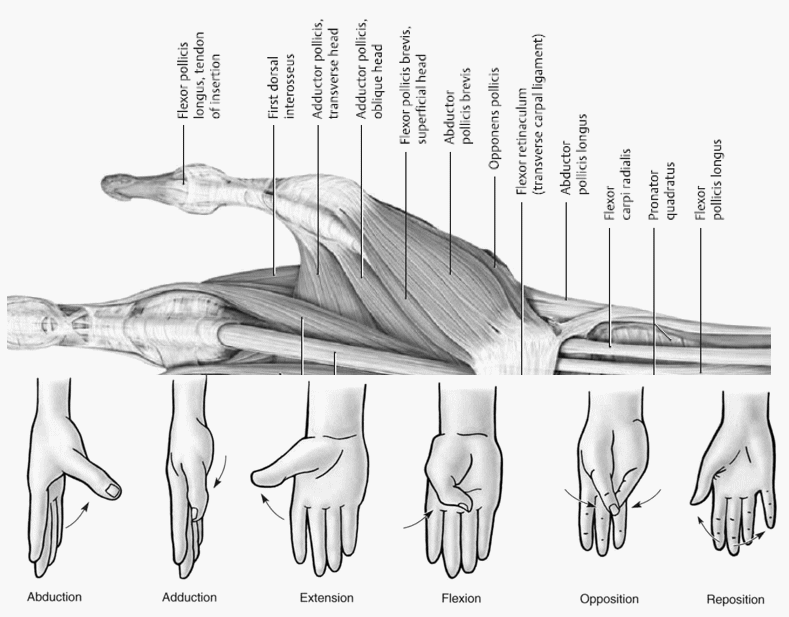
The muscles of thumb will make 2 compartments – thenar compartment and adductor compartment.
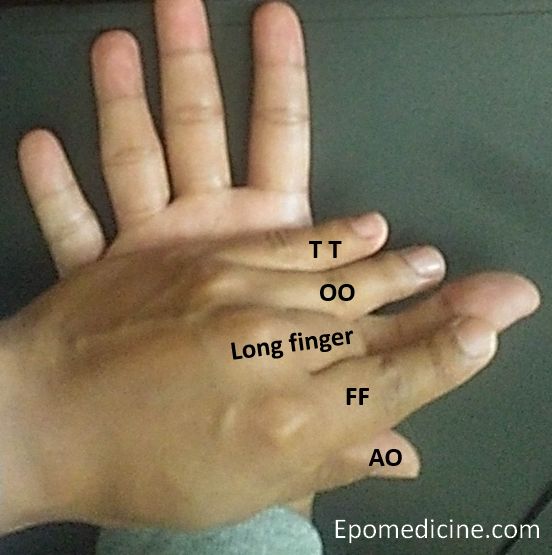
Mnemonic: Do it yourself as shown in the image below. Put your left hand with curled in middle/long finger above the palm of right hand. There are 2 muscle layers in this side of the hand. Represent the superficial layer with T-O-F-A (Transverse head, Oblique head, Flexor pollicis brevis, Abductor pollicis brevis) and the deeper later with T-O-F-O (Transverse head, Oblique head, Flexor pollicis brevis, Opponens pollicis). Curled in long finger represents the tendon of Flexor Pollicis LONGUS in the deeper layer between the OBLIQUE head of adductor pollicis and FLEXOR pollicis brevis.
The left little and ring finger on the ulnar side of right thumb represents 2 heads of adductor pollicis which forms the Adductor compartment.
Little finger (T-T): Transverse head of Adductor pollicis (in both superficial and deep layer)
- As in the image below – it will originate from 3rd metacarpal and insert into ulnar side of base of proximal phalanx of thumb.
Ring finger (O-O): Oblique head of Adductor pollicis (in both superficial and deep layer)
- This will originate from 3rd metacarpal as well as 2nd metacarpal and capitate and insert into ulnar base of proximal thumb phalanx like the transverse head.
Now moving to the radial side of the thumb. Here, the muscles are different in different layers. All these muscles make Thenar compartment.
Index finger (F-F):
- Superficial layer: FLEXOR pollicis brevis – superifical head (arises from flexor retinaculum and trapedzoid tubercle)
- Deep layer: FLEXOR pollicis brevis – deep head (arises from trapezoid)
Both the heads, insert into radial base of proximal phalanx of thumb.
Thumb (A-O):
- Superficial layer: ABDUCTOR pollicis brevis – originates from scaphoid and trapezium and insert into radial base of proximal phalanx of thumb.
- Deep layer: OPPONENS pollicis – originates from trapezium and insert into lateral surface of 1st metacarpal shaft.
Innervation: The thenar muscles are supplied by motor recurrent branch of median nerve. The adductor muscle is supplied by ulnar nerve. The flexor pollicis brevis has dual innervation. While the superficial head is supplied by the median nerve, deep head receives it’s innervation from ulnar nerve.

He is the section editor of Orthopedics in Epomedicine. He searches for and share simpler ways to make complicated medical topics simple. He also loves writing poetry, listening and playing music. He is currently pursuing Fellowship in Hip, Pelvi-acetabulum and Arthroplasty at B&B Hospital.