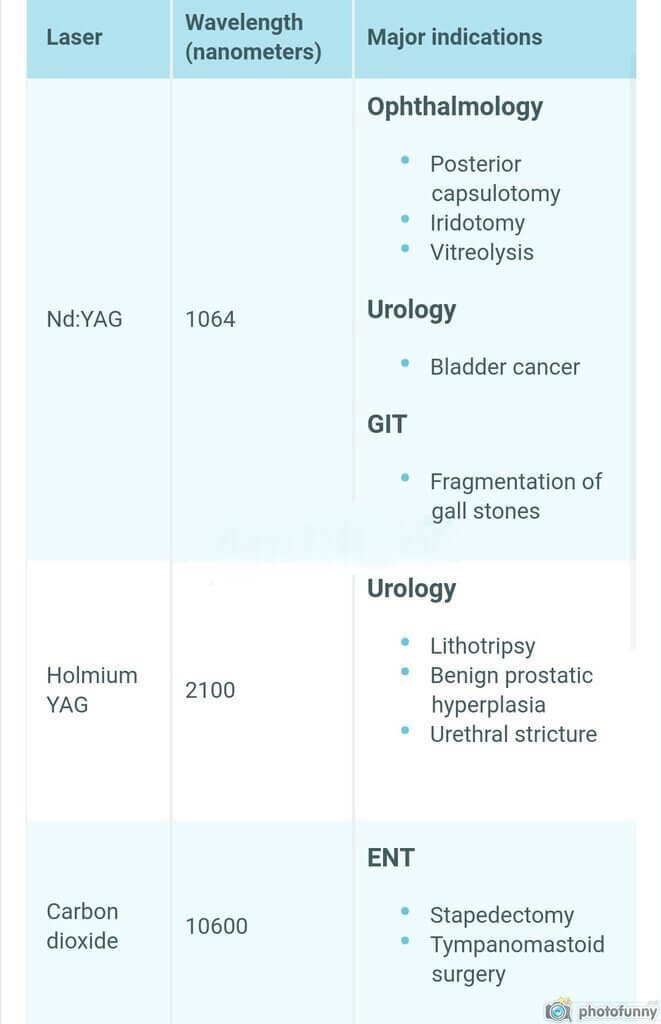
Indications of Laser
aRgon
Mnemonic: R for aRgon and R for Retina
Used in retinal photocoagulation.
pulsed Dye laser
Mnemonic: D for Dye and D for Dermatology
- Used in port wine stain
- Used in strawberry birthmarks
Carbon-di-oxide
Mnemonic: C for CO2 and C for Central/middle ear
- Stapedectomy
- Tympanomastoidectomy
Holmium YAG laser
Mnemonic: H for Holmium and H for Hollow tube
- Hollow ureter blocked: Lithotripsy
- Hollow urethra blocked: BPH or Urethral stricture
Excimer
Mnemonic: Ex for ExCimer and Ex for External eye (Cornea)
- Corneoplasty using LASIK
Nd:YAG
Mnemonic: Its use is in eye other than Cornea (excimer is used) and Retina (argon is used).
- Posteiror capsulotomy
- Iridotomy
- Vitreolysis