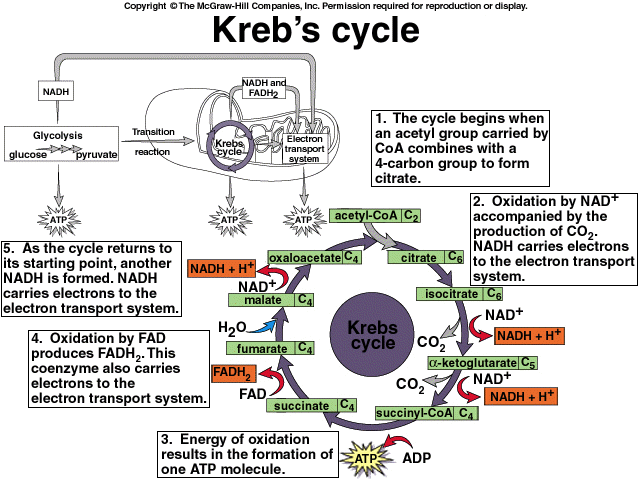
Mnemonic: Our City Is Kept Safe And Sound From Malice
- Oxaloacetate
Citrate synthase
- Citrate (may leave the mitochondria to enter CITRATE SHUTTLE for fatty acid synthesis)
Aconitase (Aconitic acid is a dehydrated citric acid)
- Isocitrate
Isocitrate dehydrogenase (dehydrogenated H+ added to NAD to form NADH & CO2)
Major control enzyme (inhibited by NADH & ATP & activated by ADP) - α-Ketoglutarate
α-Ketoglutarate dehydrogenase (dehydrogenated H+ added to NAD to form NADH & CO2)
Similar to pyruvate dehydrogenase (requires thiamine, lipoic acid, CoA, FAD, NAD)
Lack of thiamine slows oxidation of acetyl-CoA in citric acid cycle - Succinyl-CoA (also for heme synthesis & ketone body activation in extrahepatic tissues)
Succinyl-CoA synthetase (GDP+Pi = GTP - substrate level phosphorylation)
Also, called Succinate thiokinase - Succinate
Succinate dehydrogenase (dehydrogenated H+ added to FAD to form FADH2)
On mitochondrial membrnae (complex II of Electron Transport Chain) - Fumarate
Fumarase
- Malate (can leave mitochondria to enter MALATE SHUTTLE for gluconeogenesis)
Malate dehydrogenase (H+ exchanged between NAD and NADH)
- Oxaloacetate
Remember the enzymes of the cycle:
All the enzymes are in the matrix of mitochondria except succinate dehydrogenase which is in inner mitochondrial membrane.
- 2 “substrate”-ase: ACONITASE and FUMARASE
- 2 “sythase/synthetase”: CITRATE SYNTHASE and SUCCINYL-COA SYNTHETASE
- Others “dehydrogenases”: ISOCITRATE DEHYDROGENASE, α-KETOGLUTARATE DEHYDROGENASE, SUCCINATE DEHYDROGENASE, MALATE DEHYDROGENASE
In short, Kreb’s cycle is
Acetyl-CoA——————————————→ 2 CO2
3 NAD + FAD + GDP + Pi 3 NADH + FADH2 + GTPNADH production in TCA cycle:
KIM likes goNADs
After:
- alpha-Ketoglutarate
- Isocitrate
- Malate
Function: Oxidation of Acetyl-CoA to CO2 with release of energy (NADH, FADH2, GTP)
Acetyl-CoA is yielded from glucose, fatty acids, ketone bodies, ketogenic amino acids and alcohol.
Pyruvate from aerobic glycolysis enters mitochondria, where it may be converted into acetyl-CoA (irreversible reaction) under the action of enzyme Pyruvate Dehydrogenase (PDH – inhibited by it’s product acetyl-CoA) for entry into:
- If ATP is needed: Citric acid cycle
- If ATP is sufficient: Fatty acid synthesis
PDH includes cofactors and conenzymes. Easy way to remember this is – they are vitamin B or vitamin B like:
- Vitamin B1 – Thiamine (Thiamine Pyrophosphate/TPP) for PDH (E1)
- Vitamin B like – Lipoic acid for Acetyl Transferase (E2)
- Vitamin B5 – Panothenic acid (CoA/Cofactor A) for E2
- Vitamin B2 – Riboflavin (FAD) for E3
- Vitamin B3 – Nicotinamide (NAD) for E3
Another Mnemonic: Citrate Is Kreb’s Starting Substrate For Making Oxaloacetate
- Citrate
- Isocitrate
- Alpha-Ketoglutarate
- Succinyl CoA
- Succinate
- Fumarate
- Malate
- Oxaloacetate
Alcoholism and Hypoglycemia:
- Poor nutrition
- High NADH from alcohol and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase favors formation of:
- Lactate from pyruvate
- Malate from oxaloacetate
- Glycerol-3-phosphate from Dihydroxyacetone phosphate

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.